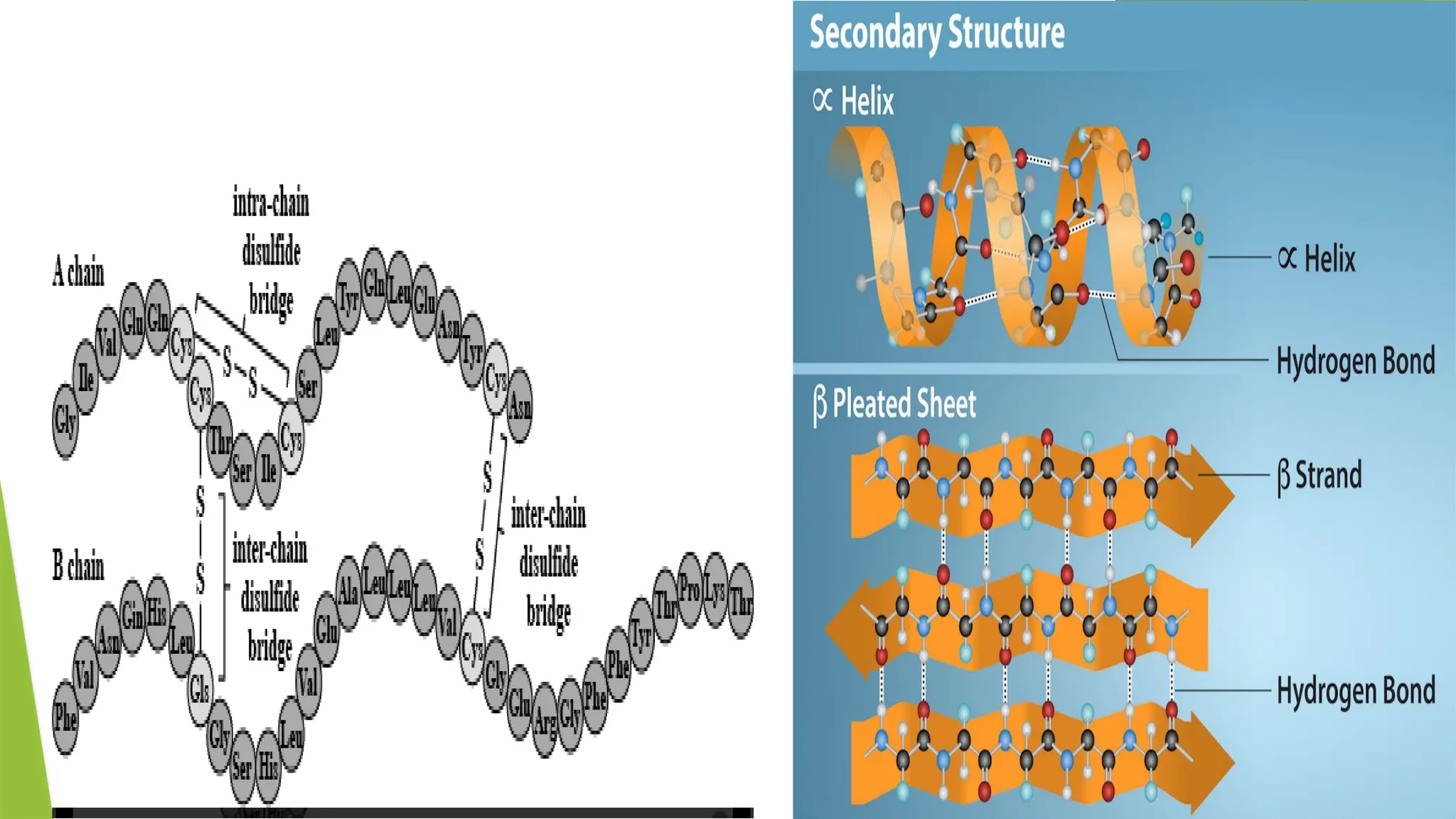
The document discusses the quaternary structure of proteins, which is the three-dimensional arrangement of multi-subunit proteins, stabilized by non-covalent interactions and disulfide bonds. It describes the types of quaternary proteins, including fibrous and globular proteins, with examples such as hemoglobin and insulin, detailing their structures and functions. Furthermore, it outlines the various forces that stabilize quaternary structures, including disulfide bonds, hydrogen bonds, and hydrophobic interactions.