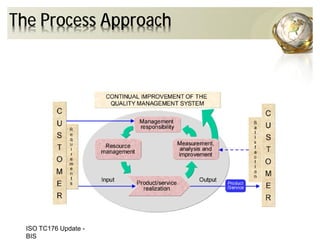
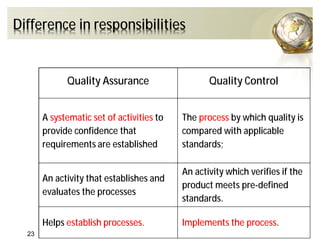
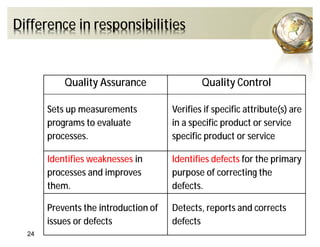
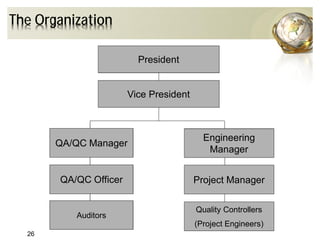
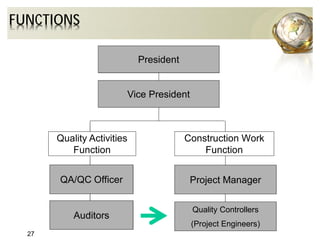
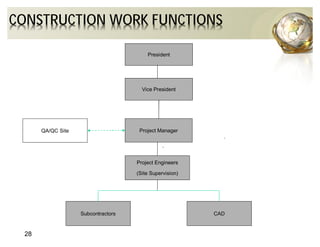
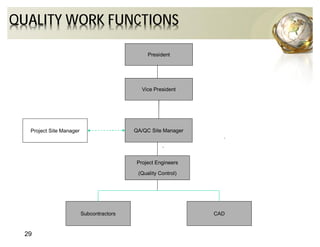
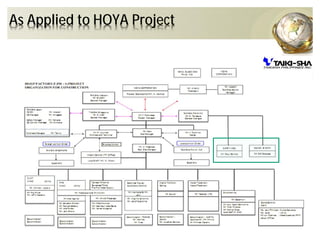
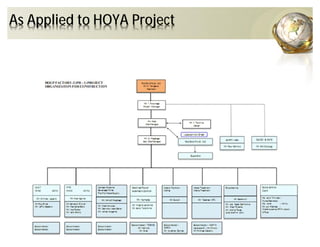
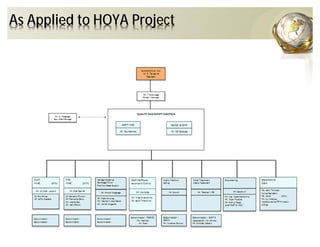
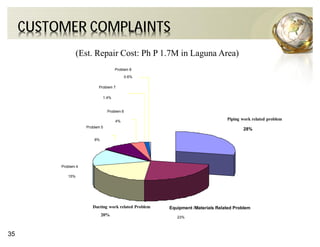
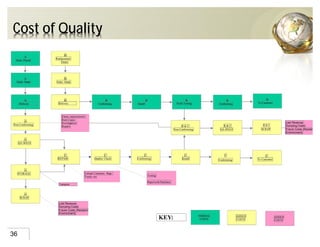
The document outlines the concepts of quality assurance (QA) and quality control (QC) in construction based on the ISO 9001:2008 standard, highlighting the importance of a systematic quality management system. It details various levels of quality documentation and procedures, emphasizing customer focus and continual improvement. The document concludes with reflections on the importance of preventing defects over correcting them to improve efficiency and customer relations.