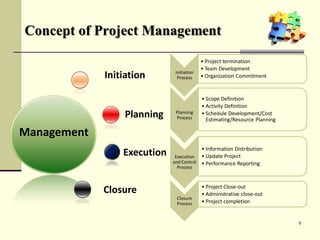
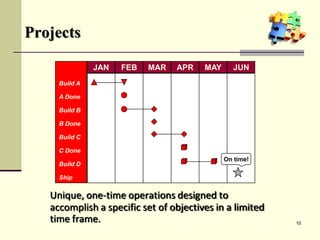
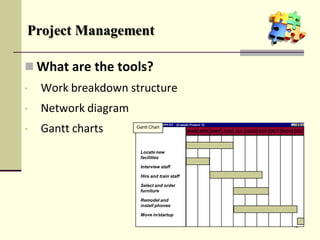
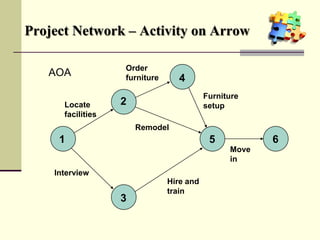
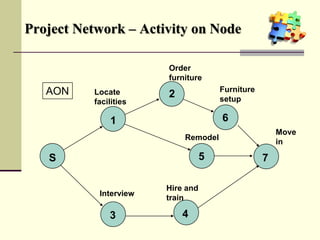
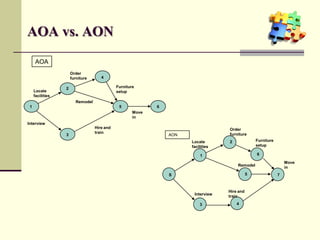
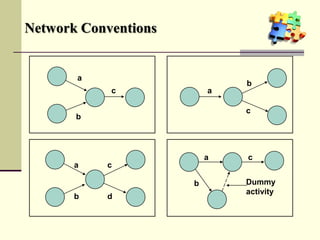
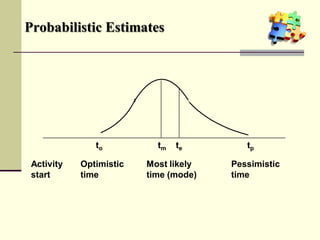
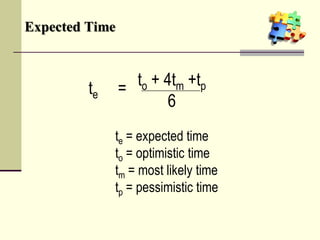
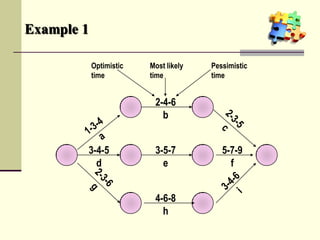
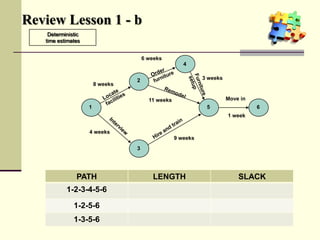
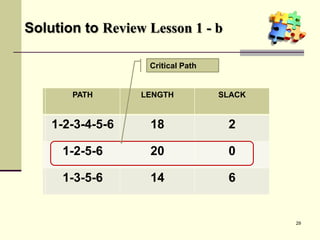
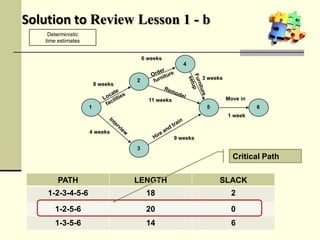
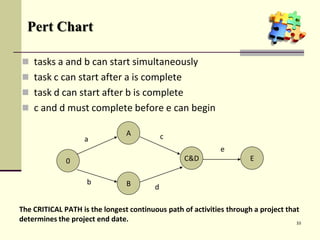
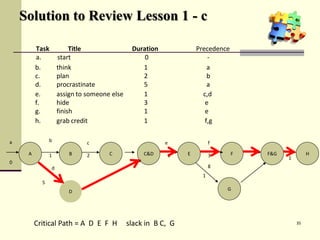
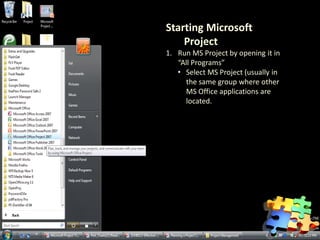
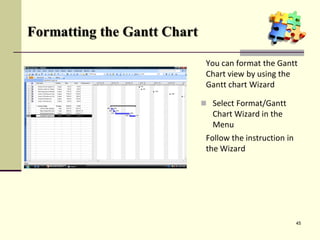
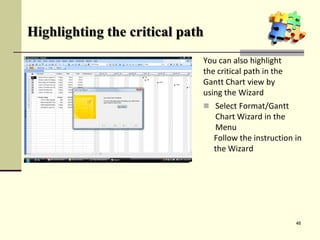
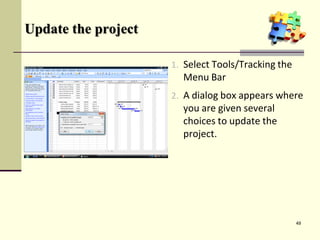
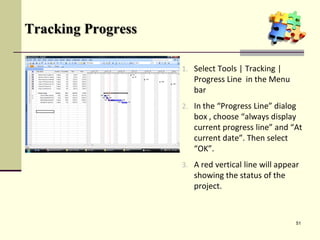
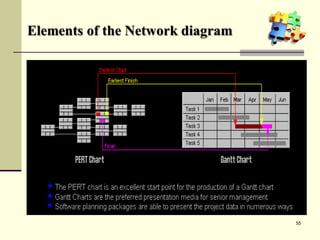
This document is a training module for Microsoft Project 2007, authored by Eng’r Sid Calayag, providing an introduction to project management concepts and the software's functionalities. It outlines course objectives, contents including project management terminology, critical path methods, and practical instructions on using Microsoft Project for planning and scheduling. Participants will learn to manage tasks and resources effectively within time and cost constraints to achieve project goals.