1) Dentinogenesis is the process of dentin formation by odontoblasts. Undifferentiated dental papilla cells proliferate and differentiate into proodontoblasts and then into odontoblasts.
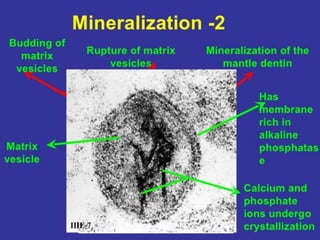
2) Odontoblasts synthesize and deposit the organic matrix of mantle dentin, which consists mainly of Type III collagen. This is the first sign of dentin formation.
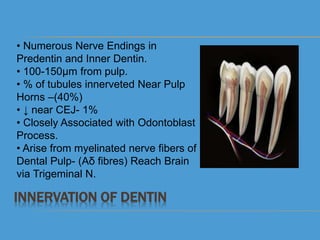
3) The hydrodynamic theory is currently the most accepted explanation for how dentin transmits pain signals. According to this theory, external stimuli cause movement of fluid within dentin tubules, activating nerve endings associated with odontoblasts and transmitting pain sensations.