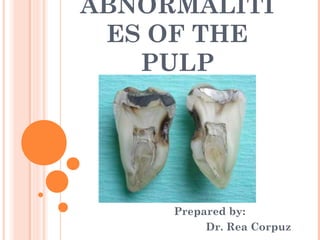
Abnormalities of the pulp
- 1. ABNORMALITI ES OF THE PULP Prepared by: Dr. Rea Corpuz
- 2. Pulp Calcification may be located pulp chamber OR root canals
- 3. Pulp Calcification Cause no clear-cut etiology no relation between inflammation + irritation • since pulp calcification can be found in unerupted teeth
- 4. Sundell Schematic Presentation Local Metabolic Hyalinization Vascular Trauma Dysfunction of injured cell Damage Thrombosis Growth Mineralization Fibrosis Vessel Wall Damage Pulp Stones
- 5. Classification Three types : (1) Denticles (2) Pulp stones (3) Diffuse linear calcifications
- 6. (1) Denticles believed to form as a result of epitheliomesenchymal interaction within developing pulp form during period of root development occur in root canal + pulp chamber adjacent to furcation areas of multirooted teeth
- 7. (2) Pulp Stones believed to develop around central nidus of pulp tissue examples: collagen fibril ground substance formed within coronal portions of pulp
- 8. (2) Pulp Stones may arise as part of age- related or local pathologic changes most develops after tooth formation is completed usually free or attached some instances, may be embedded
- 9. (3) Diffuse Linear Calcifications doesn’t demonstrate lamellar organization of pulp stones exhibit areas of: fine fibrillar irregular calcification may be present in pulp chamber or canals frequency increases with age
- 10. (3) Diffuse Linear Calcifications Clinical Significance: very little clinical significance except insofar as they may obstruct endodontic treatment
- 11. (3) Diffuse Linear Calcifications Clinical Significance: discovered on radiograph only as radioopacity may cause pain from mild pulpal neuralgia to severe excruciating pain resembling tic douloureux • as denticle may impinge on nerve of pulp
- 12. (3) Diffuse Linear Calcifications Clinical Significance: difficulty may be encountered in extirpating pulp during root canal therapy
- 13. (3) Diffuse Linear Calcifications Treatment & Prognosis No treatment is required
- 14. Resorption of the Teeth deciduous teeth are progressively loosened result of progressive resorption of roots physiological process arising from pressure of underlying successors resorption of permanent is always pathological
- 15. Resorption of the Teeth Pathology pressure is probably main factor resorption is mainly carried out by osteoclast humoral mediators, such as prostgalndins • may contribute to resorption
- 16. Idiopathic Resorption (1) Internal Resorption (2) External Resorption
- 17. Idiopathic Resorption Internal Resorption pink spot curious + uncommon condition dentin is resorbed from within the pulp
- 18. Idiopathic Resorption (1) Internal Resorption tends to be localized well-defined rounded area of rediolucency in crown can affect any part of teeth NO signs until pulp is opened + allows access to infection
- 19. Idiopathic Resorption (1) Internal Resorption may be detected by chance in routine radiograph
- 20. Idiopathic Resorption (1) Internal Resorption
- 21. Idiopathic Resorption (1) Internal Resorption
- 22. Idiopathic Resorption (2) External Resorption may be localized or generalized unkown cause mild degree of inflammation is often suspected
- 23. Idiopathic Resorption (2) External Resorption
- 24. Idiopathic Resorption (2) External Resorption Heithersay Classification
- 25. Idiopathic Resorption (2) External Resorption usually a limited area of root is attacked from external surface near amelocemental junction • resorption goes on until pulp is reached
- 26. Idiopathic Resorption (2) External Resorption often preferentially destroys root before penetrating the pulp
- 27. Idiopathic Resorption (2) External Resorption accessible defects may be amenable to restoration with mineral trioxide or other materials long term success in infrequent; unpredictable
- 28. Idiopathic Resorption (2) External Resorption Pathology • vascular granulation tissue replaces part or periodontal ligament or pulp • osteoclasts border the affected dentin or enamel
- 29. Idiopathic Resorption (2) External Resorption Treatment • usually untreatable • if a pink spot in an incisor tooth is noticed at an early stage endodontic treatment should be carried out before
- 30. Idiopathic Resorption (2) External Resorption Treatment • resorption of teeth may result from pressure exerted by impacted teeth indication for removal of unerupted teeth
- 31. DISEASES OF PERIAPICALTISSU ES Prepared by: Dr. Rea Corpuz
- 32. Diseases of Periapical Tissues (1) Periapical Abscess (2) Periapical Granuloma (3) Radicular Cyst (4) Phoenix Abscess (5) Condensing Osteitis
- 33. (1) Periapical Abscess also known as Dento-alveolar Abscess; Alveolar Abscess acute or chronic supporative process of dental periapical region usually arises as a result of infection
- 34. (1) Periapical Abscess abcess ay develop directly as an acute apical periodontitis following an acute pulpitis but more commonly it originates in an area of chronic infection
- 35. (1) Periapical Abscess Clinical Feature presents features of acute inflammation of apical peridontium tooth is extremely painful slightly extruded from its socket
- 36. (1) Periapical Abscess Clinical Feature chronic periapical abscess generally presents no clinical features mild, circumscribed area of suppuration that shows little tendency to spread from local area
- 37. (1) Periapical Abscess Radiographic Feature except for SLIGHT thickening of periodontal membrane no roentgenographic evidence of its presence chronic abscess, developing in a periapical granuloma • radioluscent area at apex
- 39. (1) Periapical Abscess Histopathologic Features area of suppuration is composed chiefly of central area of disintegrating polymorphonuclear leukocytes dilation of blood vessels in periodontal ligament
- 40. (1) Periapical Abscess Histopathologic Features tissue surrounding area of suppuration contains serous exudate
- 41. (1) Periapical Abscess Treatment & Prognosis drainage must be established • open pulp chamber • extract the tooth
- 42. (1) Periapical Abscess Treatment & Prognosis under some circumstances tooth may be retained • root canal therapy
- 43. (1) Periapical Abscess Treatment & Prognosis left untreated, spread of infection • osteomyelitis • cellulitis • bacterimia • formation of fistulous tract opening on skin or oral mucosa
- 44. (2) Periapical Granuloma also known as Apical Periodontitis one of the most common sequeala of pulpitis localized mass of chronic granulation tissue response to infection
- 45. (2) Periapical Granuloma Clinical Features 1st evidence; spread beyond confines of tooth pulp may be noticeable sensitivity of involved tooth to percussion mild pain when biting or chewing on solid food
- 46. (2) Periapical Granuloma Clinical Features some cases tooth feels elongated in its socket sensitivity is due to • hyperemia • edema • inflammation of apical periodontal ligament
- 47. (2) Periapical Granuloma Radiographic Features earliest evidence, thickening of ligament at root apex proliferation of granulation tissue concomitant resorption of bone continue
- 48. (2) Periapical Granuloma Radiographic Features appear as a radiolucent area of variable size seemingly attached to root apex some cases, well circumscribed lesion • definitely demarcated from surrounding bone
- 49. (2) Periapical Granuloma Histologic Features arises as chronic process from onset does not pass through an acute phase
- 50. (2) Periapical Granuloma Histologic Features begins as: • hyperemia • edema of periodontal ligament with infiltration of chronic inflammatory cells chiefly lymphocytes plasma cells
- 51. (2) Periapical Granuloma Histologic Features inflammation + locally increased vascularity of tissue • induce resorption of supporting bone adjacent to this area
- 52. (2) Periapical Granuloma Histologic Features as bone is resorbed • proliferation of fibroblast + endothelial cells • formation of more tiny vascular channels • numerous delicate connective tissue fibrils
- 53. (2) Periapical Granuloma Treatment & Prognosis extraction of involved teeth under certain conditions, root canal therapy with or without subsequent apicoectomy
- 54. (2) Periapical Granuloma Treatment & Prognosis
- 55. (2) Periapical Granuloma Treatment & Prognosis left untreated, may undergo transformation into an apical periodontal cyst • proliferation of epithelial rests in the area
- 56. (3) Radicular Cyst also known as Apical Periodontal Cyst; Periapical Cyst; Root End Cyst common not inevitable sequela of periapical granuloma originating as a result of: bacterial infection necrosis of dental pulp following carious involvement of tooth
- 57. (3) Radicular Cyst Pathogenesis initial reaction leading to cyst formation • proliferation of epithelial rest in the periapical area involved by granuloma • epithelial proliferation follows an irregular pattern of growth
- 58. (3) Radicular Cyst Clinical Features asymptomatic present no clinical evidence of their presence seldom painful or even sensitive to percussion
- 59. (3) Radicular Cyst Clinical Features represents chronic inflammatory process • develops only over a long period of time
- 60. (3) Radicular Cyst Radiographic Features identical with periapaical granuloma since the lesion is a chronic progressive one developing in a pre-existing granuloma • cyst may be of greater size than granuloma • due to longer duration
- 61. (3) Radicular Cyst Radiographic Features occasionally, exhibits thin, radioopaque line around the periphery of radiolucent area • indicates reaction of bone to slowly expanding mass
- 62. (3) Radicular Cyst Radiographic Features
- 63. (3) Radicular Cyst Histologic Features epithelium lining apical periodontal cyst is usually stratified squamous in type
- 64. (3) Radicular Cyst Treatment & Prognosis similar to periapical granuloma • involved tooth may be removed • periapical tissue carefully curetted
- 65. (3) Radicular Cyst Treatment & Prognosis under some condition; • root canal therapy • with apicoectomy of cystic lesion
- 68. (4) Phoenix Abscess localized collection of pus surrounded by an area of inflammed tissue hyperemia infiltration of leucocytes
- 71. (4) Phoenix Abscess can occur immediately following root canal treatment another cause is due to untreated necrotic pulp (chronic apical periodontitis) result of inadequate debridement during endodontic procedure
- 72. (4) Phoenix Abscess Bacteriology Staphylococci are frequently associated with pus formation • produce enzyme called coagulase • causes fibrin formation • helps in walling off of lesion
- 73. (4) Phoenix Abscess Bacteriology • coagulase promotes virulence by inhibiting phagocytosis
- 74. (4) Phoenix Abscess Clinical Features when palpated clinically • superficial abscess is fluctuant offending tooth is carious + mobile symptoms of acute inflammation • swelling • fever
- 75. (4) Phoenix Abscess Treatment repeating endodontic treatment with improved debridement tooth extraction antibiotics may be indicated to control a spreading or systemic infection
- 76. (5) Condensing Osteitis also known as Chronic Focal Sclerosing Osteomyelitis unusual reaction of bone occuring in instances of extremely high tissue resistance or in cases of low grade infection
- 77. (5) Condensing Osteitis Clinical Features occurs in almost young person before the age of 20 years old commonly affected is mandibular 1st molar with large carious lesion
- 80. (5) Condensing Osteitis Clinical Features associated with non vital teeth or teeth undergoing process of degeneration tooth is usually asymptomatic some cases, pain or tenderness • percussion • palpation
- 81. (5) Condensing Osteitis Radiographic Features well circumscribed radiopaque mass of sclerotic bone surrounding extending below apex of one or more roots
- 82. (5) Condensing Osteitis Histologic Features dense mass of bony trabeculae with little interstitial marrow tissue
- 83. (5) Condensing Osteitis Histologic Features dense mass of bony trabeculae with little interstitial marrow tissue chronic inflammatory cells; plasma cells, lymphocytes are seen scanty in bone marrow
- 84. (5) Condensing Osteitis Treatment & Prognosis endodontic treatment extraction surgical removal of sclerotic should not be attempted unless symptomatic
- 85. References: Books Cawson, R.A: Cawson’s Essentials of Oral Oral Pathology and Oral Medicine, 8th Edition • (page 70-72) Ghom, Ali & Mhaske, Shubhangi: Textbook of Oral Pathology • (pages 429-433) Neville, et. al: Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology 3rd Edition • (pages 127-138) Shafer, et al: A textbook of Oral Pathology, 3rd Edition
