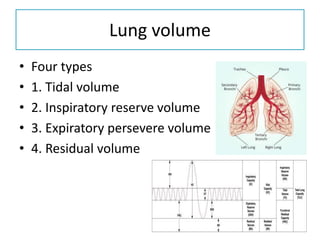
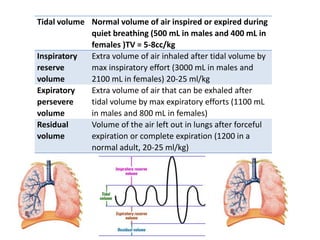
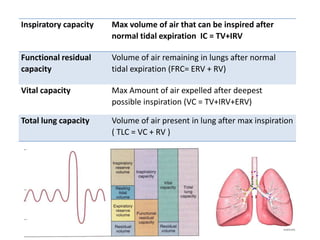
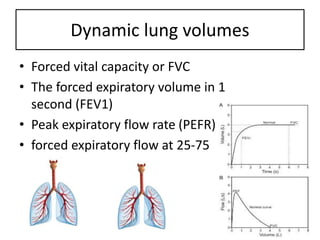
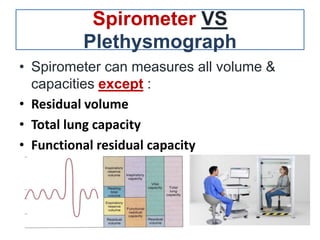
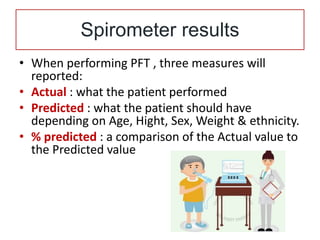
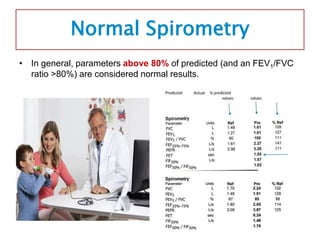
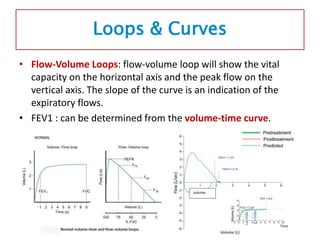
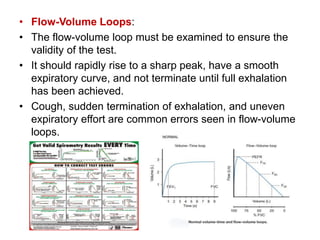
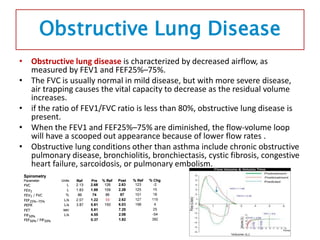
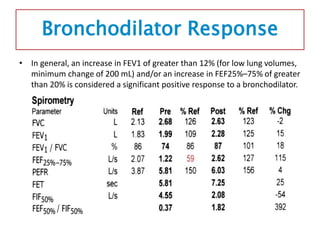
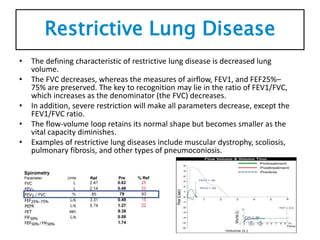
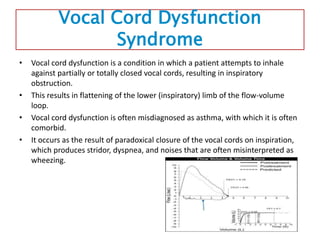
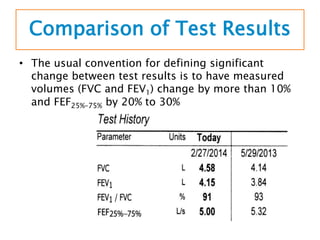
Spirometry is a noninvasive pulmonary function test that measures lung volumes and airflow. It is useful for diagnosing and monitoring respiratory diseases like asthma in children who are able to perform the test properly. Key measurements include forced vital capacity (FVC), forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1), and ratios like FEV1/FVC. Obstructive patterns show reduced airflow while restrictive patterns show reduced lung volumes. Spirometry provides objective data to guide treatment and monitor response to medications like bronchodilators.