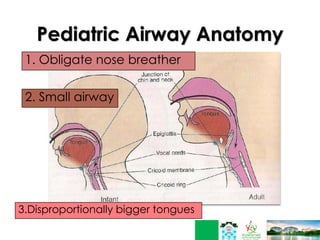
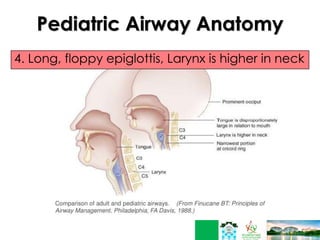
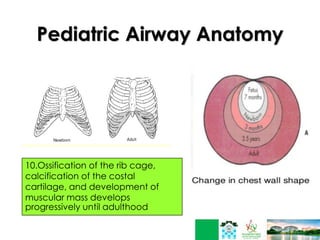
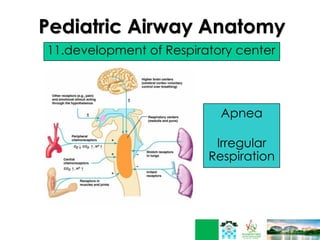
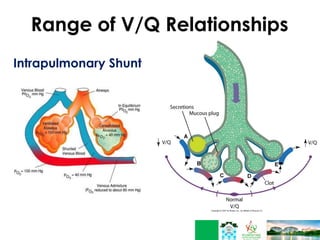
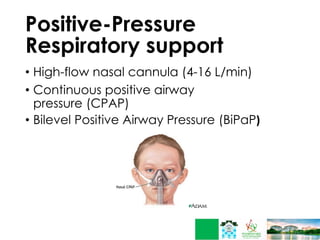
This document discusses respiratory failure in pediatrics. It begins by defining respiratory failure as insufficient oxygenation and ventilation to meet metabolic demands. It then discusses why respiratory failure occurs more commonly in children than adults, noting several key differences in pediatric airway anatomy compared to adults that make them more susceptible. These include a higher larynx, floppier epiglottis, and still developing alveoli. Common causes of respiratory failure in children are also outlined, including airway obstruction, lung disease, and ventilatory pump failure. Signs and symptoms are described along with diagnostic tests like blood gases. Management is focused on treating the underlying cause, providing adequate oxygenation initially through supplemental oxygen, and positive pressure support like CP