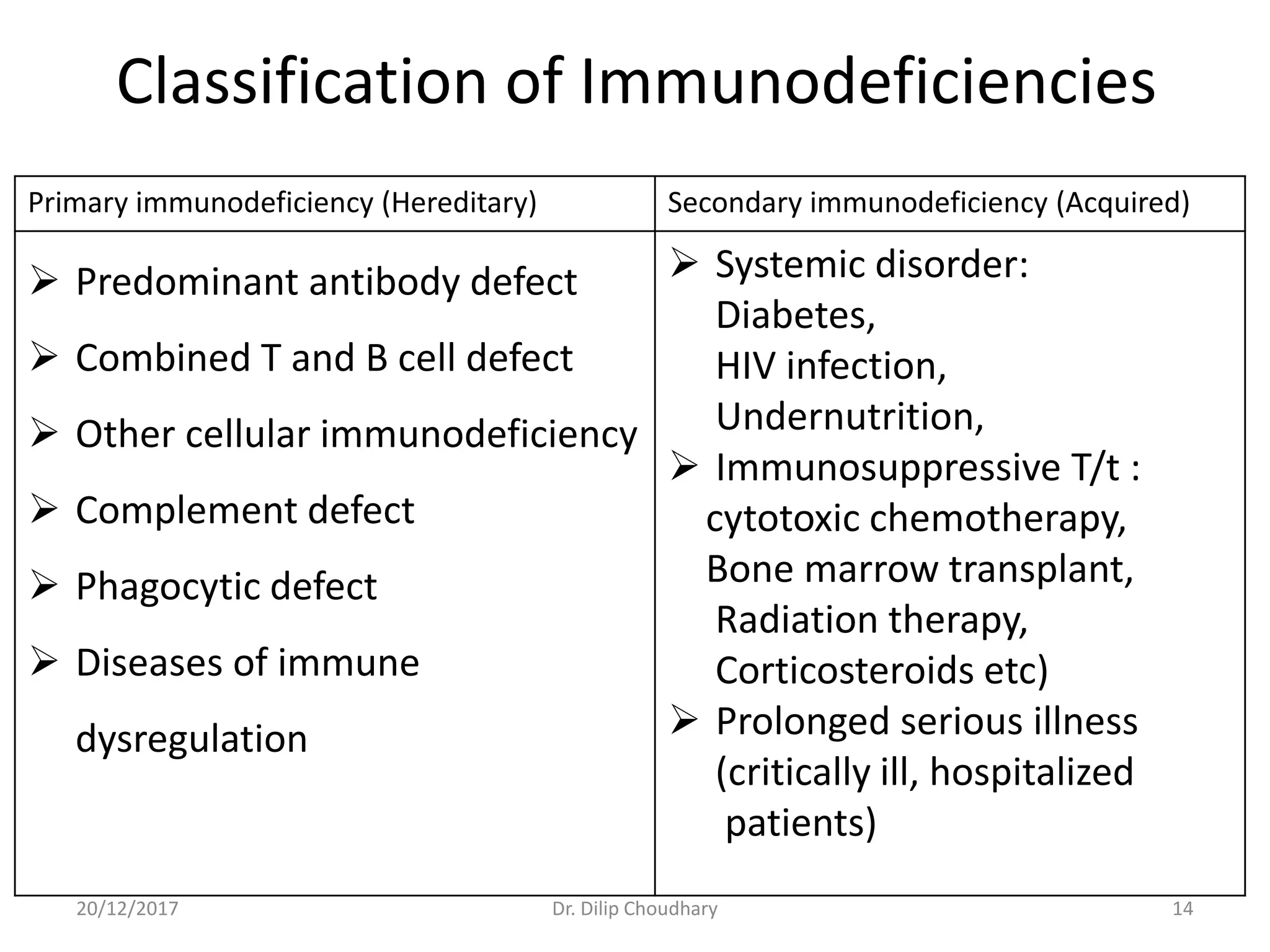
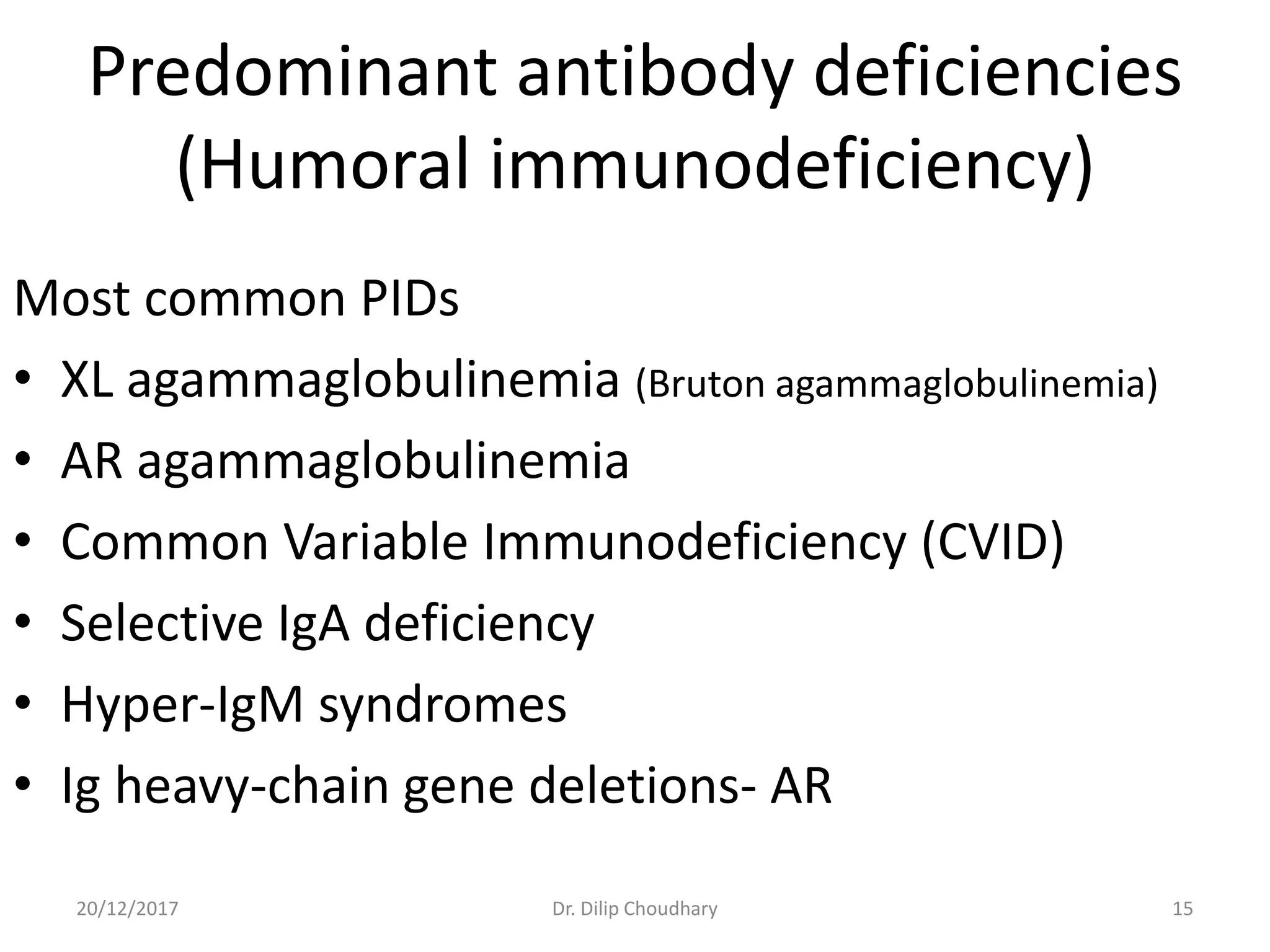
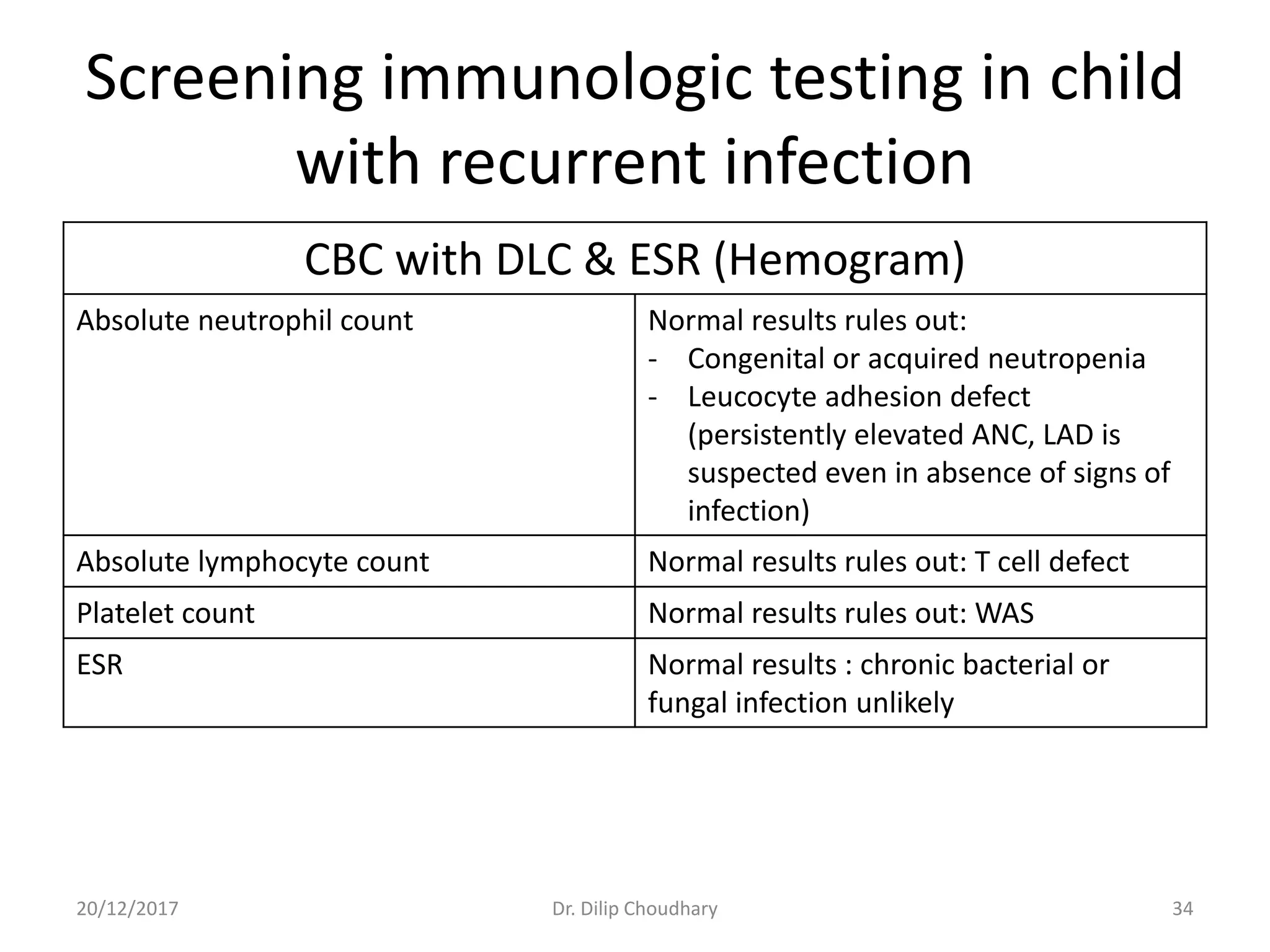
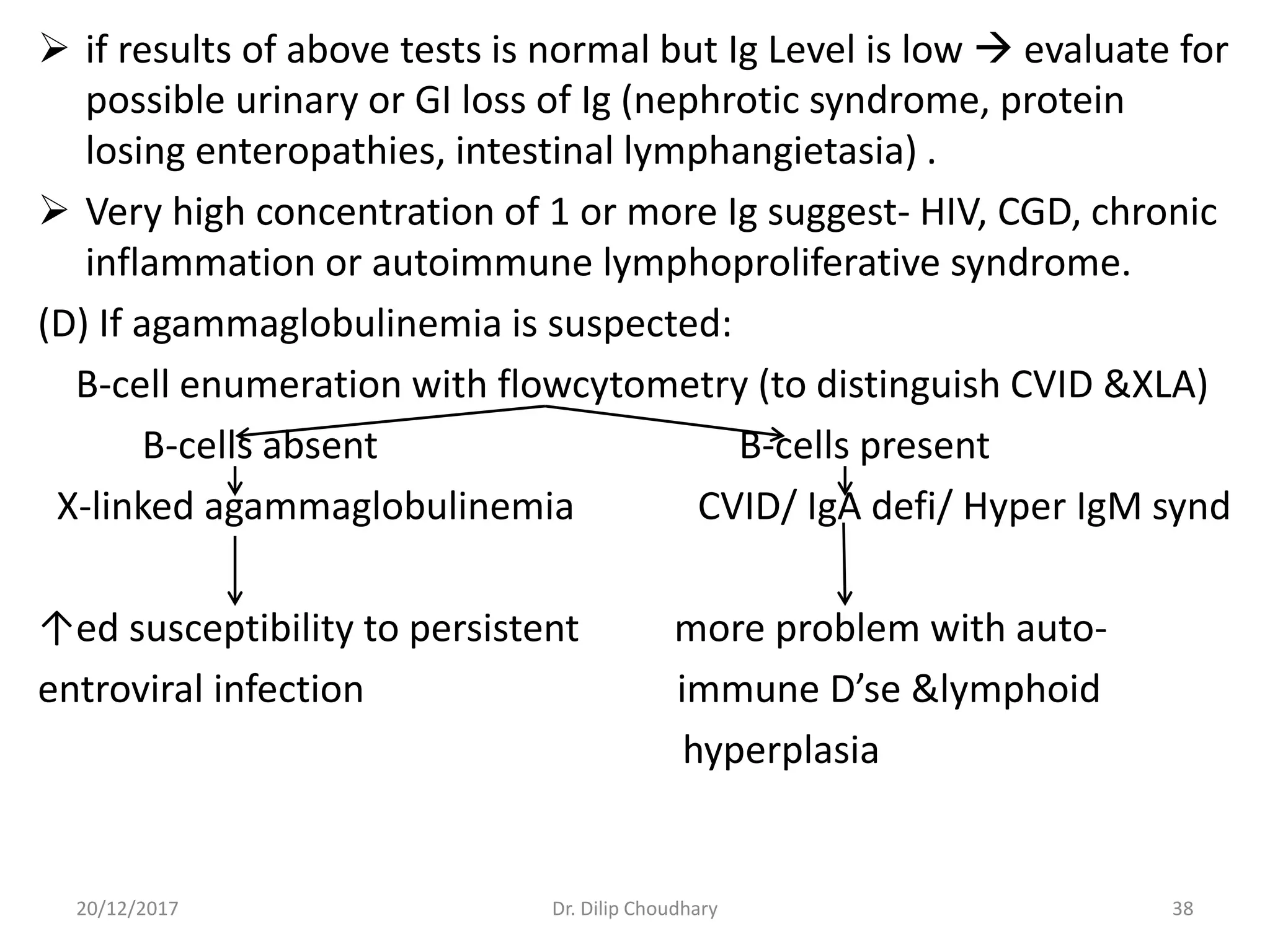
The document discusses the approach to diagnosing and managing pediatric patients with suspected immunodeficiency disorders, highlighting a case of a 5-month-old child with recurrent infections. It details various types of immunodeficiencies, their clinical features, differential diagnoses, and necessary investigations, along with criteria for suspicion and screening tests. Additionally, it addresses treatment options and the importance of prenatal diagnosis and genetic counseling for certain immunodeficiency disorders.