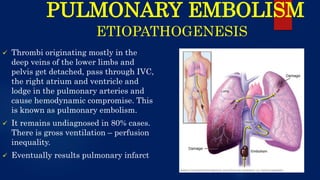
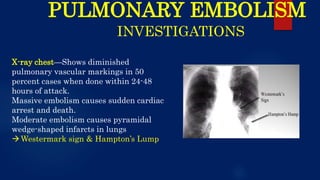
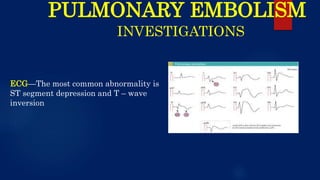
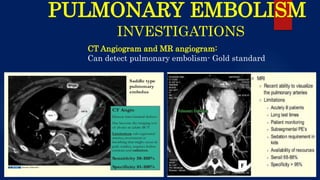
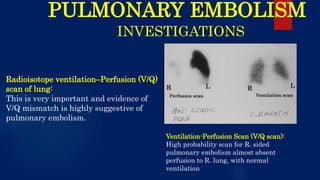
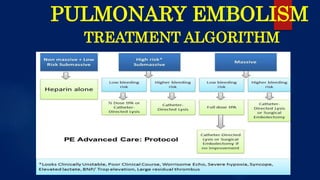
The document provides a comprehensive overview of pulmonary embolism, detailing its etiopathogenesis, which involves thrombi detaching from deep veins and obstructing pulmonary arteries. Clinical features include a triad of dyspnea, chest pain, and hemoptysis, with a range of symptoms from sudden collapse to progressive breathing difficulties. Investigations such as CT angiography and V/Q scans are essential for diagnosis, while treatments include anticoagulation, thrombolysis, and embolectomy in severe cases.