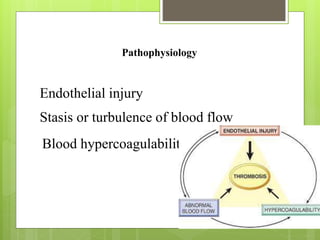
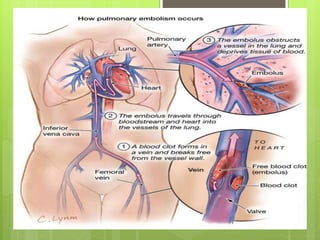
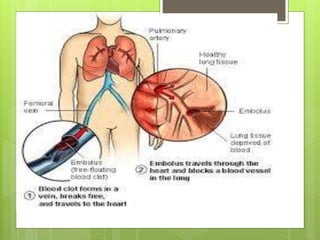
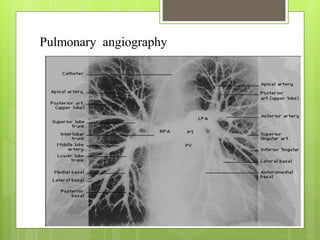
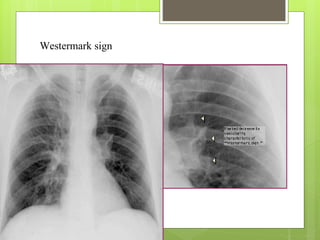
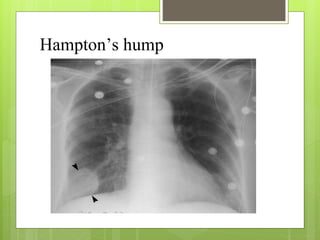
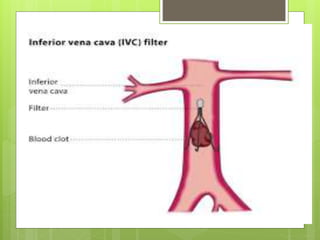
Pulmonary embolism refers to obstruction of the pulmonary artery or its branches by material such as blood clots that originate elsewhere. It is caused by alterations in blood flow, vessel wall factors, or hypercoagulable blood. Clinically, it presents with chest pain, shortness of breath, and hypoxia. Diagnosis involves tests such as D-dimer, CT angiogram, and V/Q scan. Treatment consists of anticoagulation with heparin or warfarin as well as thrombolysis for massive cases. Complications include right heart strain, pulmonary hypertension, and death.