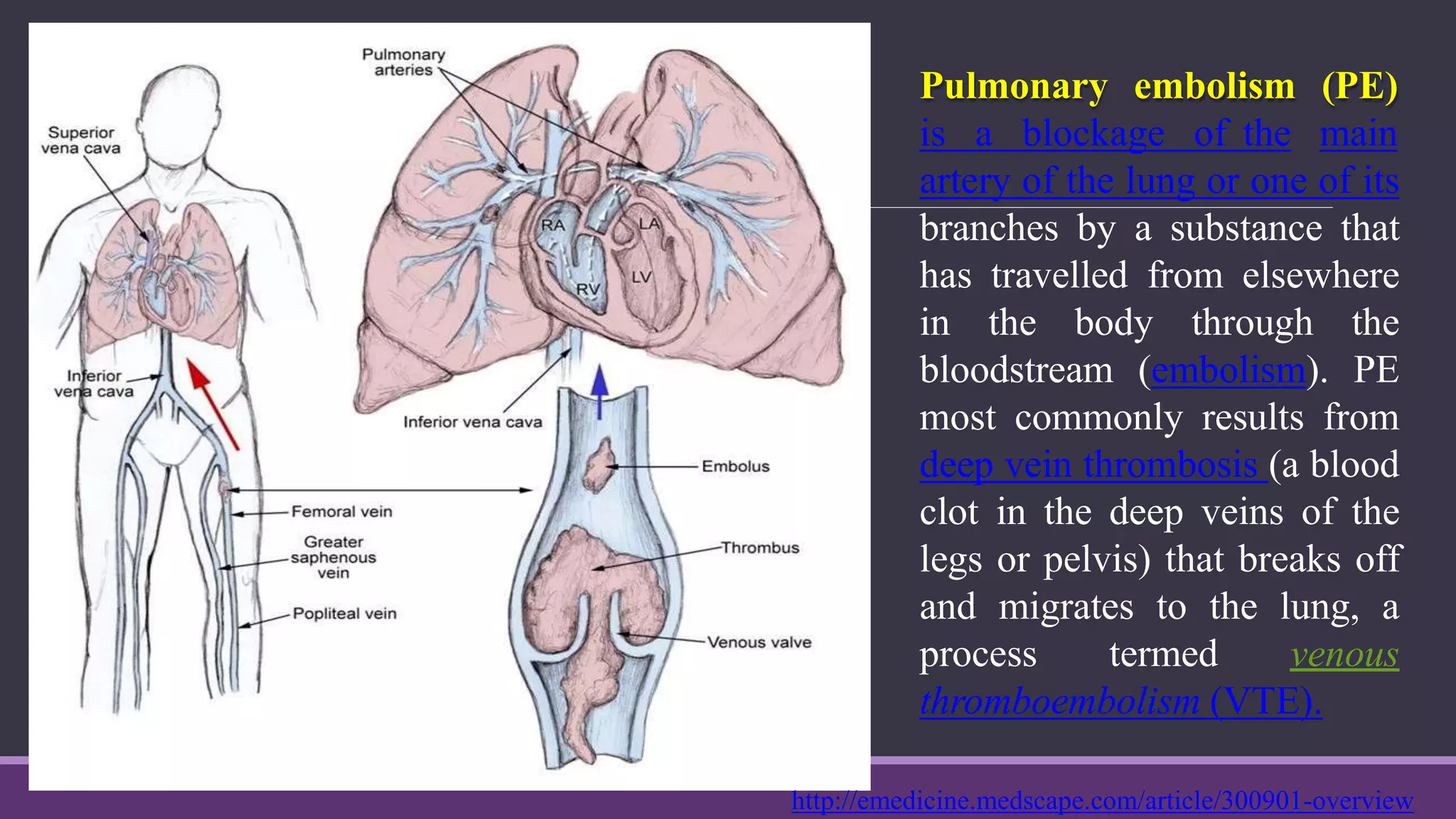
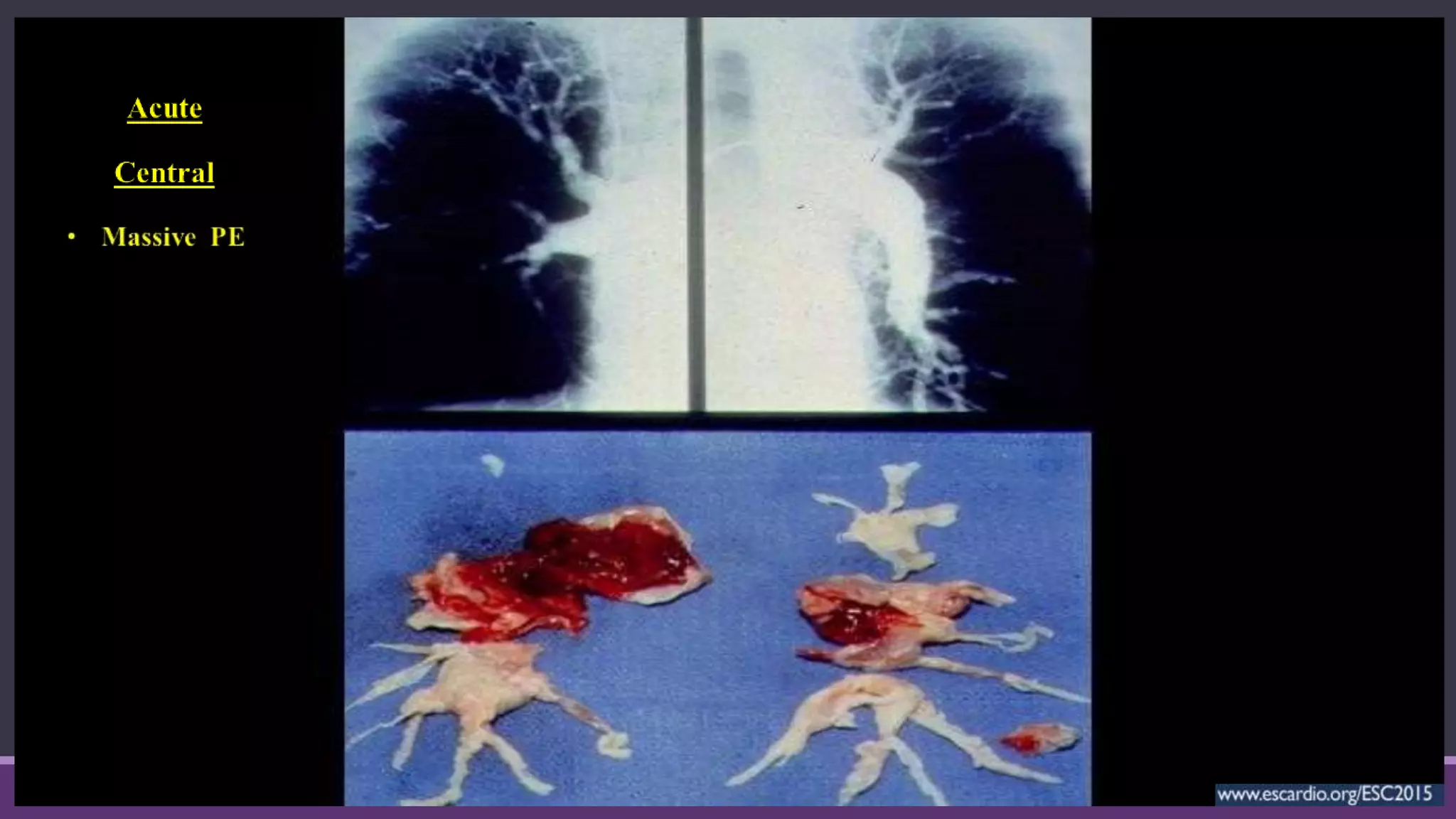
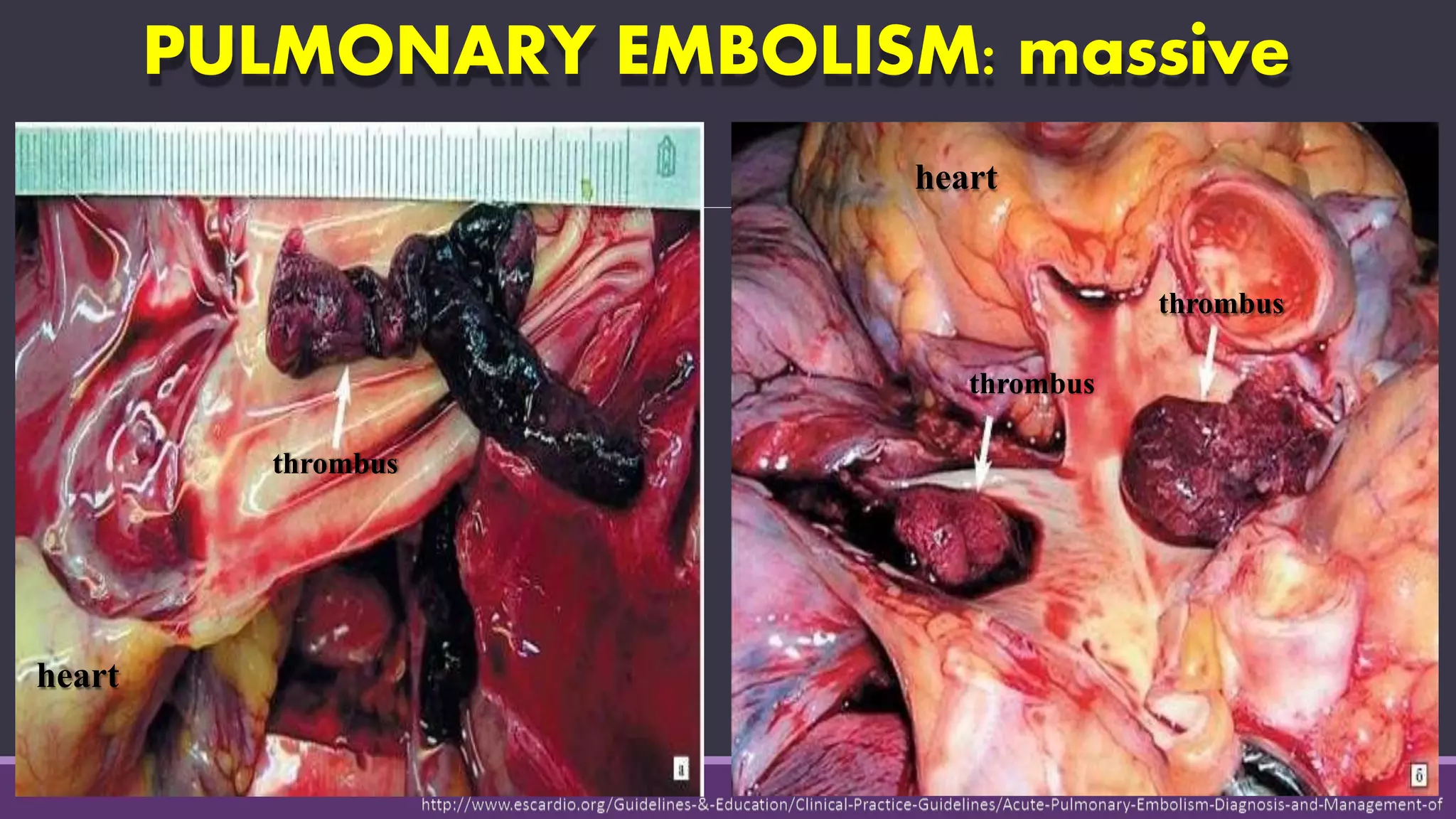
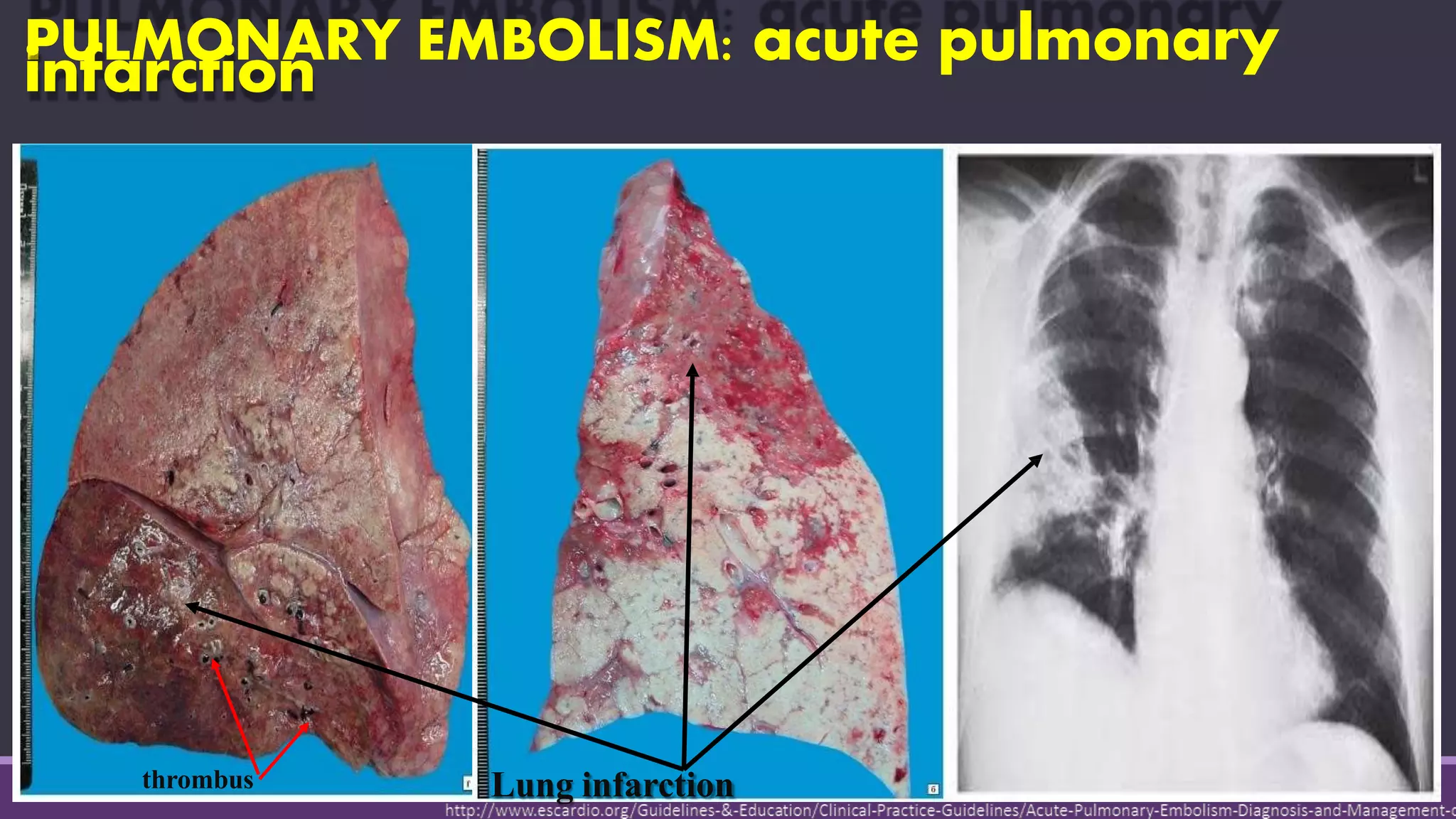
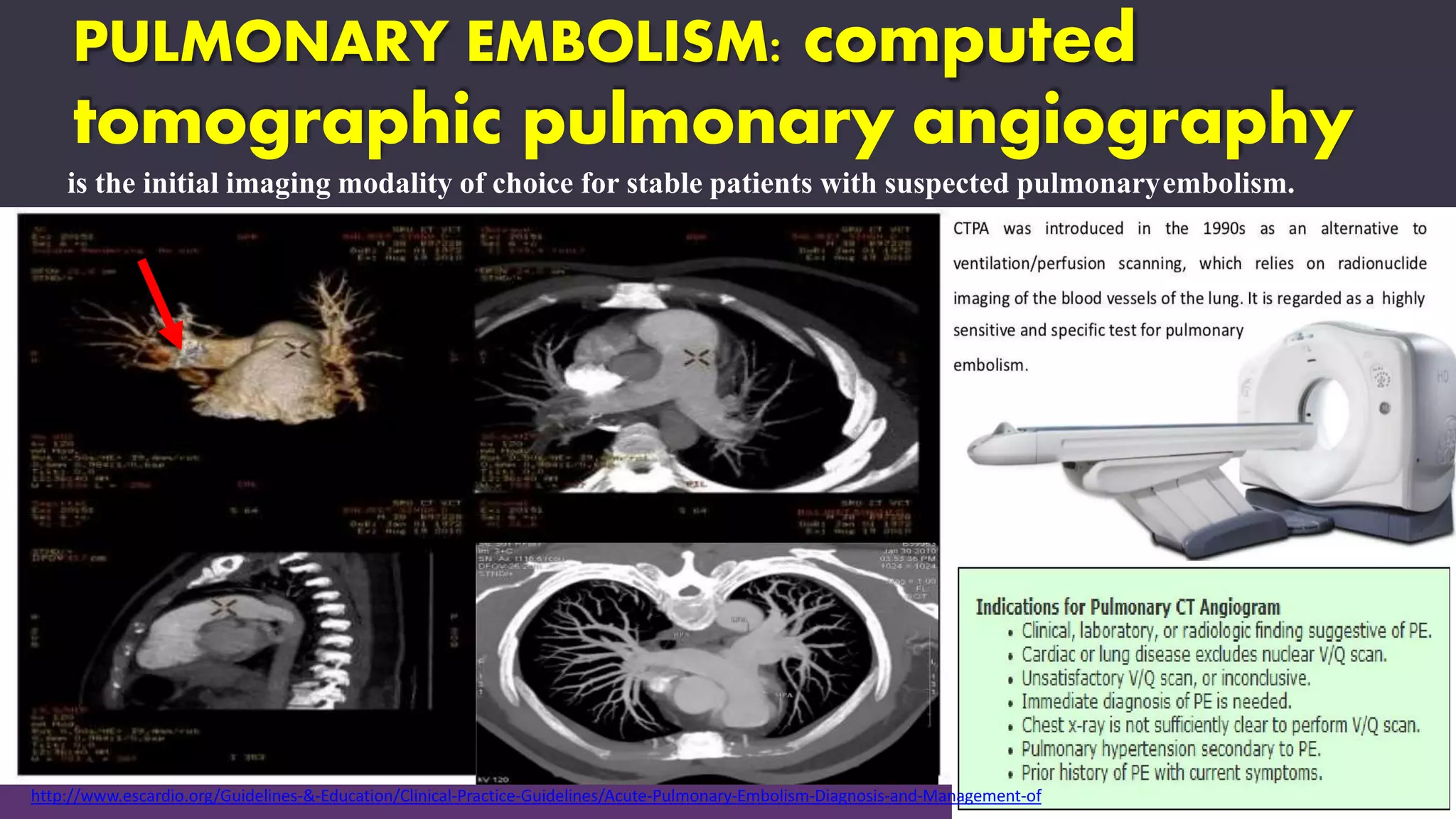
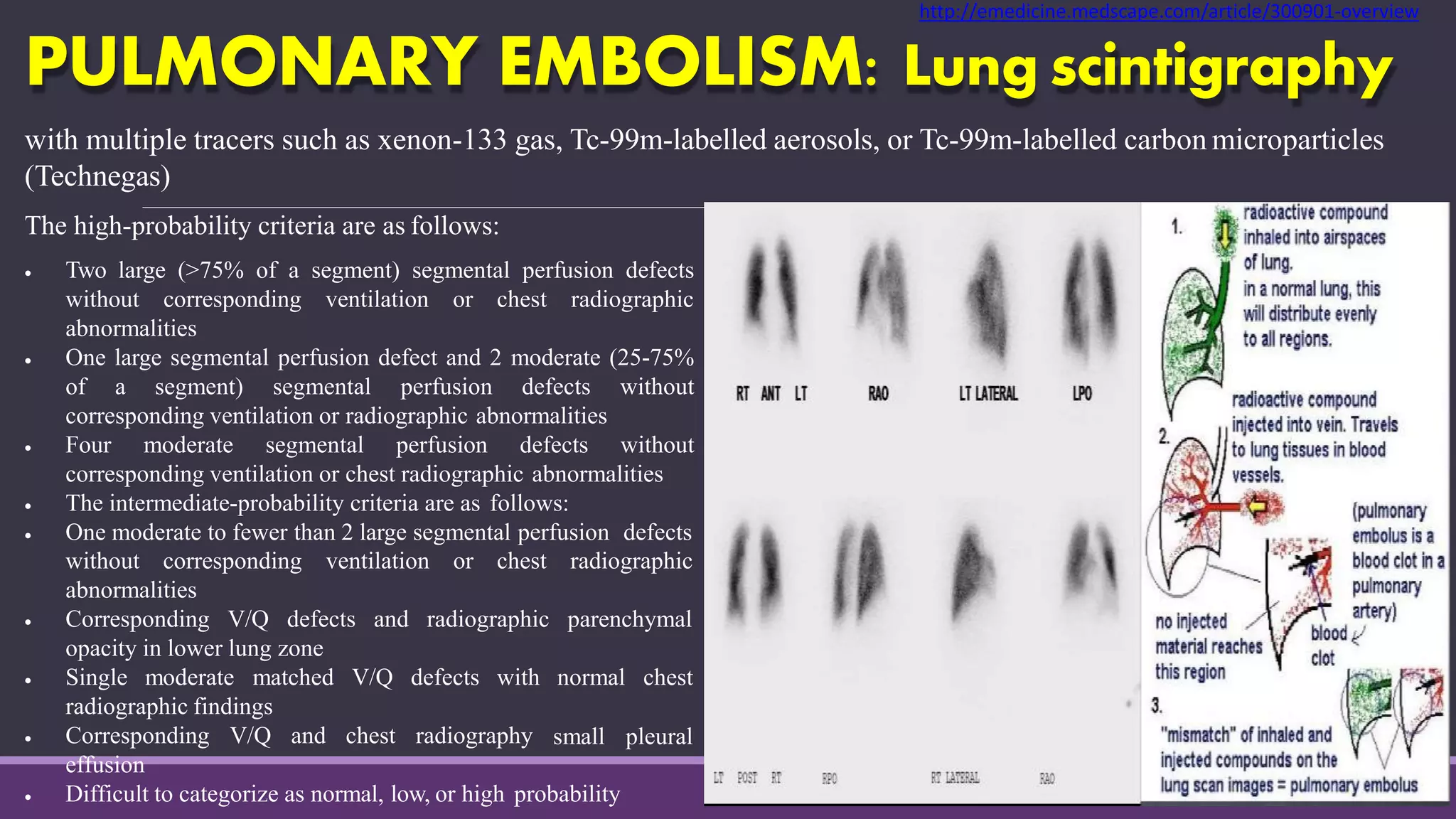
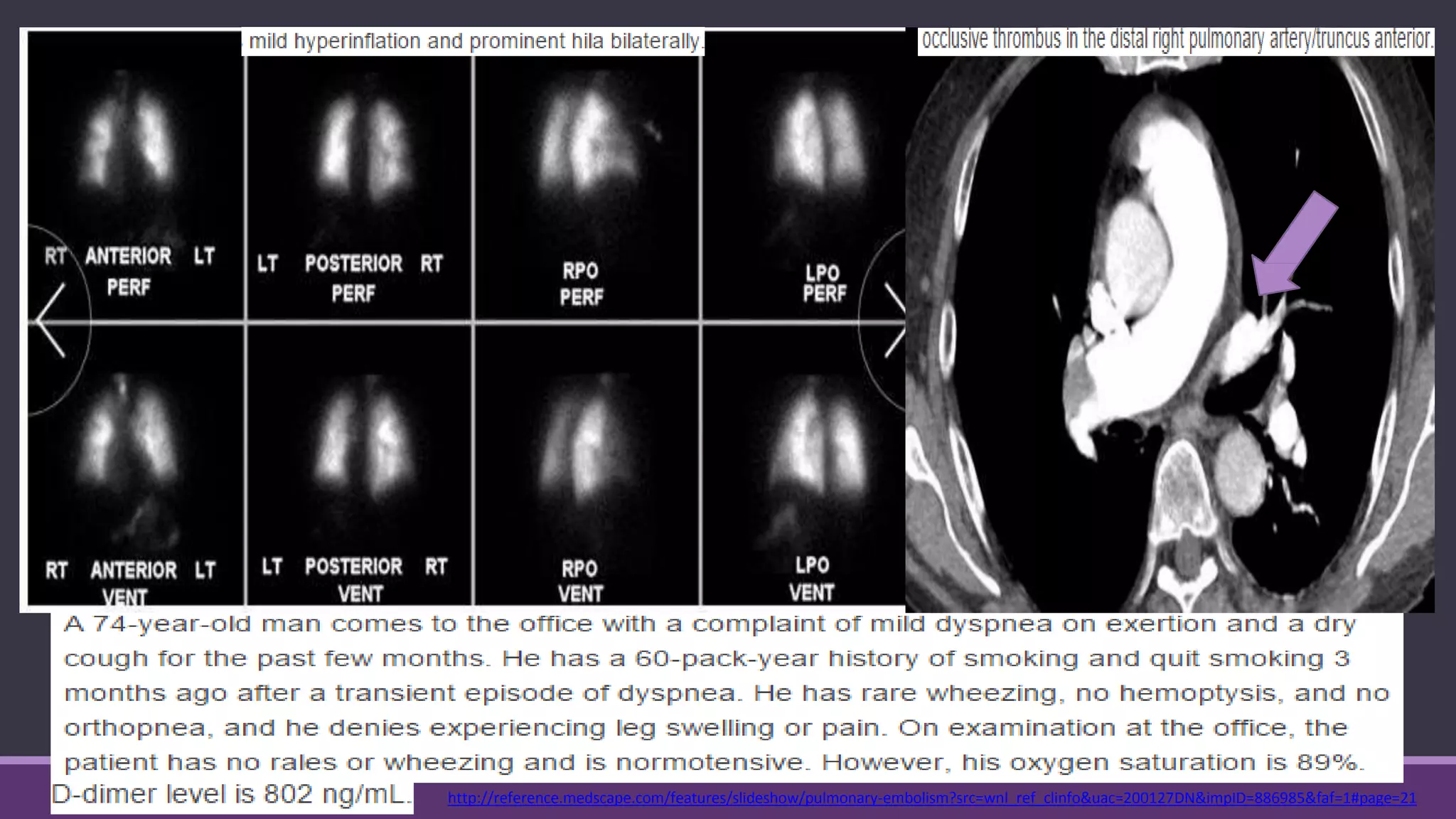
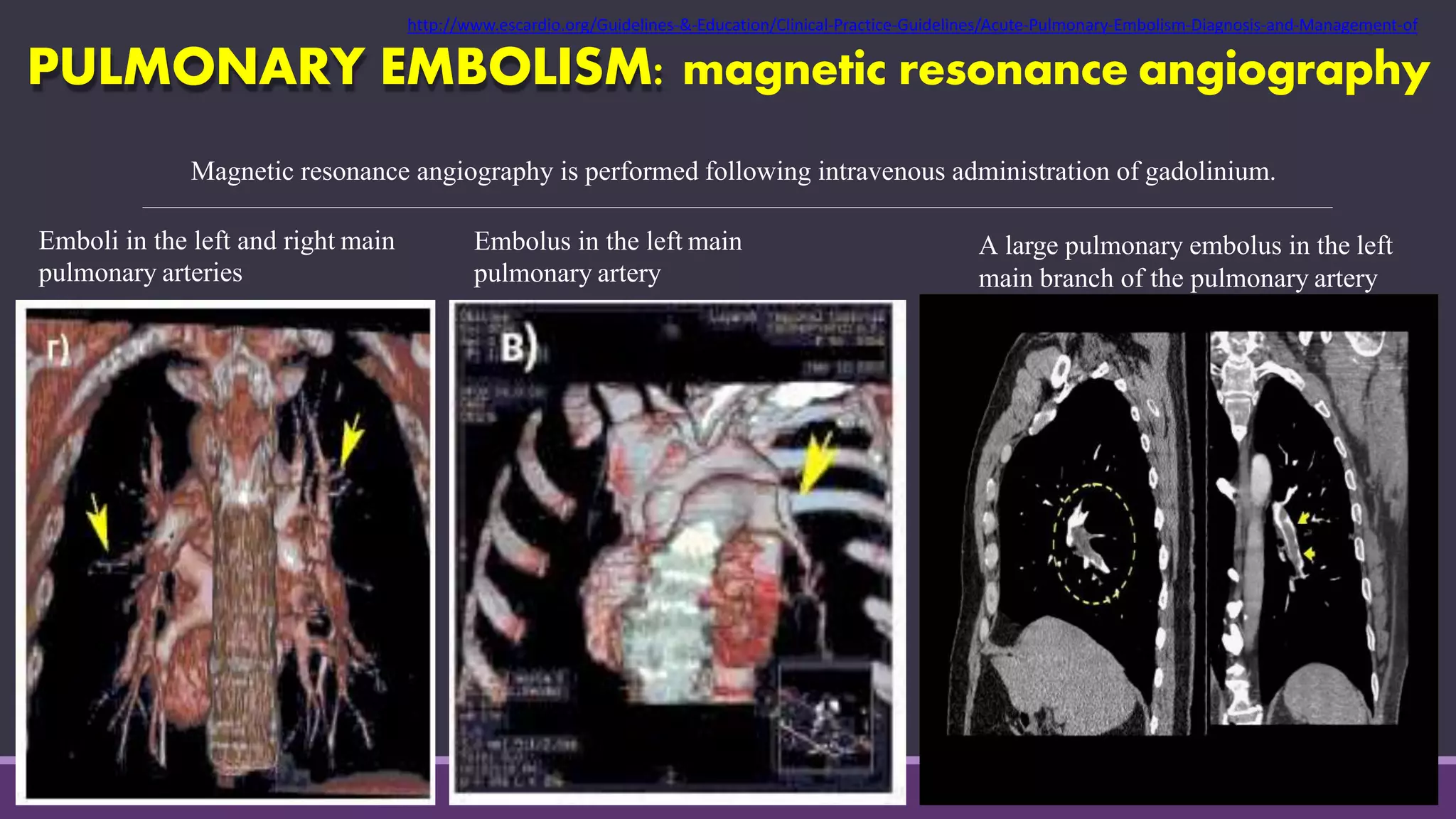
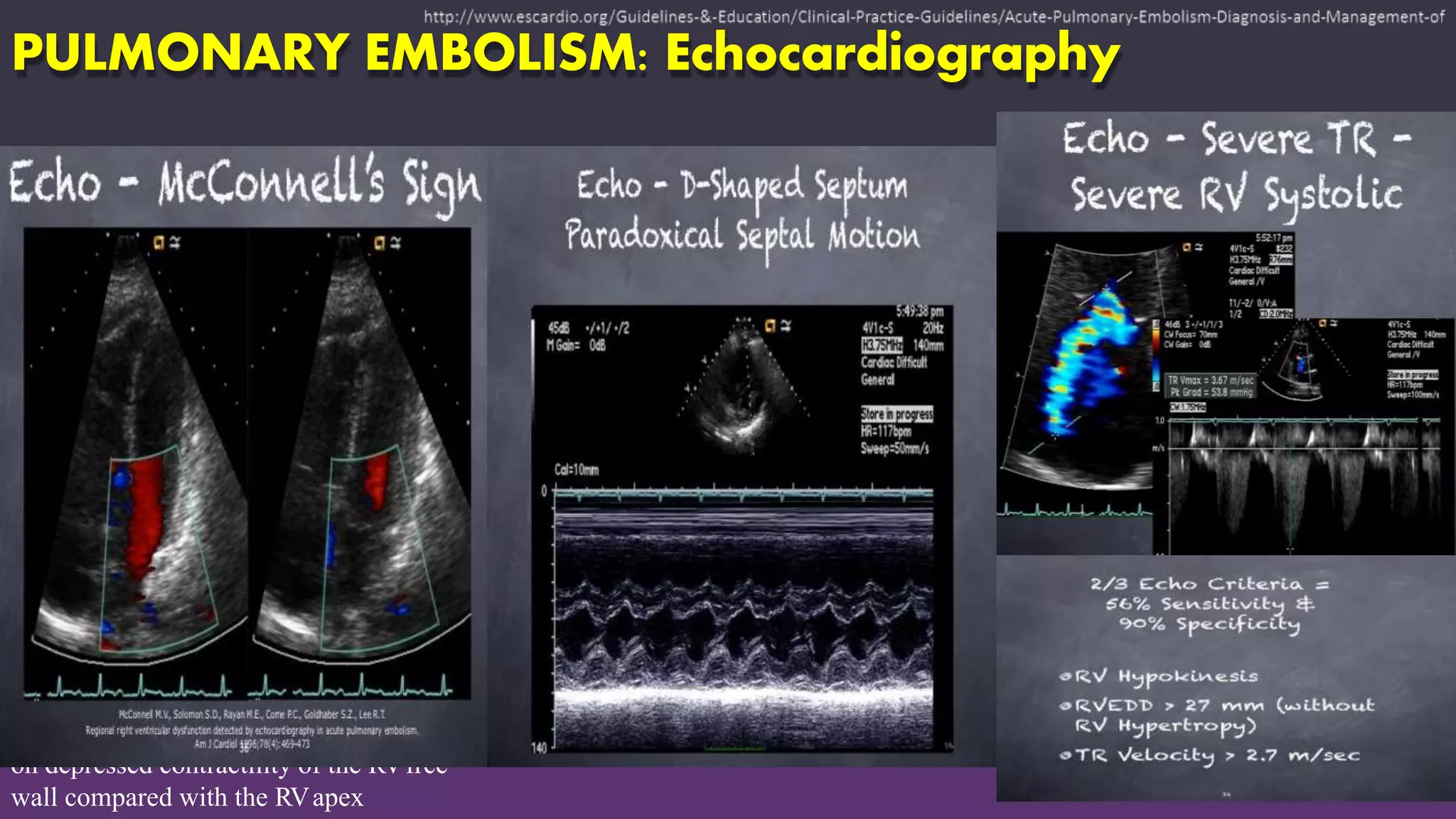
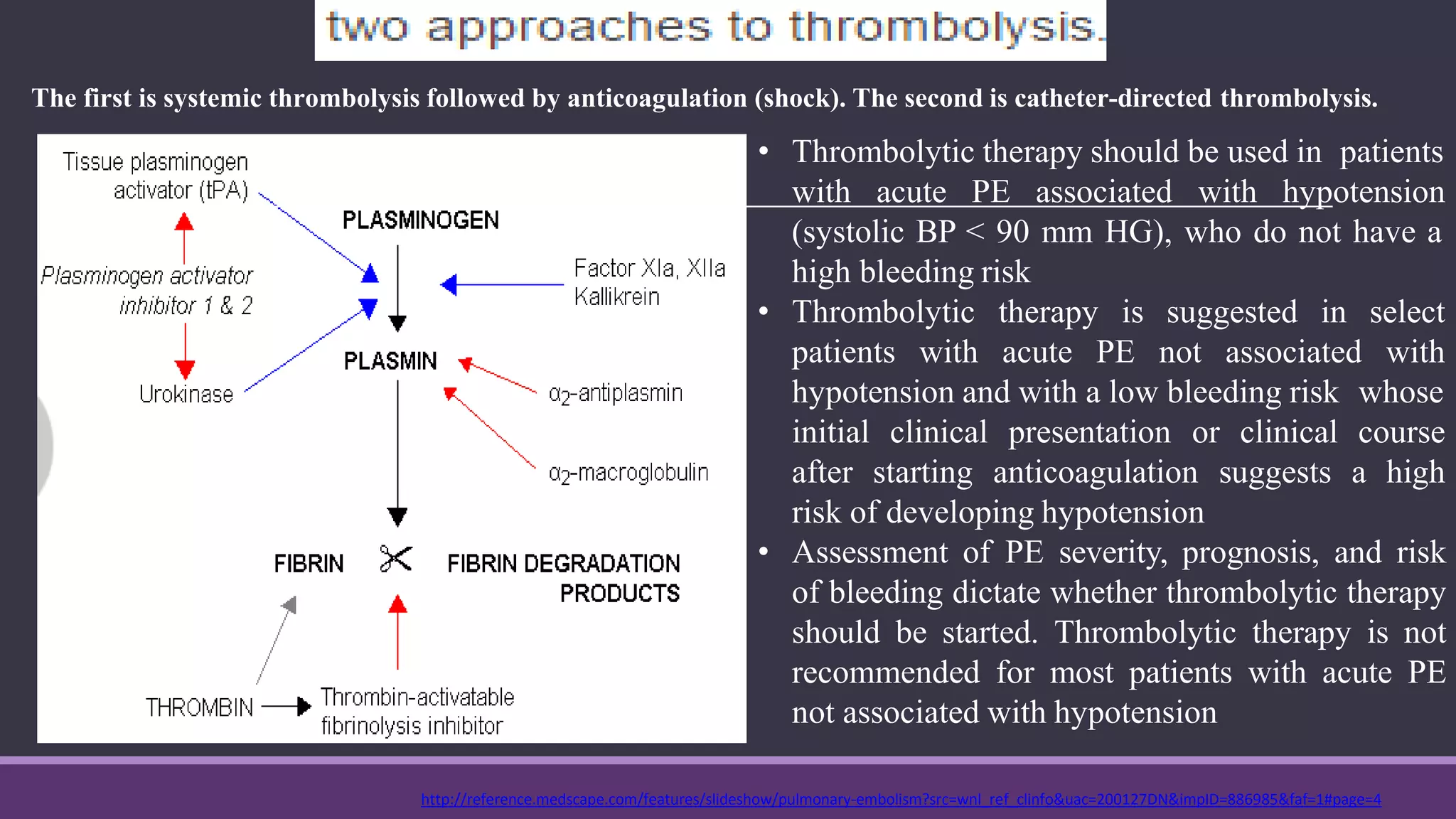
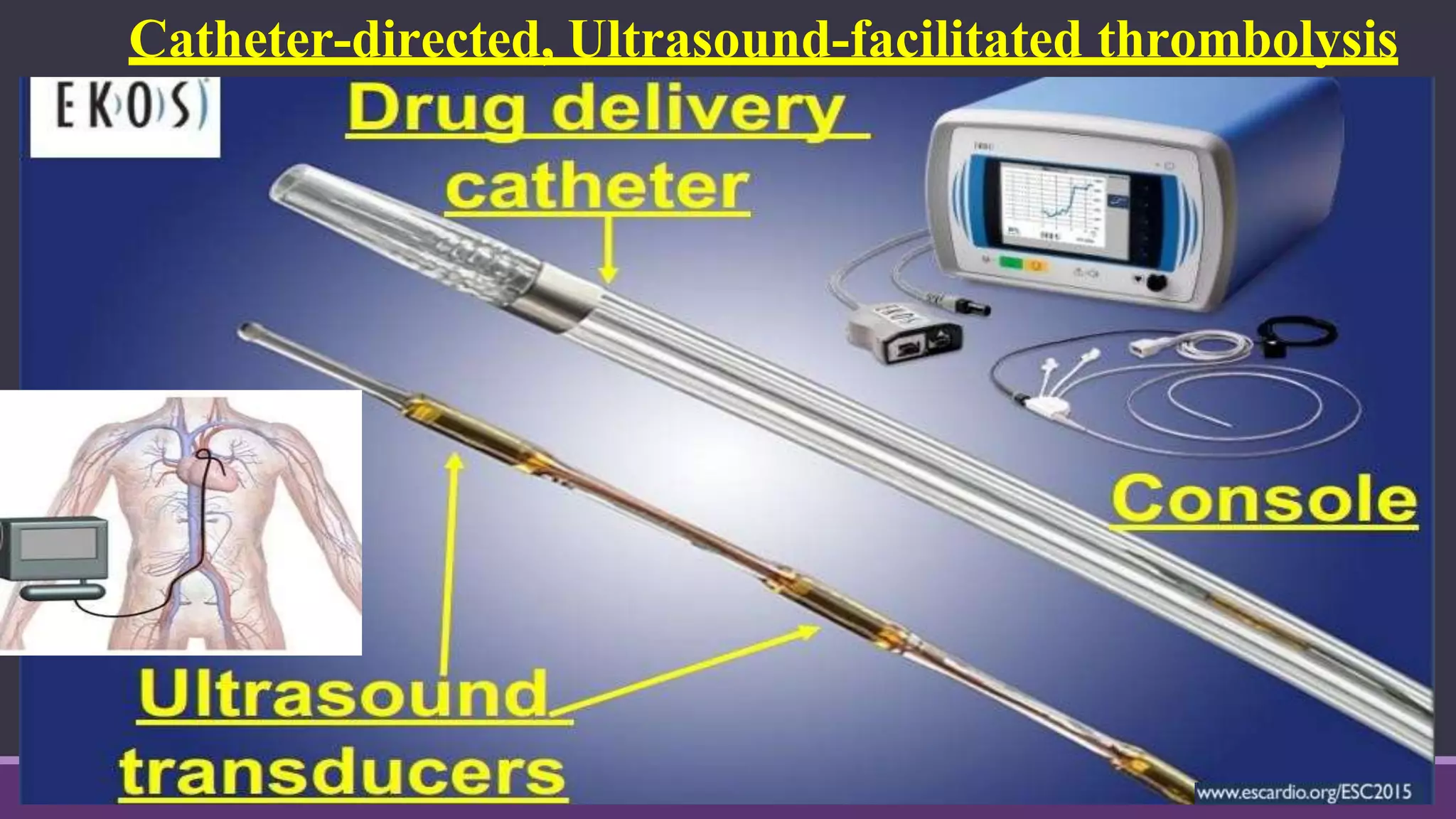
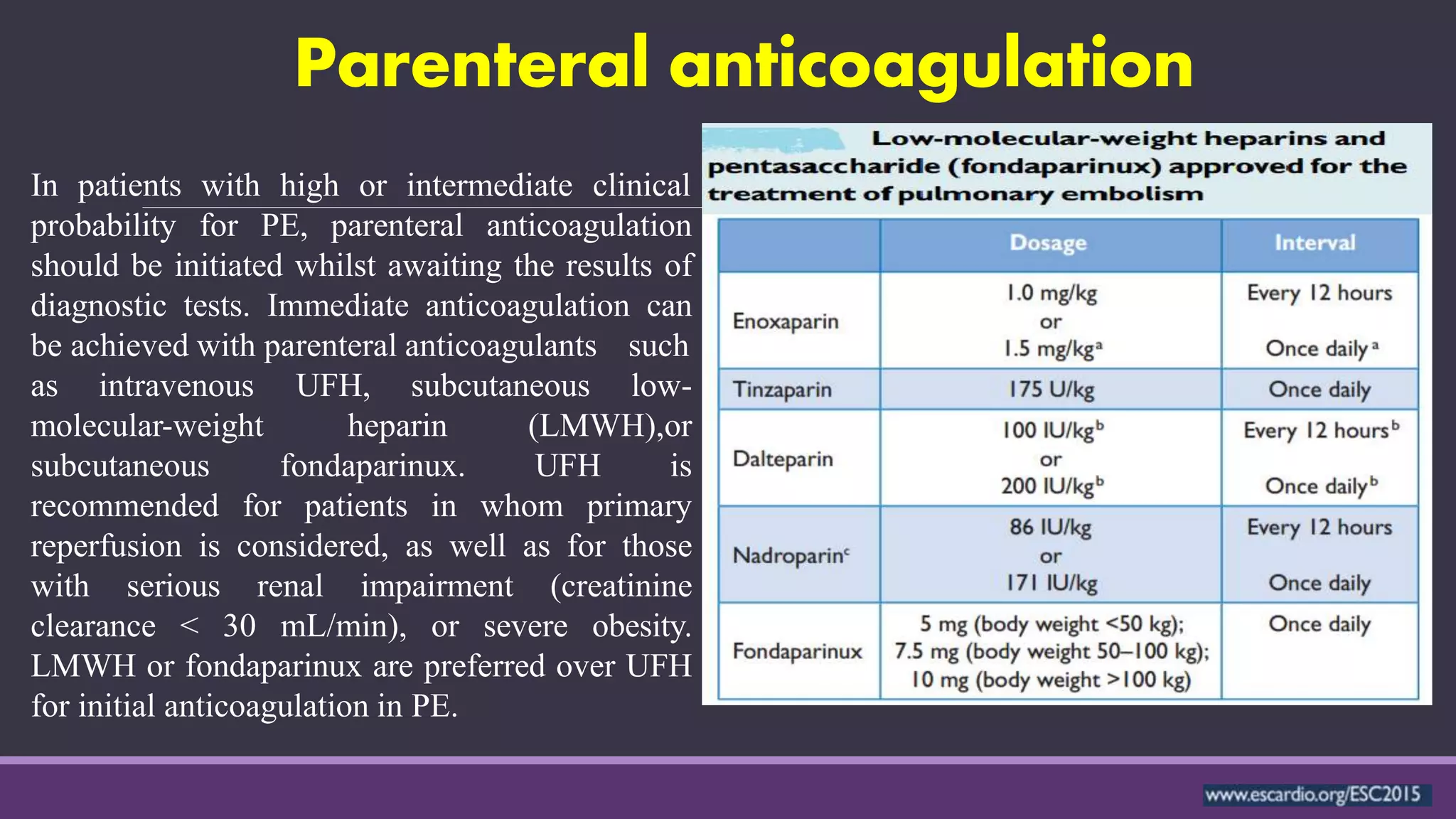
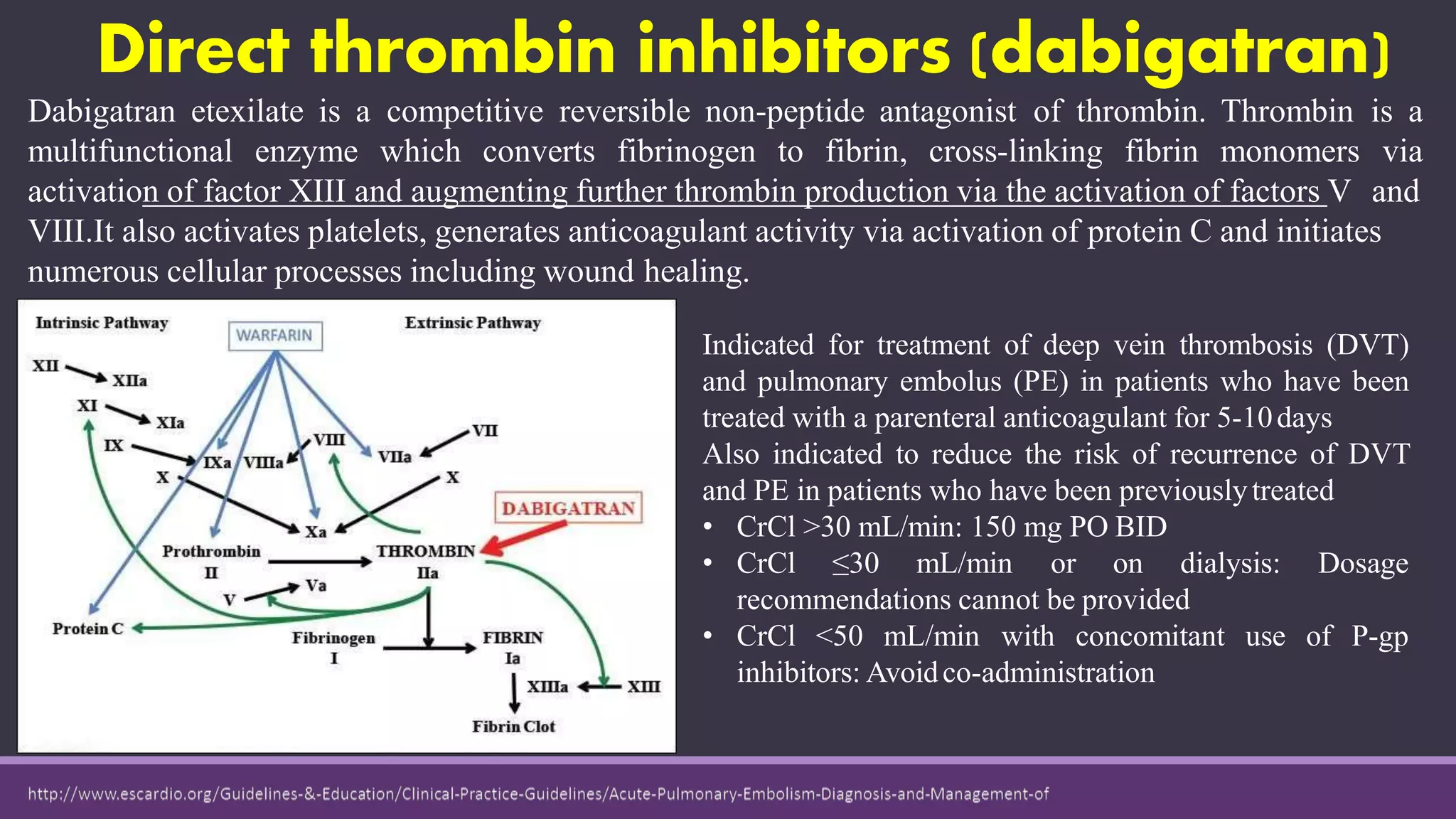
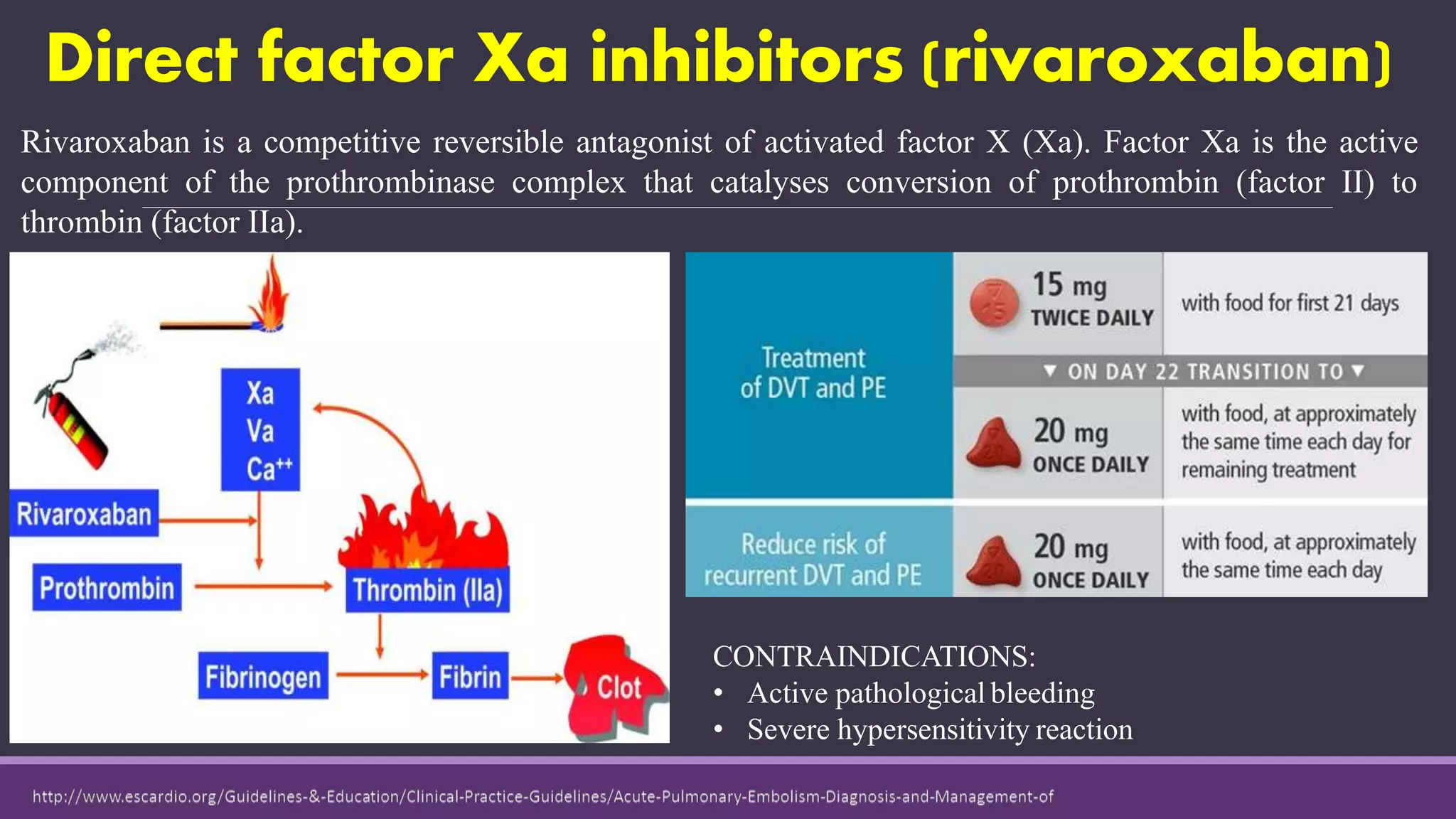
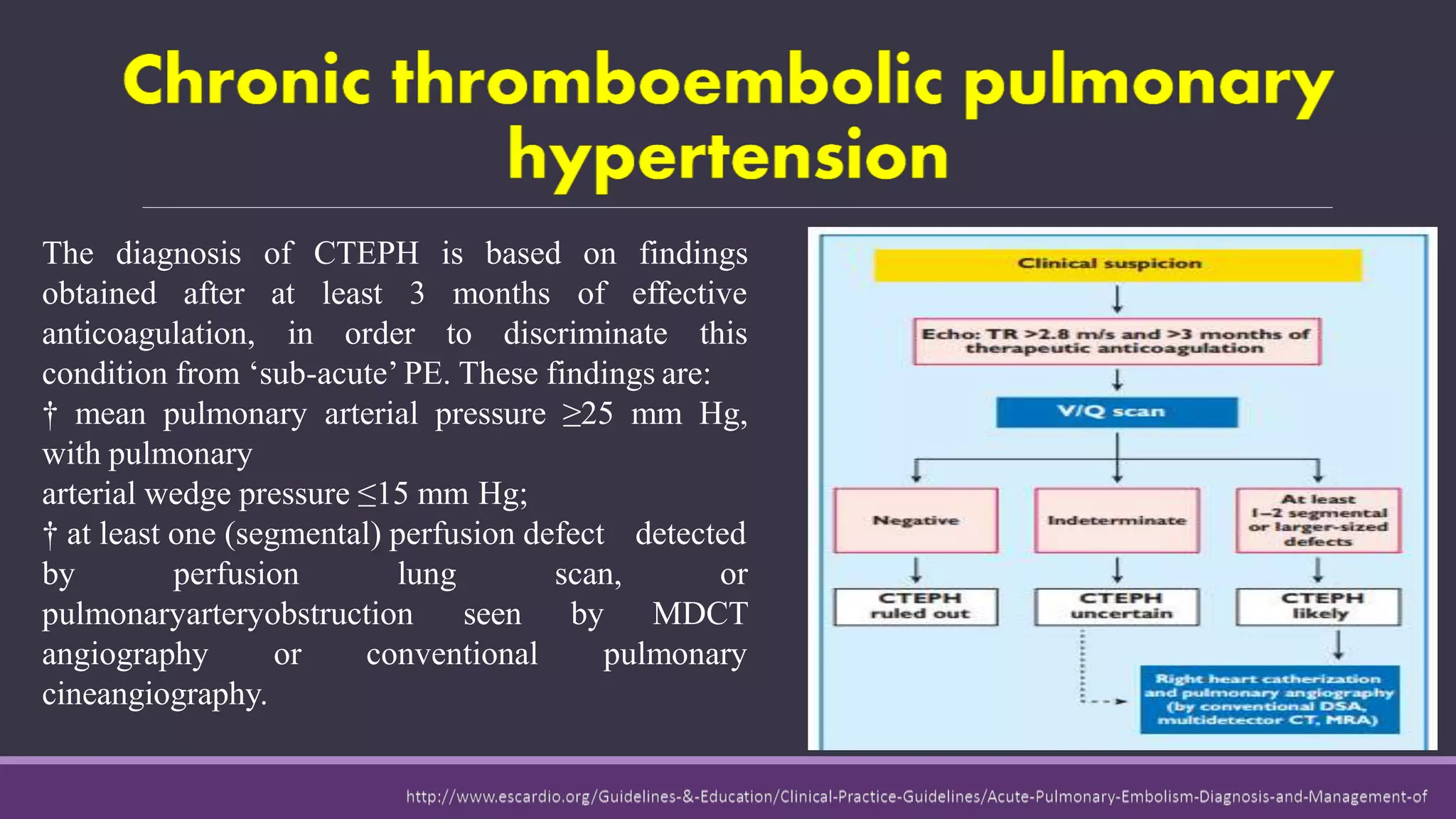
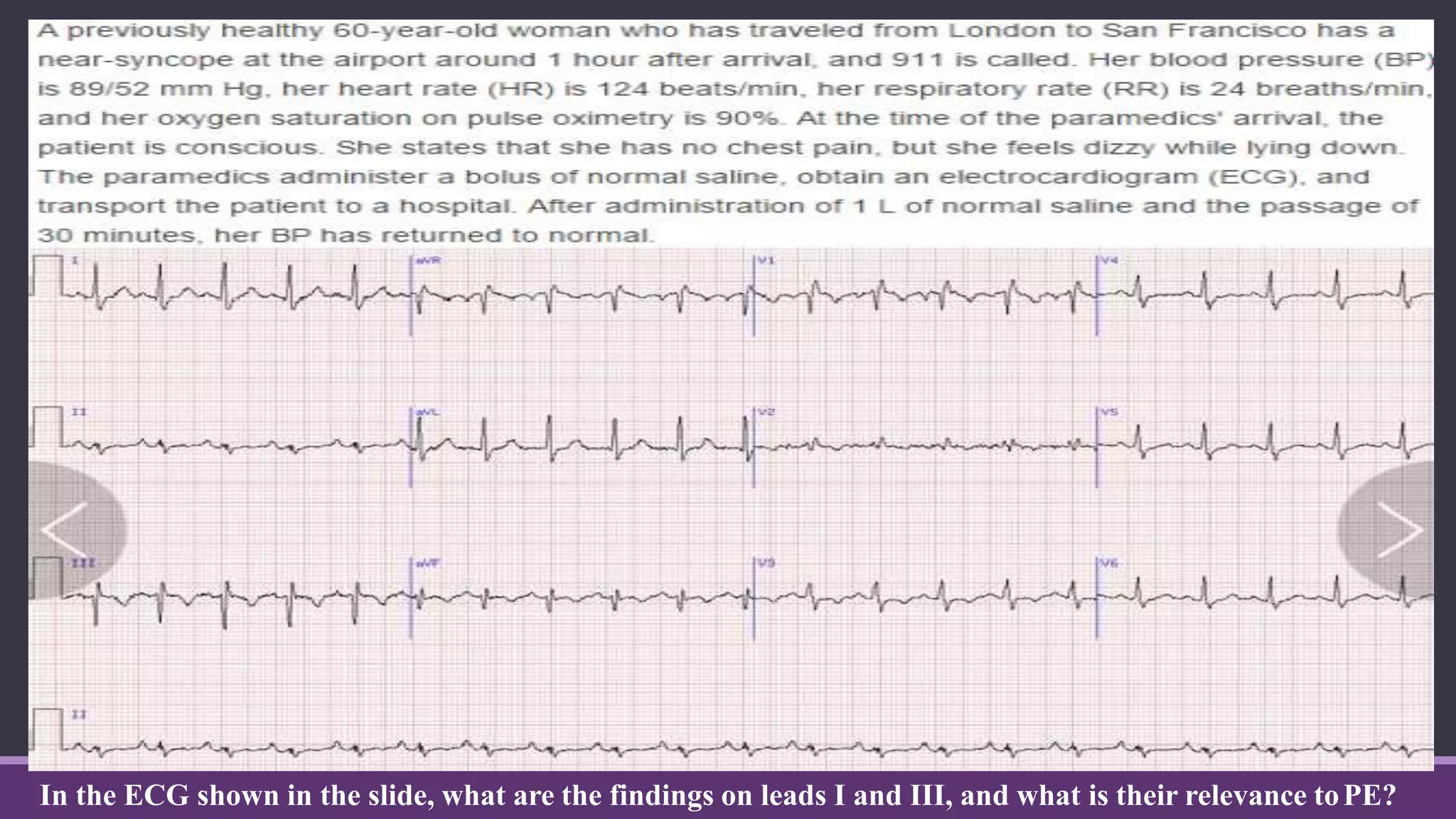
Pulmonary embolism is a blockage in the pulmonary artery or its branches by material that travels from elsewhere in the body through the bloodstream. It is commonly caused by deep vein thrombosis. Pulmonary embolisms are classified based on size and location as massive, submassive, low-risk, central or peripheral. Diagnosis involves assessing clinical probability, D-dimer testing, imaging like CT pulmonary angiography, ventilation-perfusion scanning, pulmonary angiography, and echocardiography. Treatment of acute pulmonary embolism includes supportive care, anticoagulation, thrombolytic therapy for high-risk cases, and sometimes surgical or catheter-based interventions.