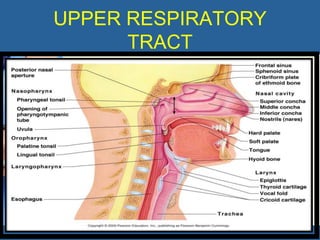
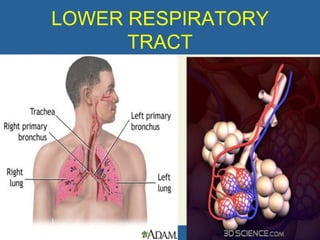
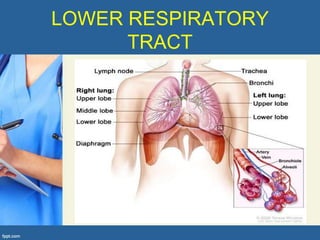
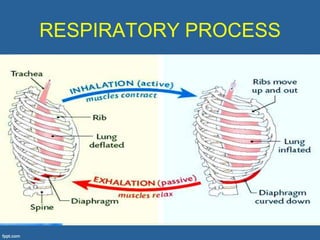
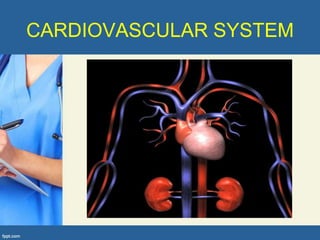
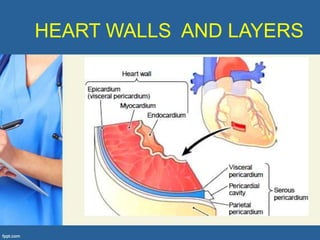
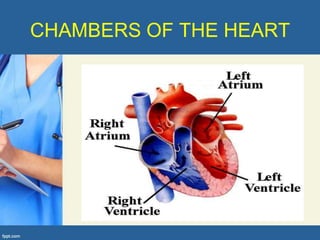
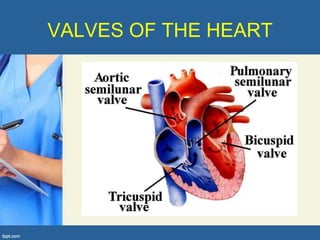
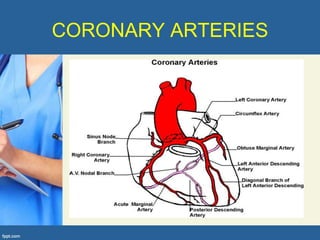
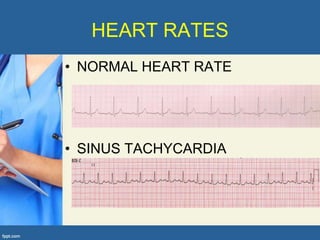
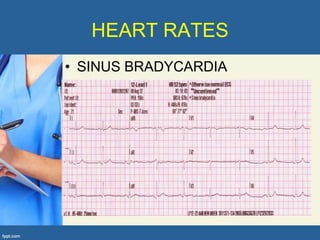
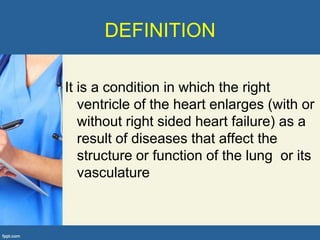
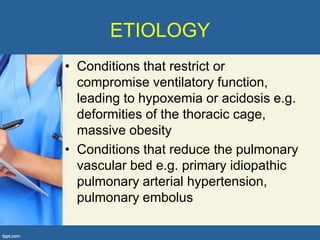
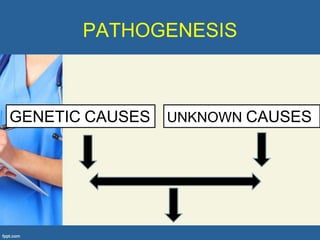
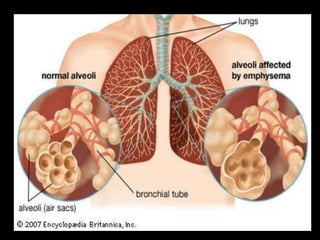
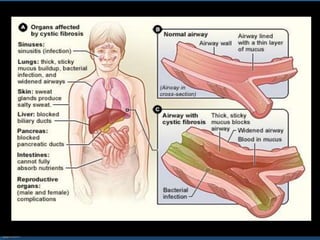
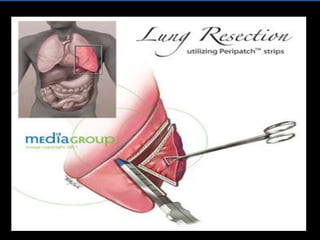
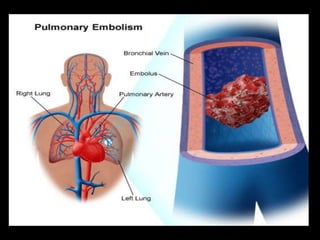
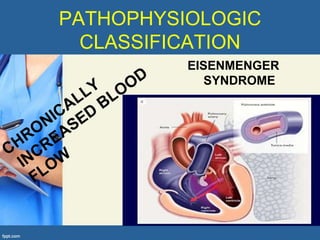
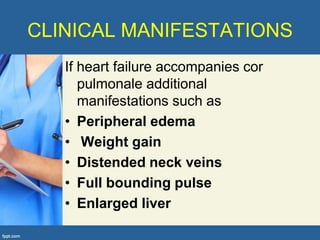
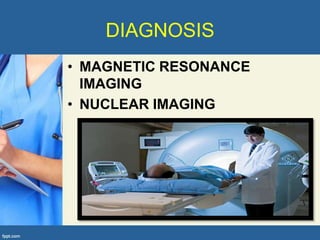
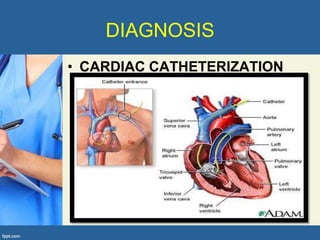
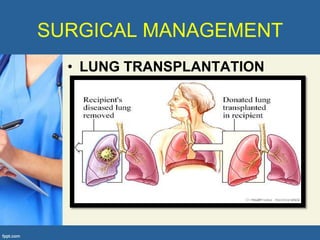
This document provides an overview of cor pulmonale, including its objectives, definitions, etiology, pathogenesis, clinical manifestations, diagnosis, management, and nursing considerations. Cor pulmonale is defined as enlargement of the right ventricle due to lung disease and results in pulmonary hypertension. Common causes include COPD and pulmonary embolism. Symptoms include dyspnea and edema. Diagnosis involves physical exam, imaging, and cardiac catheterization. Treatment includes oxygen, diuretics, and lung transplantation in severe cases. Nursing focuses on managing symptoms and promoting rest and nutrition.
































![REFERENCES
• Padmavati S, Pathak S.N. Chronic
Cor Pulmonale in Delhi. American
Heart Association[Internet].aug
28.2012.available from
http://circ.ahajournals.org/
• Kings E.S, Mandel J.Cor
pulmonale[internet].july
9,2012.Available at
www.uptodate.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/corpulmonale-130120073258-phpapp01/85/Cor-pulmonale-67-320.jpg)
![REFERENCES
• Opotowsky a.r, Vedanthan .R,
Mamlin J.J. A Case Report of Cor
Pulmonale in a Woman Without
Exposure to Tobacco Smoke: An
Example of the Risks of Indoor
Wood Burning.The Medscape
journal of
Medicine[internet].January
29,2008.available from
www.pubmed.com](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/corpulmonale-130120073258-phpapp01/85/Cor-pulmonale-68-320.jpg)
