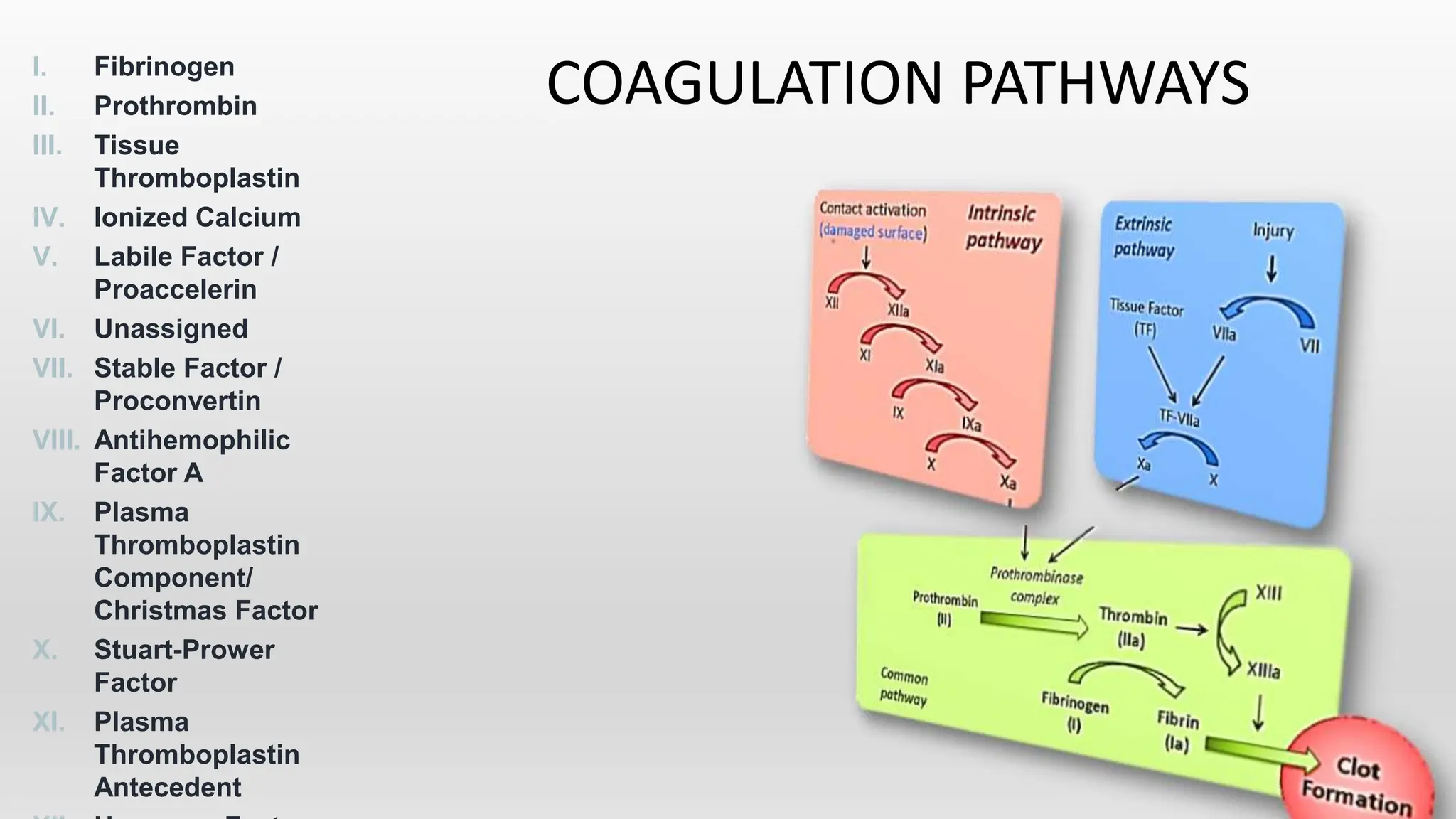
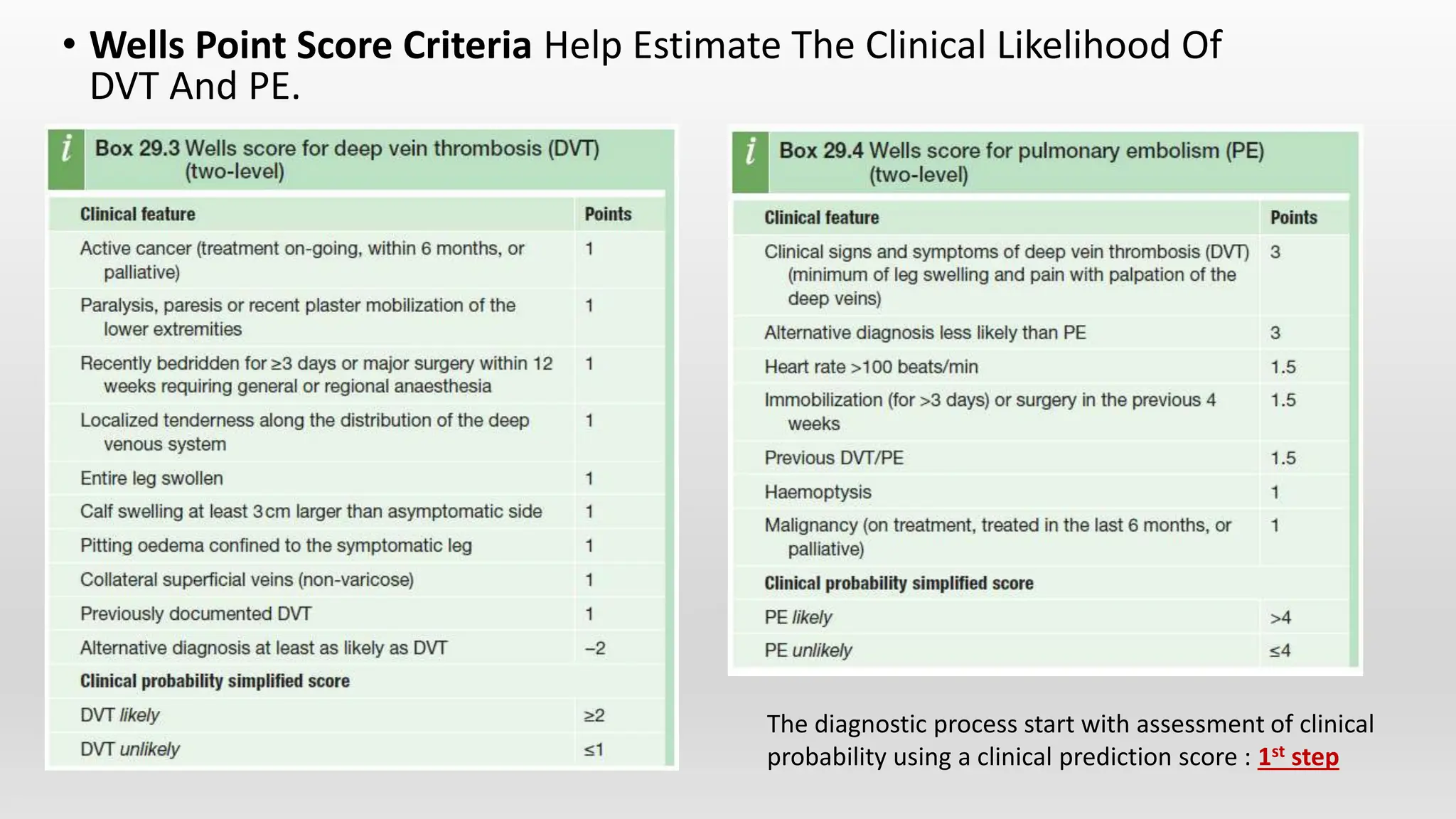
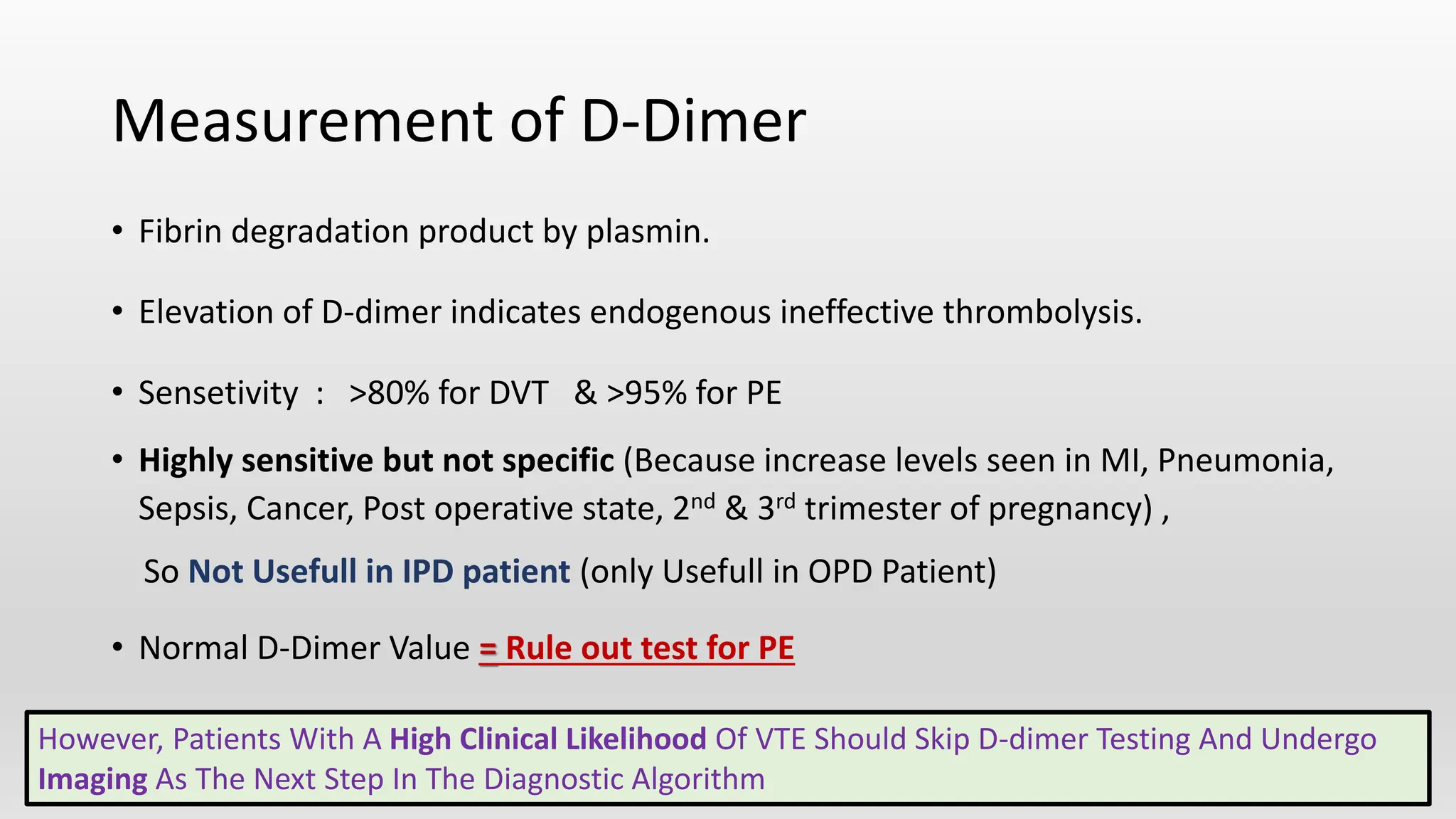
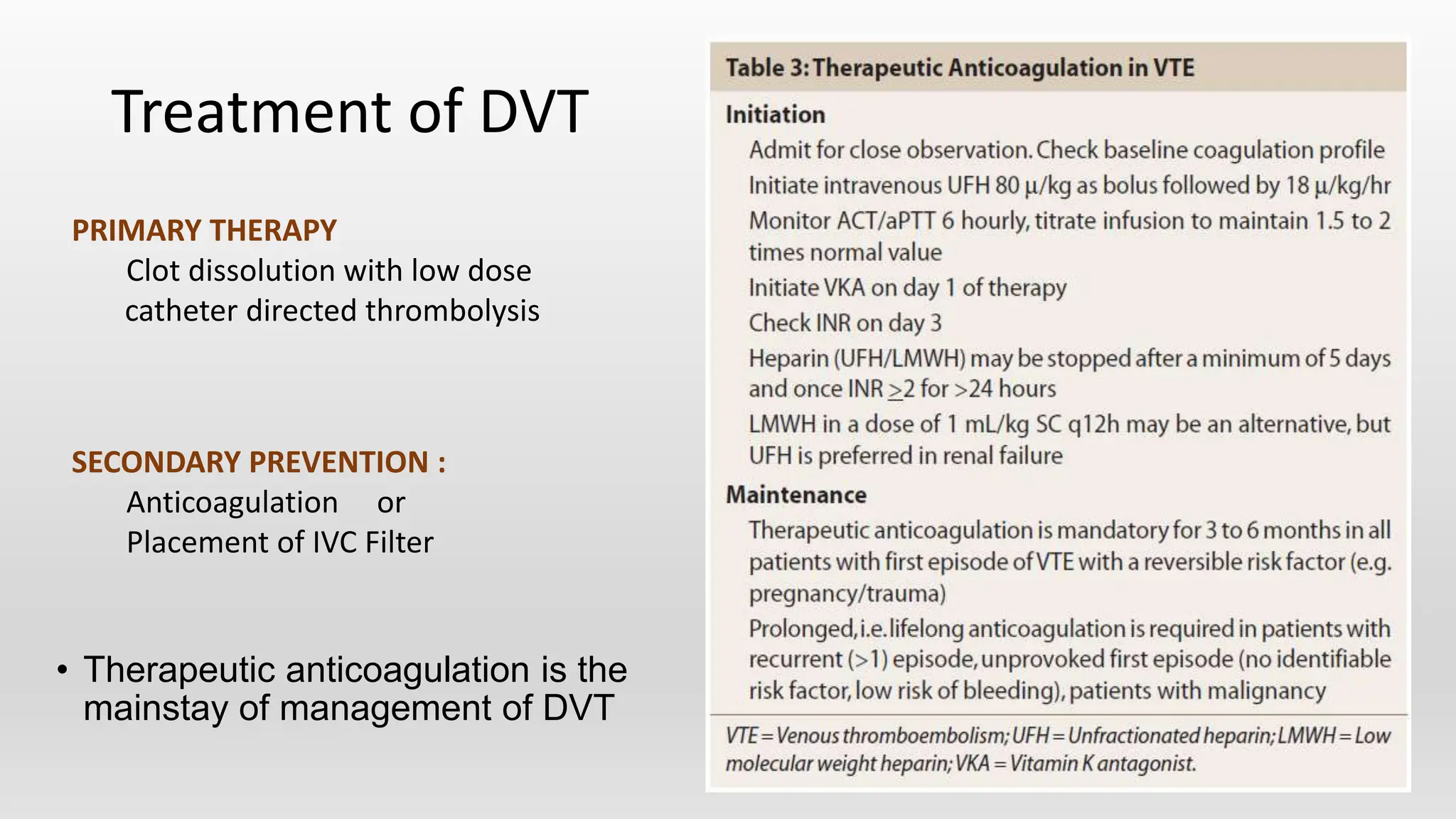
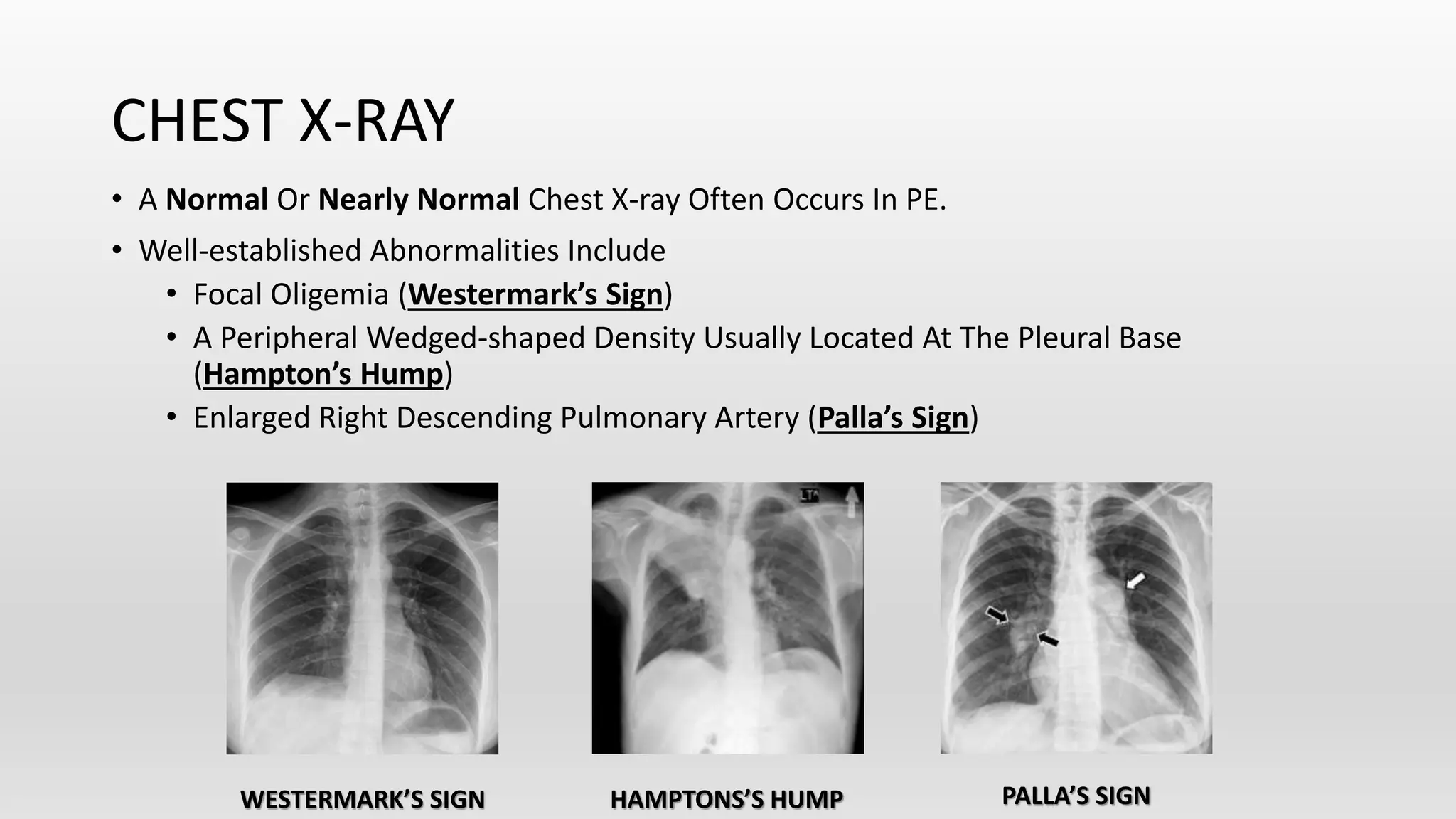
This document discusses venous thromboembolism (VTE), which includes deep vein thrombosis (DVT) and pulmonary embolism (PE). It covers the risk factors, pathophysiology, classification, clinical presentation, diagnostic modalities including imaging and labs, and treatment including anticoagulation options for VTE. The standard treatment is anticoagulant therapy to prevent further clot formation and extension. Parenteral anticoagulants such as heparin are initially used and then transitioned to oral anticoagulants such as warfarin or newer oral agents.