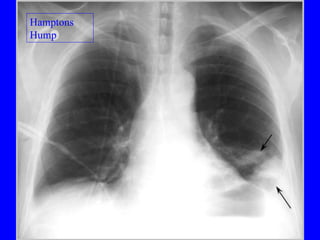
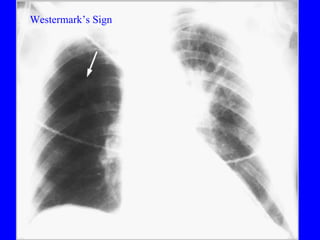
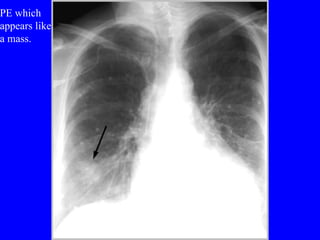
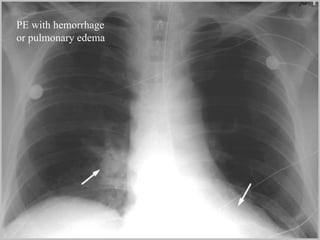
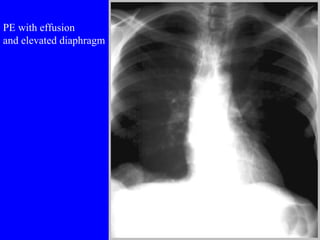
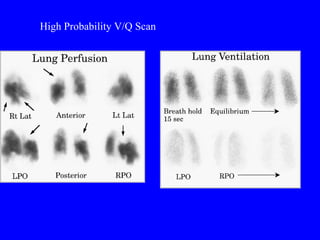
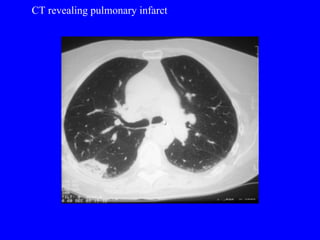
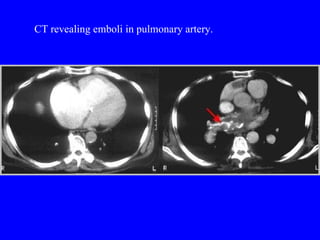
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a common and potentially fatal condition where blood clots block arteries in the lungs. An estimated 5 million venous thromboses occur annually worldwide, with 10-30% of PE cases correctly diagnosed. Risk factors include cancer, obesity, pregnancy, prolonged immobility, and genetic hypercoagulable states. Diagnosis involves assessing clinical probability, d-dimer testing, imaging like CT scans or V/Q scans, and echocardiography. Treatment consists of anticoagulants like heparin or warfarin to prevent further clotting while the body breaks down existing clots.