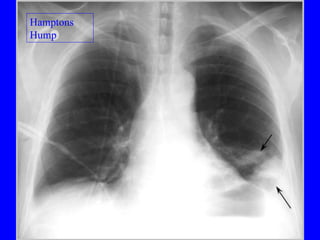
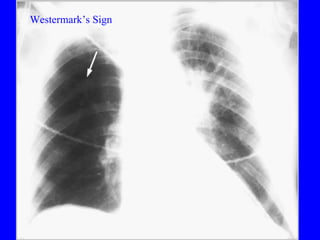
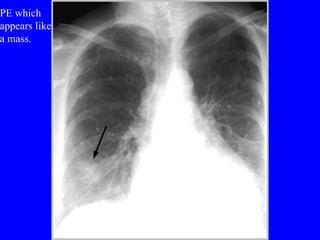
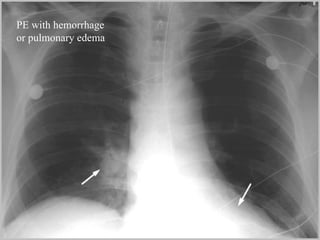
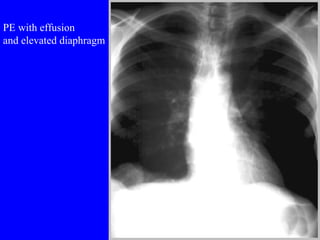
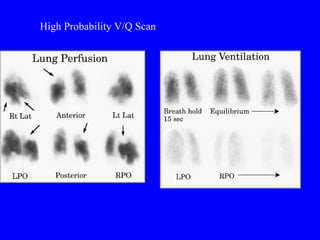
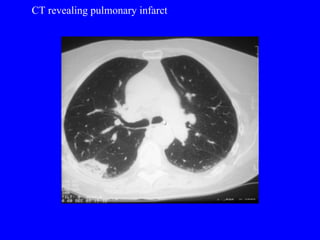
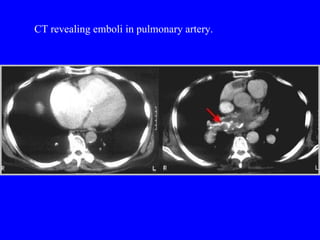
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is a common and potentially fatal condition where blood clots block arteries in the lungs. An estimated 5 million venous thromboses occur annually worldwide, with 10-30% of cases resulting in PE. Risk factors include immobilization, surgery, cancer, and estrogen use. Diagnosis involves assessing clinical probability based on symptoms and risk factors, followed by tests like D-dimer, chest imaging, ultrasound, V/Q scan, CT, or angiogram. Treatment aims to prevent further clotting with anticoagulants like heparin and warfarin, provide supportive care, and in some severe cases utilize thrombolysis or embolectomy.