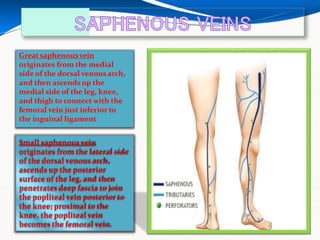
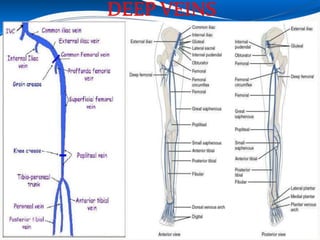
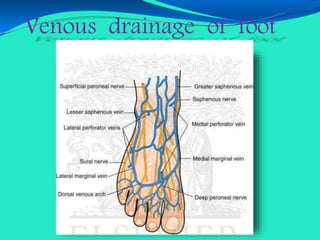
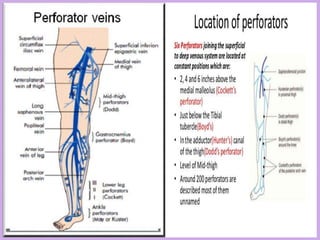
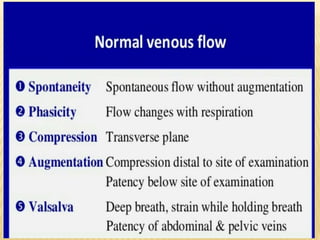
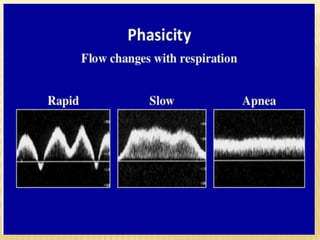
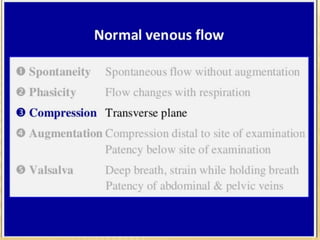
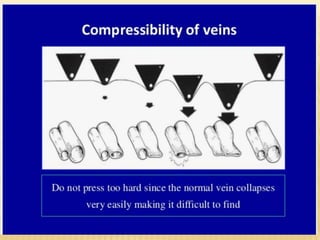
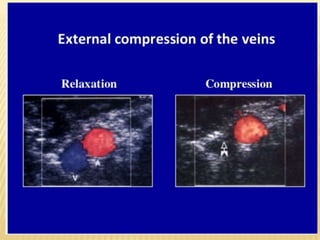
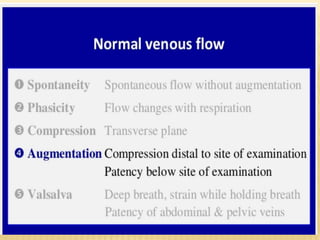
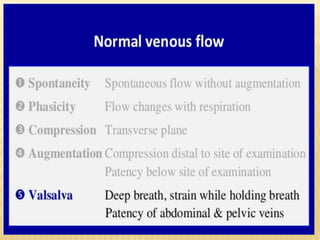
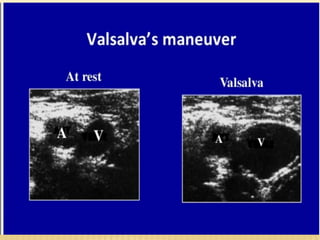
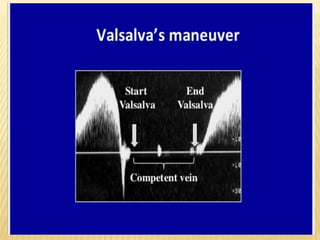
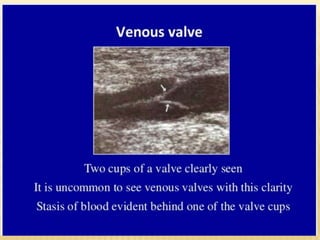
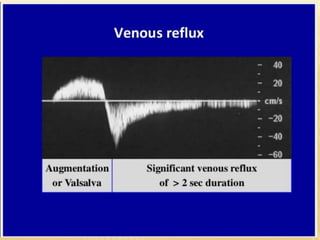
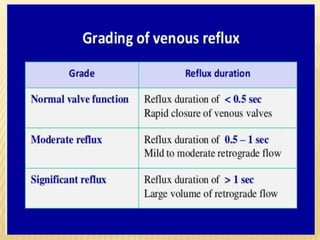
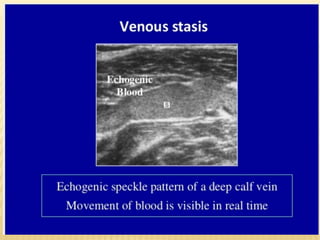
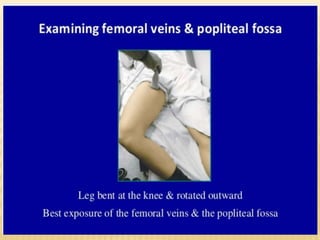
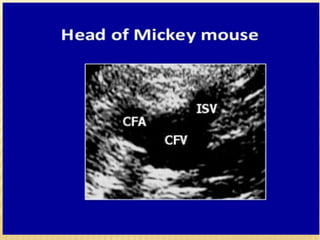
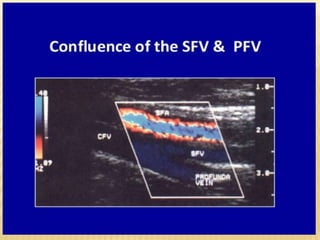
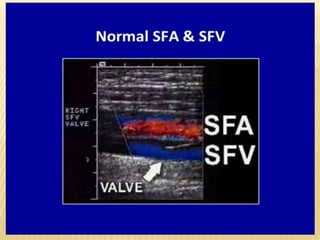
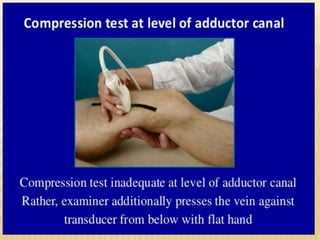
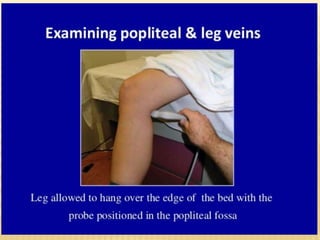
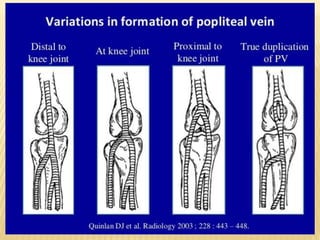
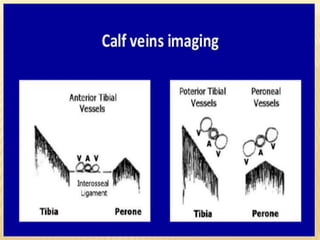
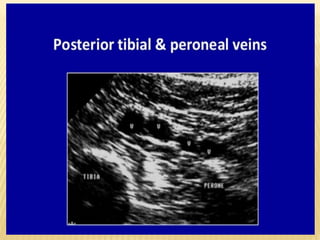
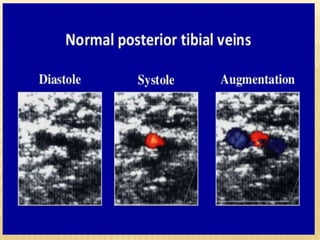
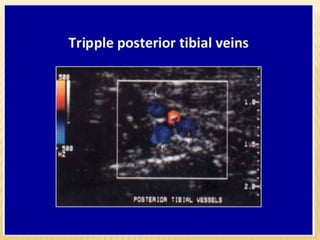
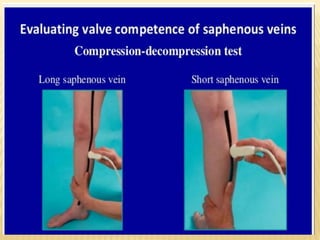
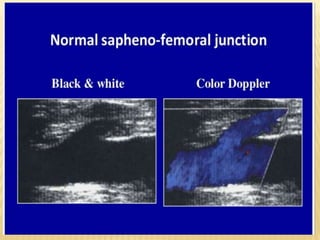
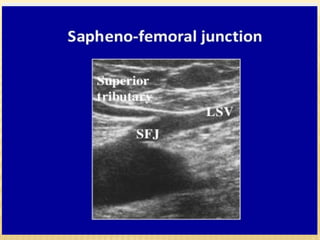
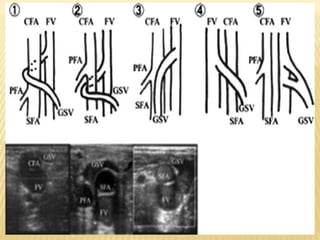
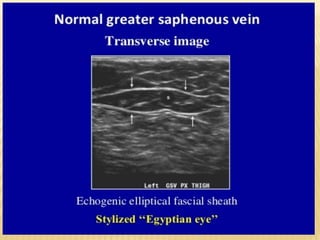
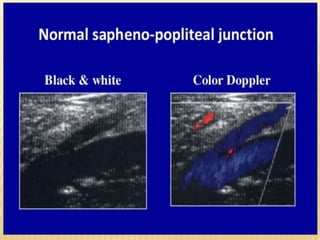
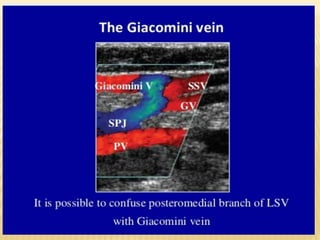
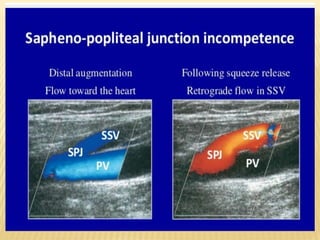
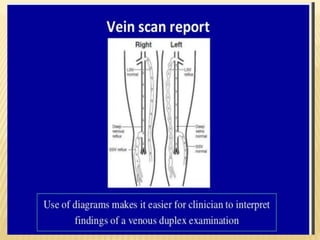
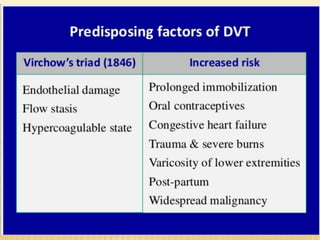
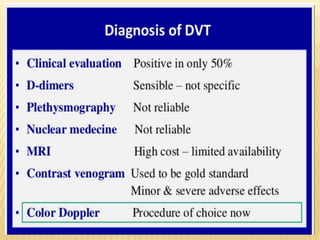
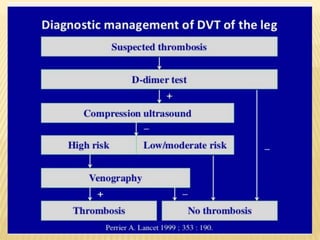
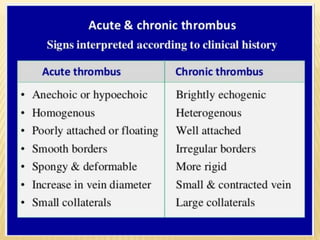
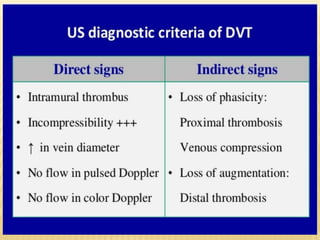
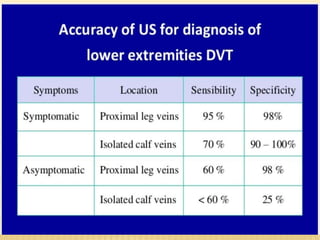
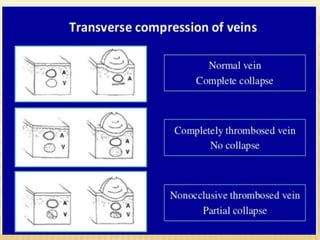
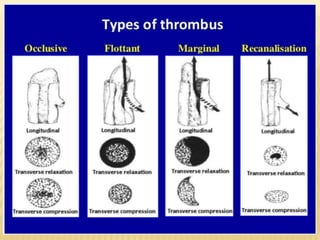
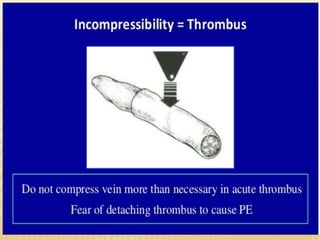
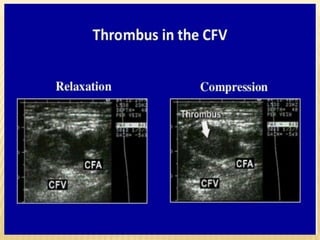
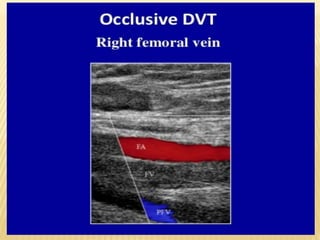
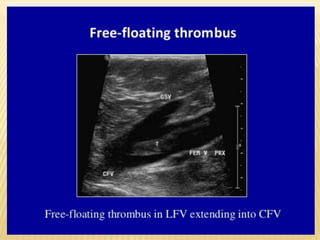
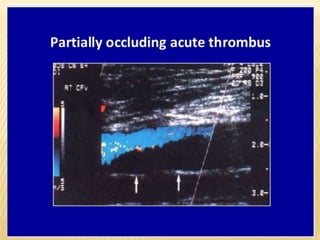
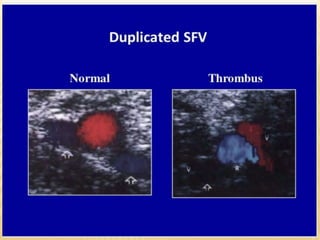
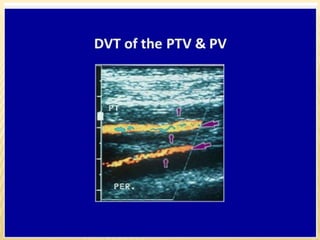
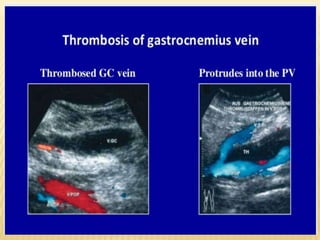
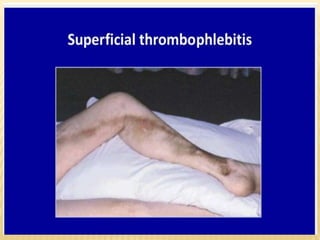
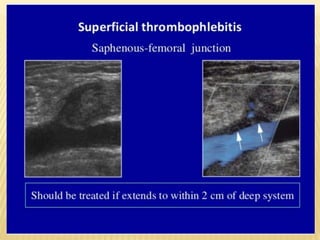
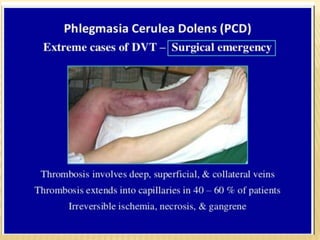
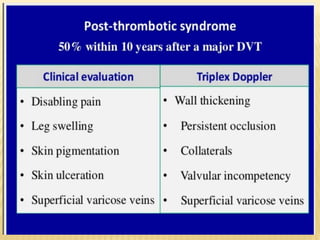
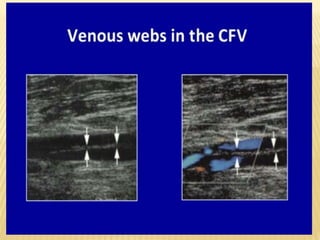
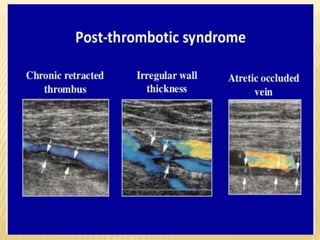
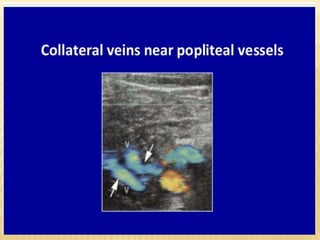
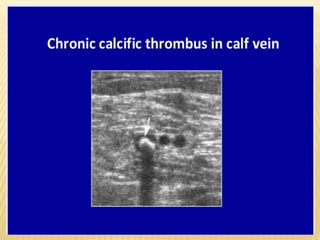
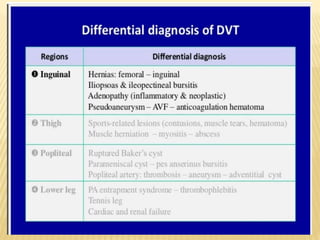
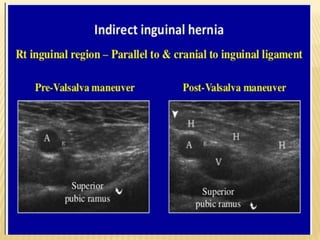
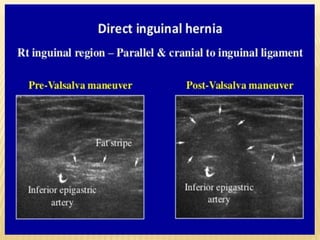
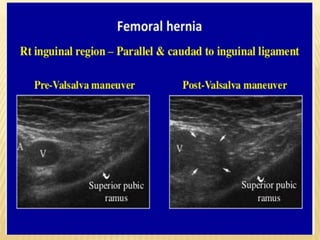
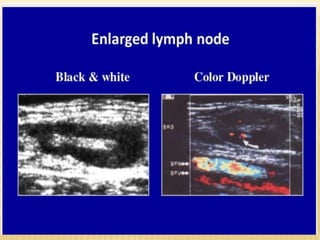
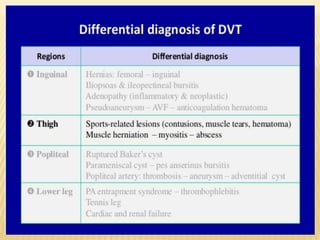
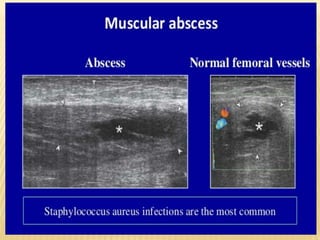
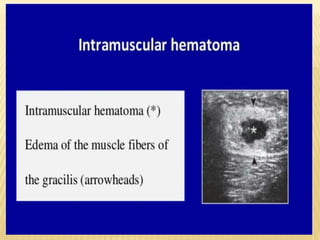
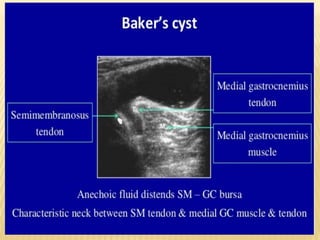
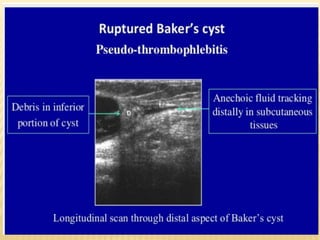
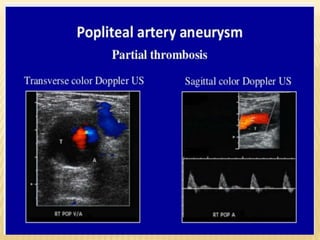
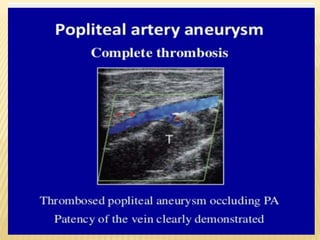
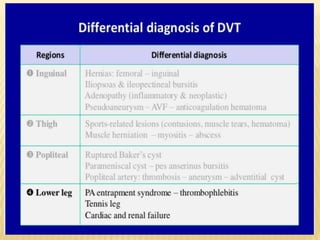
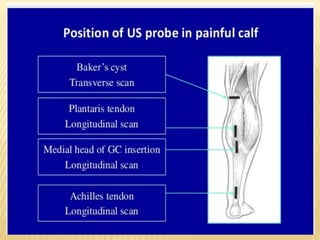
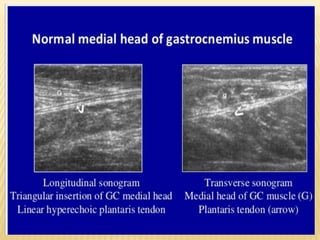
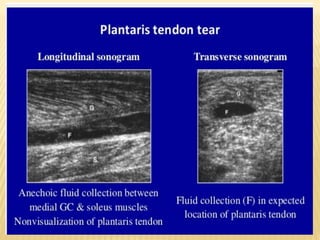
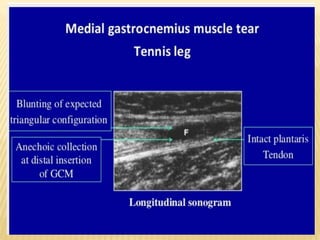
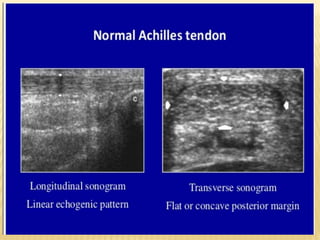
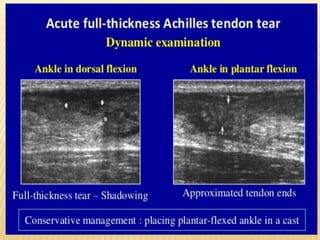
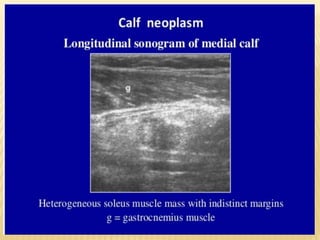
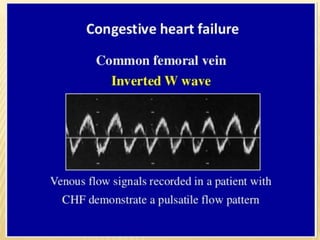
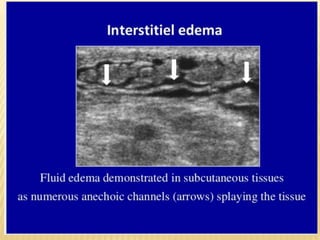
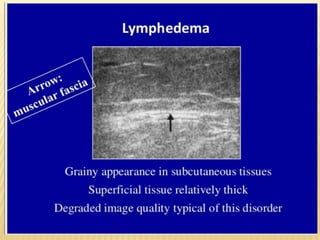
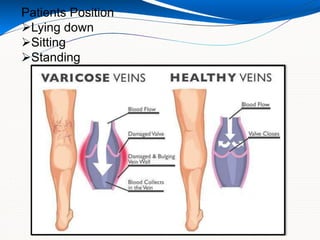
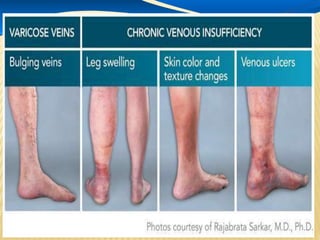
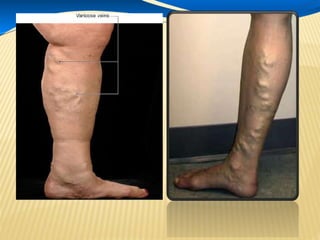
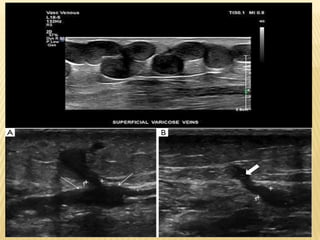
This document provides information about lower limb venous Doppler ultrasound techniques and findings. It begins with an overview of venous anatomy of the lower limbs. Key points about performing a lower limb venous Doppler exam are provided, including the importance of understanding anatomy, obtaining a thorough patient history, and focusing on Doppler waveforms and symmetry between limbs. Common venous conditions like deep vein thrombosis and varicose veins are also summarized. The document concludes with techniques for performing lower limb venous Doppler ultrasound exams.