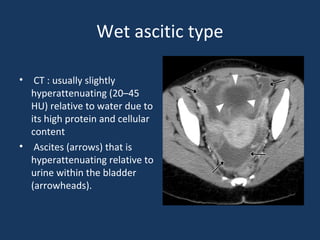
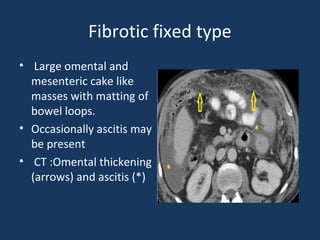
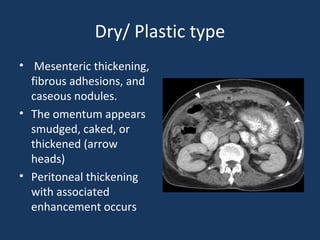
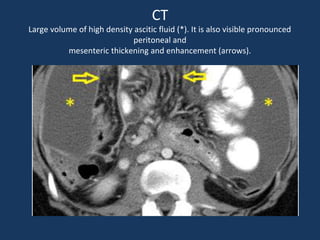
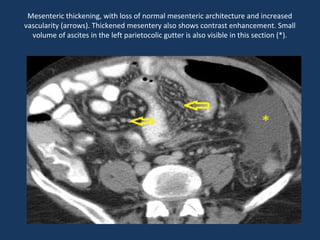
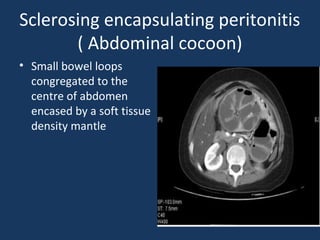
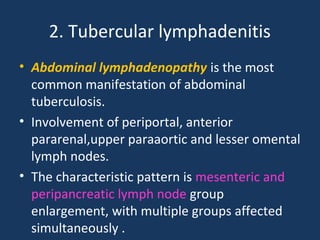
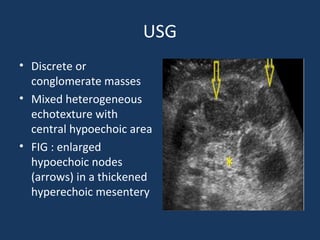
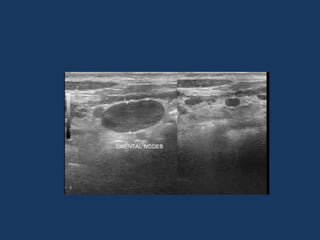
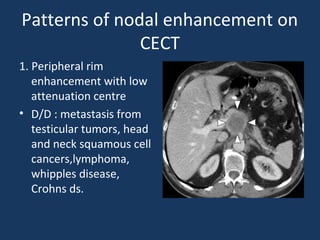
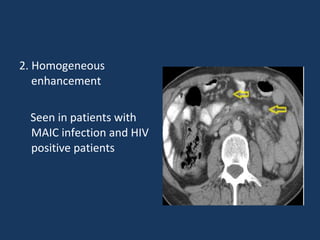
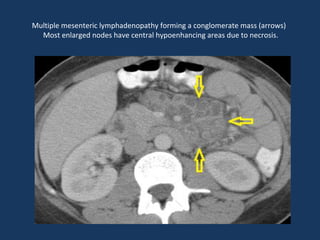
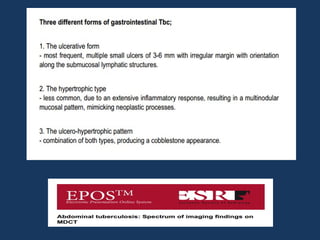
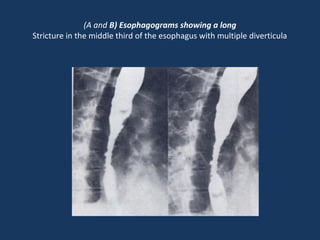
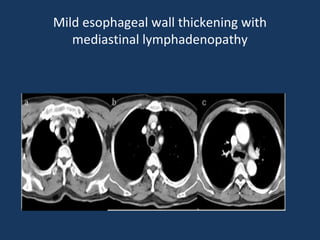
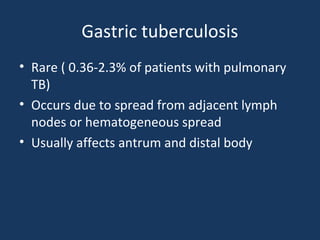
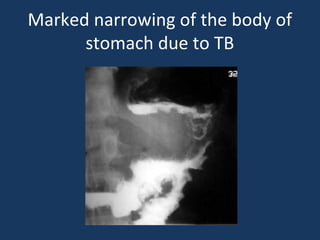
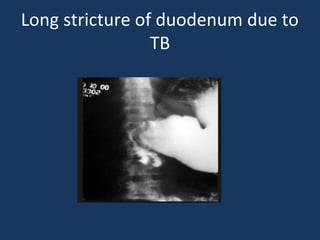
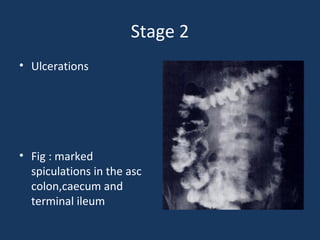
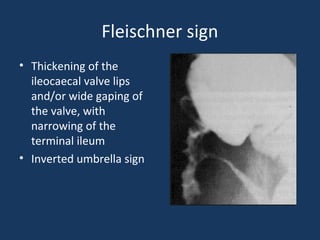
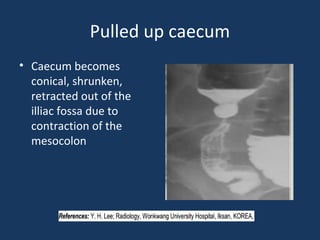
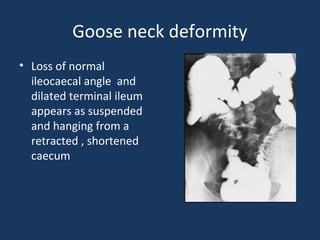
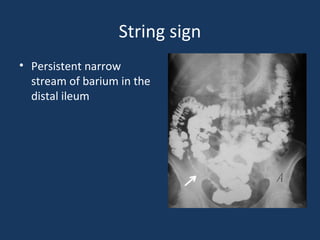
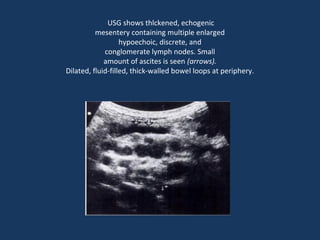
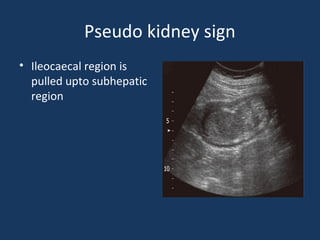
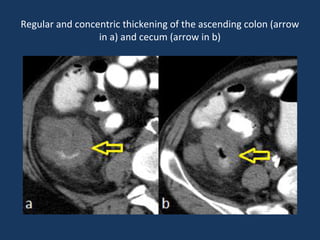
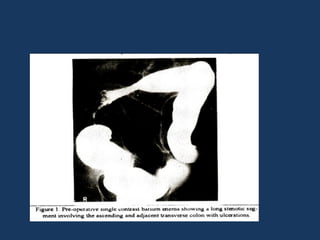
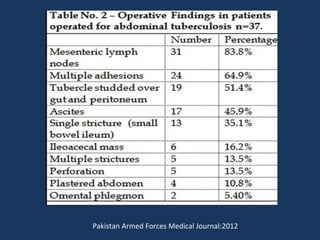
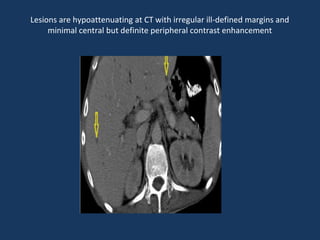
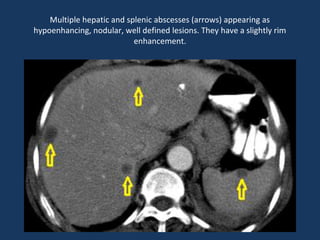
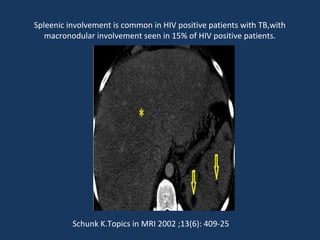
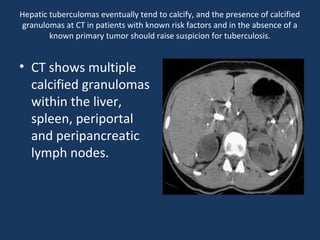
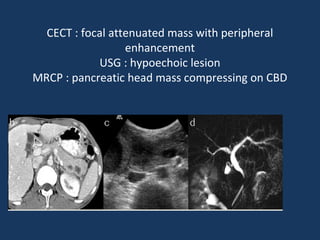
The document discusses abdominal tuberculosis, a condition where tuberculosis infects the abdomen, affecting the peritoneum, gastrointestinal tract, lymphatics, and solid organs. It details various forms of the disease, clinical presentations, diagnostic imaging techniques, and classifications, including peritoneal tuberculosis, gastrointestinal tuberculosis, and lymphadenitis. Additionally, it highlights the imaging characteristics on ultrasound, CT, and MRI to differentiate abdominal tuberculosis from other conditions.