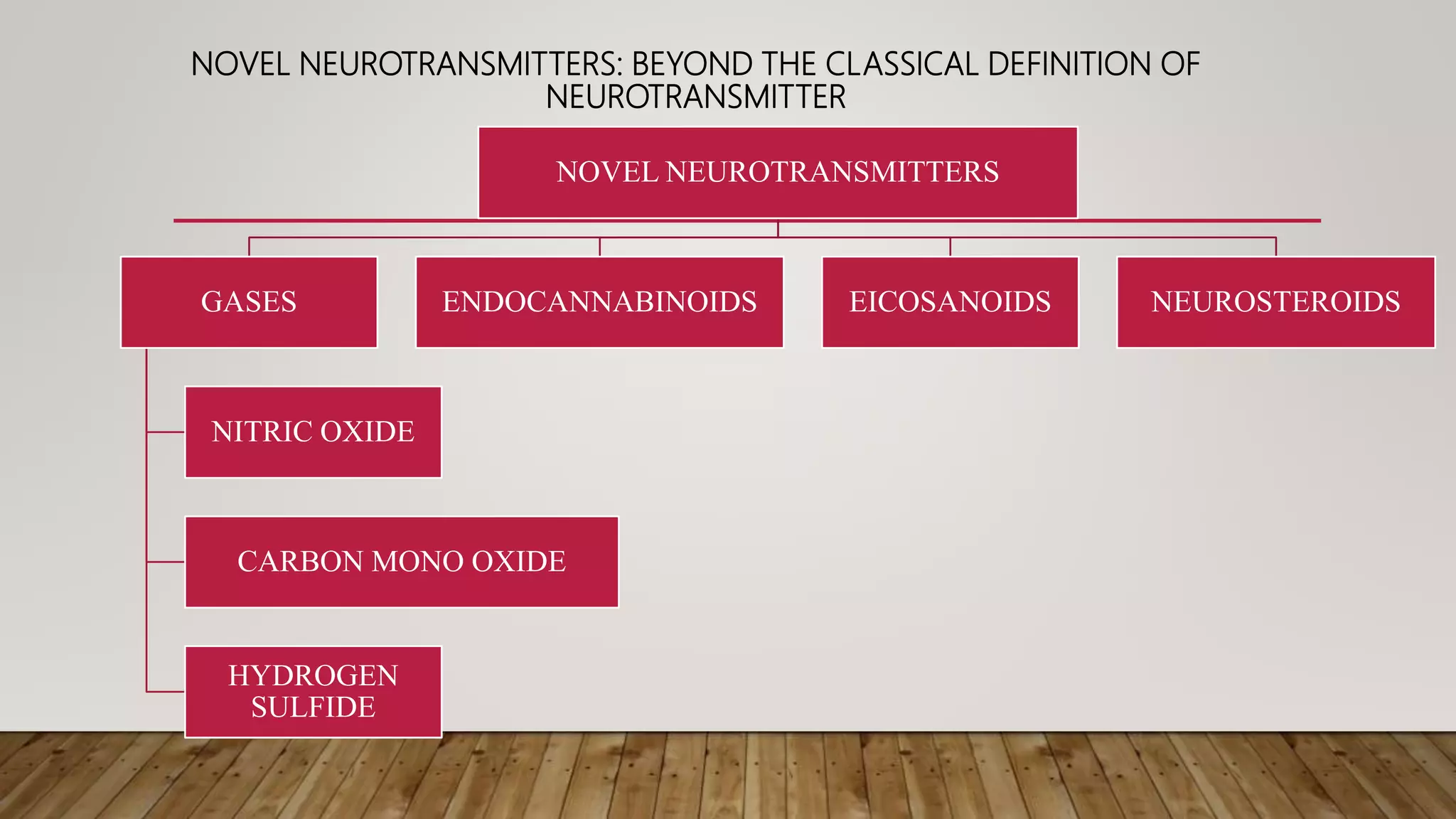
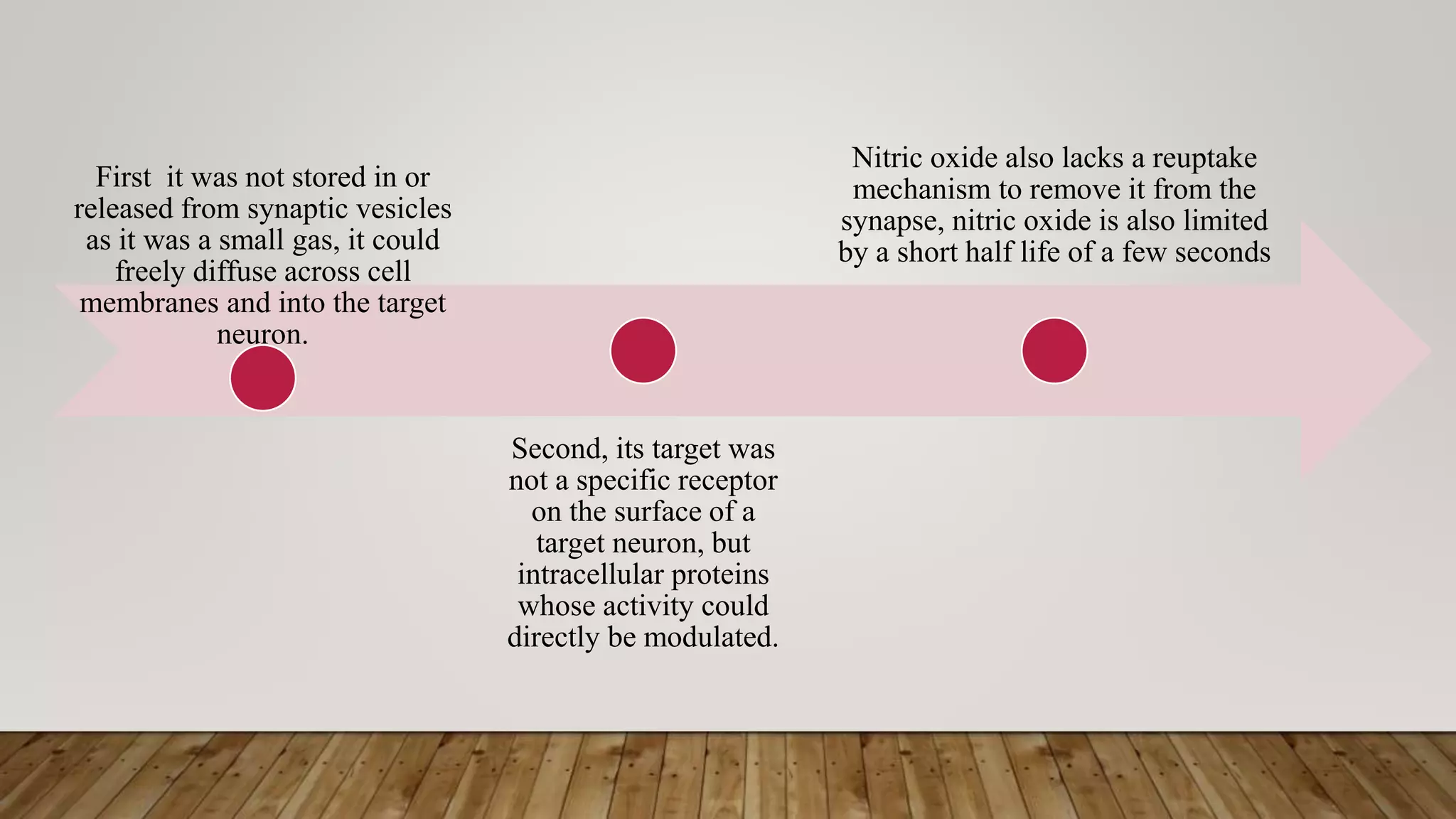
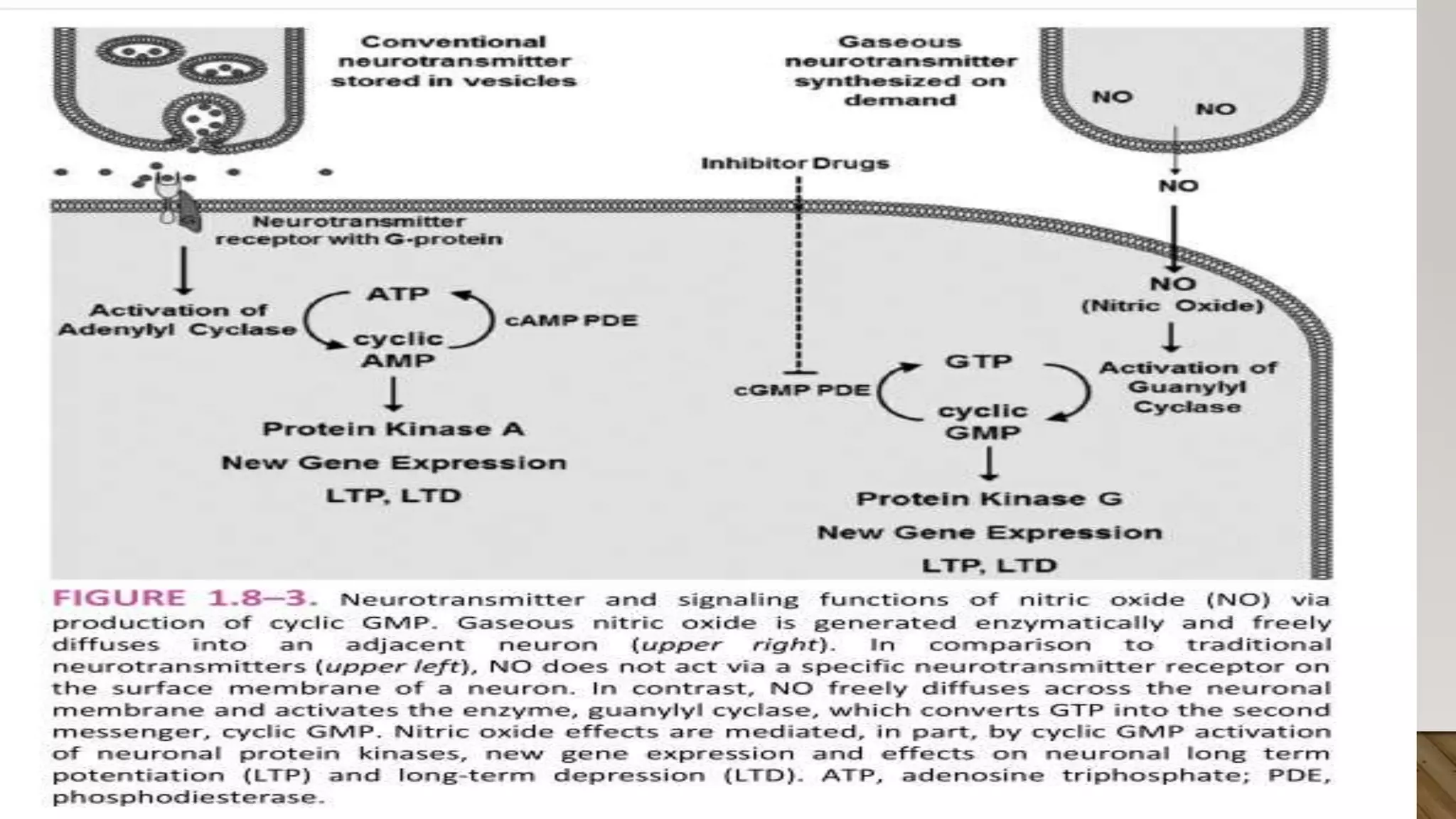
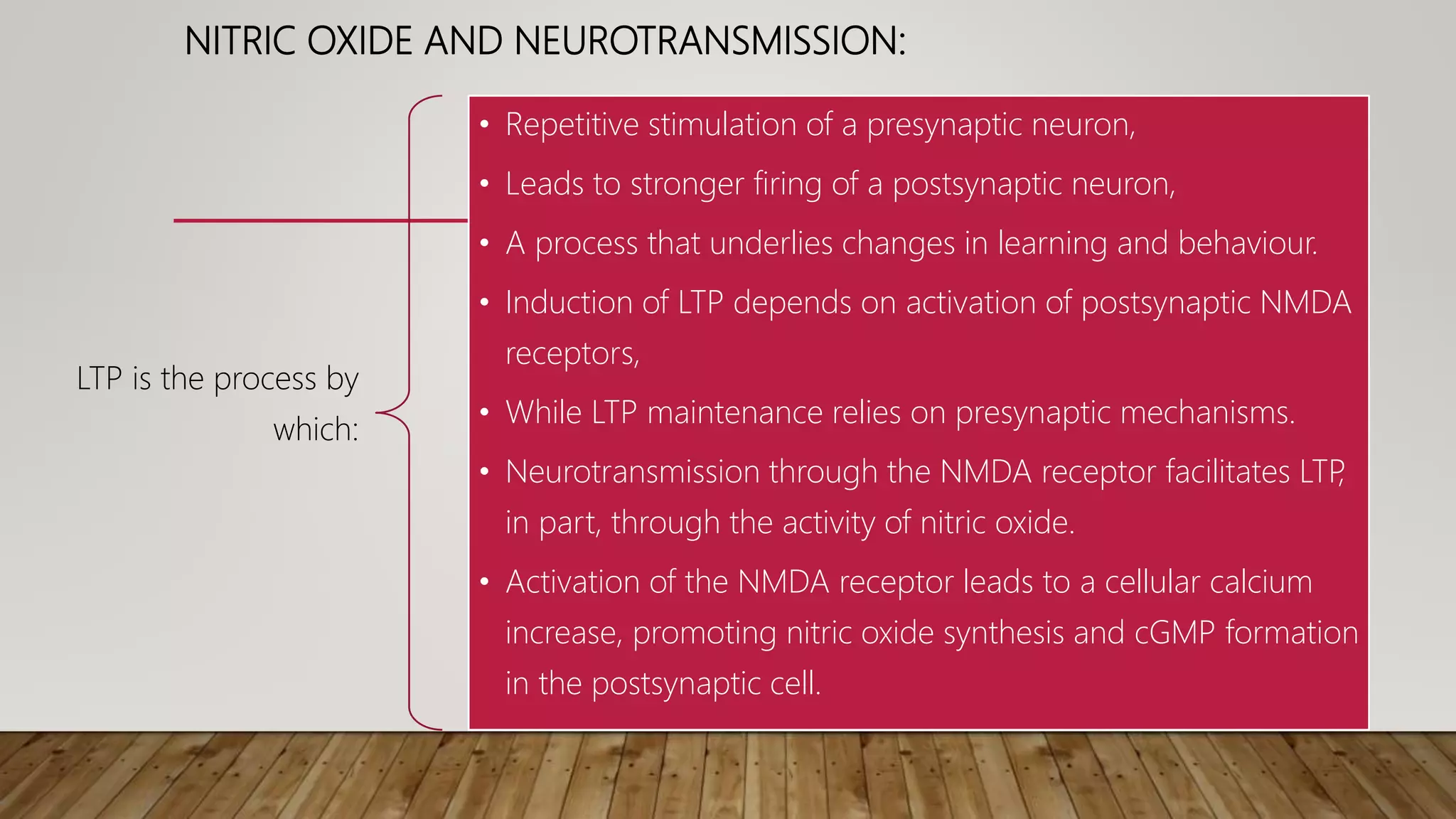
This document discusses novel neurotransmitters beyond the classical ones. It describes nitric oxide, carbon monoxide, hydrogen sulfide, endocannabinoids, eicosanoids, and neurosteroids. Nitric oxide is produced in neurons from arginine and acts through cGMP. It is involved in long term potentiation and erectile function. Carbon monoxide regulates olfaction and vasodilation. Hydrogen sulfide is produced from cysteine and acts as a gaseous messenger. Endocannabinoids like anandamide signal retrogradely through CB1 receptors. Eicosanoids are derived from arachidonic acid. Neurosteroids are synthesized in the brain from cholesterol and include allopregn