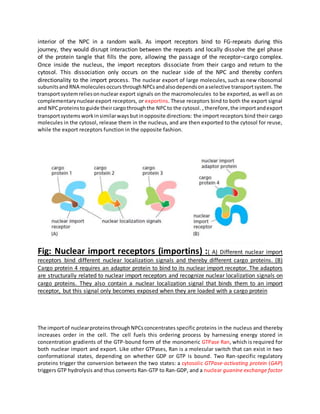
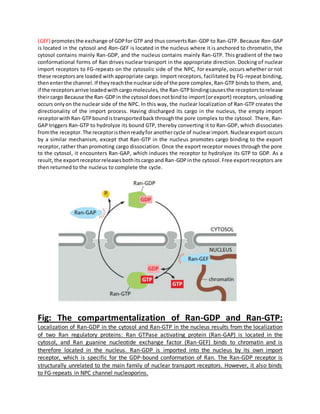
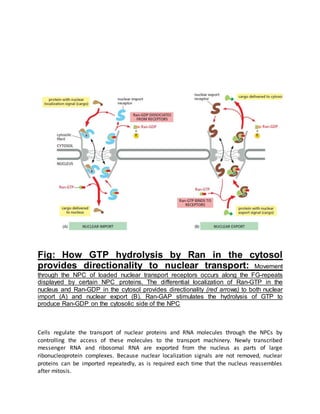
Proteins must be properly located within cells to carry out their functions. Protein targeting refers to how cells transport proteins to the correct locations after synthesis. There are several mechanisms for protein targeting. Some proteins diffuse through the cytosol and bind to receptors at their destination site, while others contain targeting sequences like nuclear localization signals that bind nuclear transport receptors to be actively transported into the nucleus. The import and export of proteins between the cytosol and nucleus is directed by gradients of Ran-GTP and Ran-GDP concentrations established by regulatory proteins localized to different cellular compartments. This compartmentalization of Ran states provides directionality to nuclear transport.