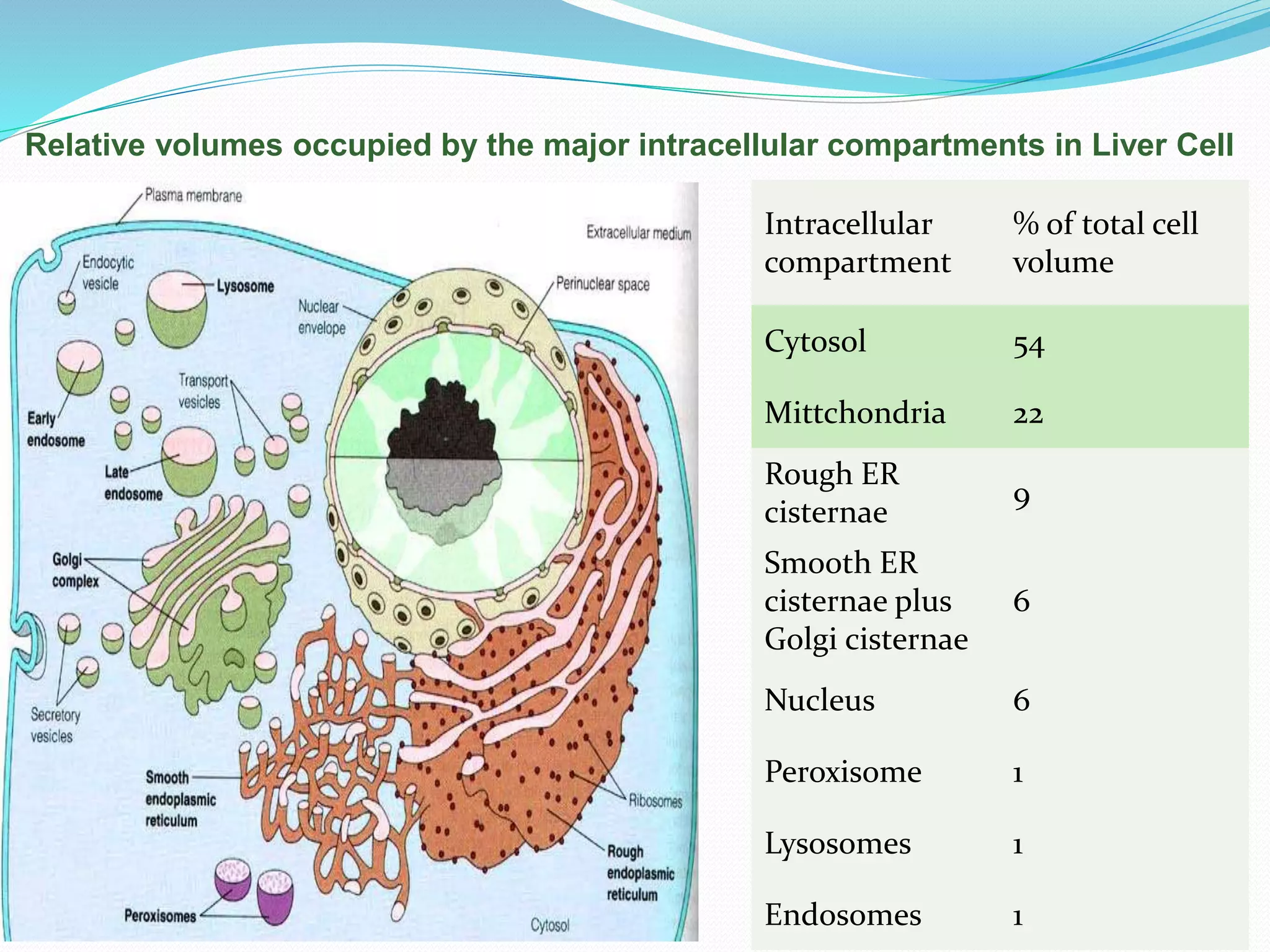
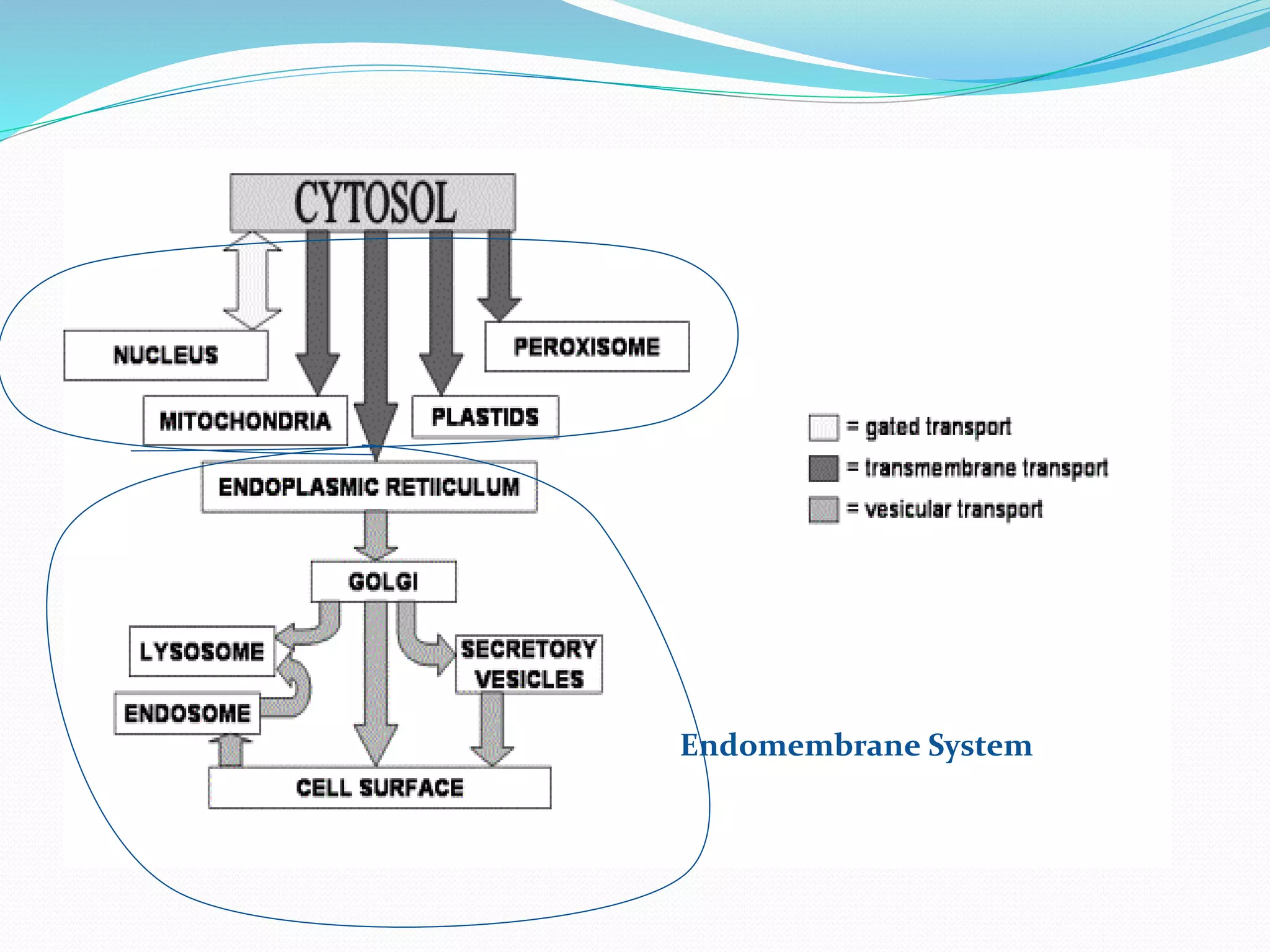
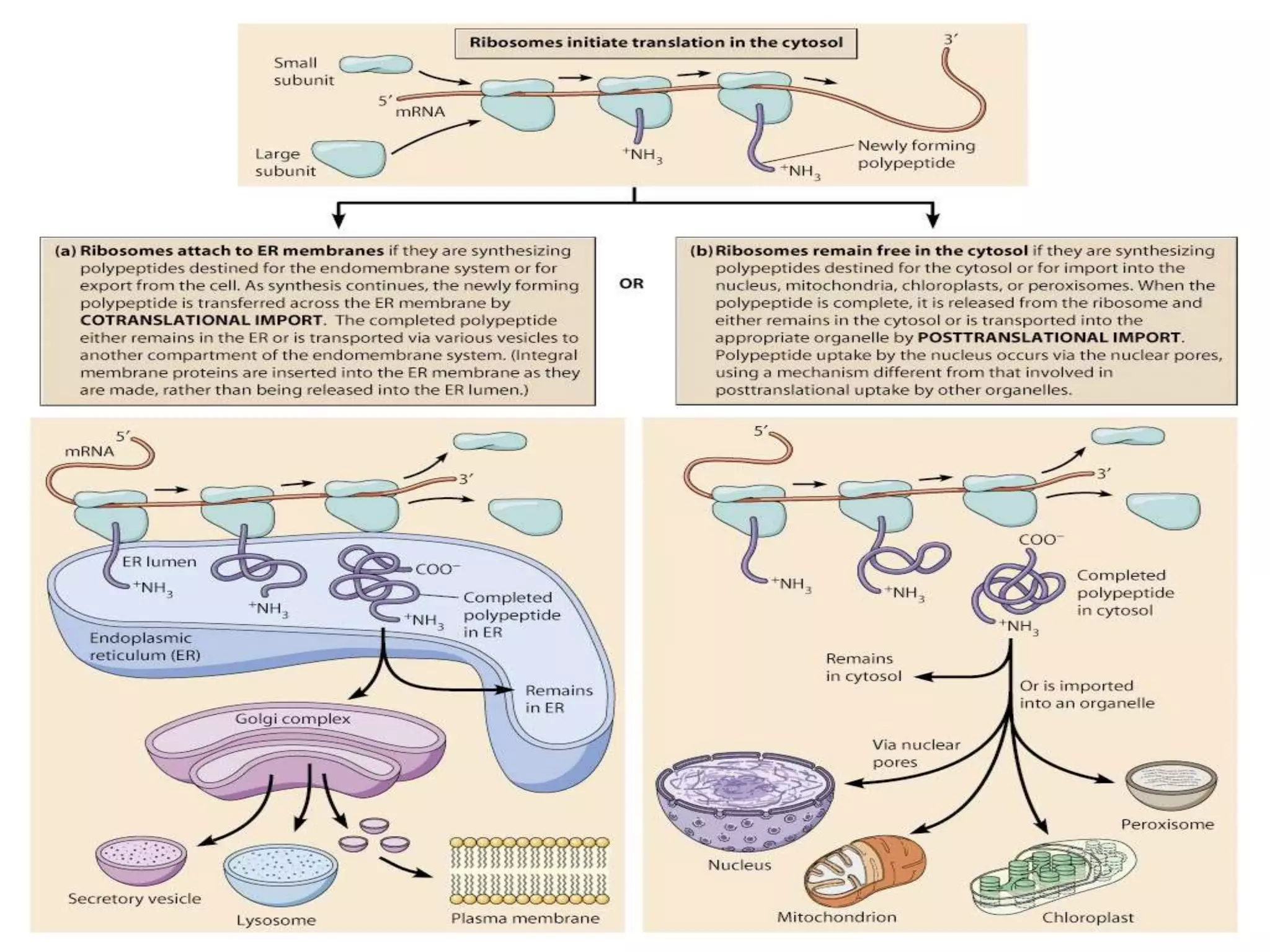
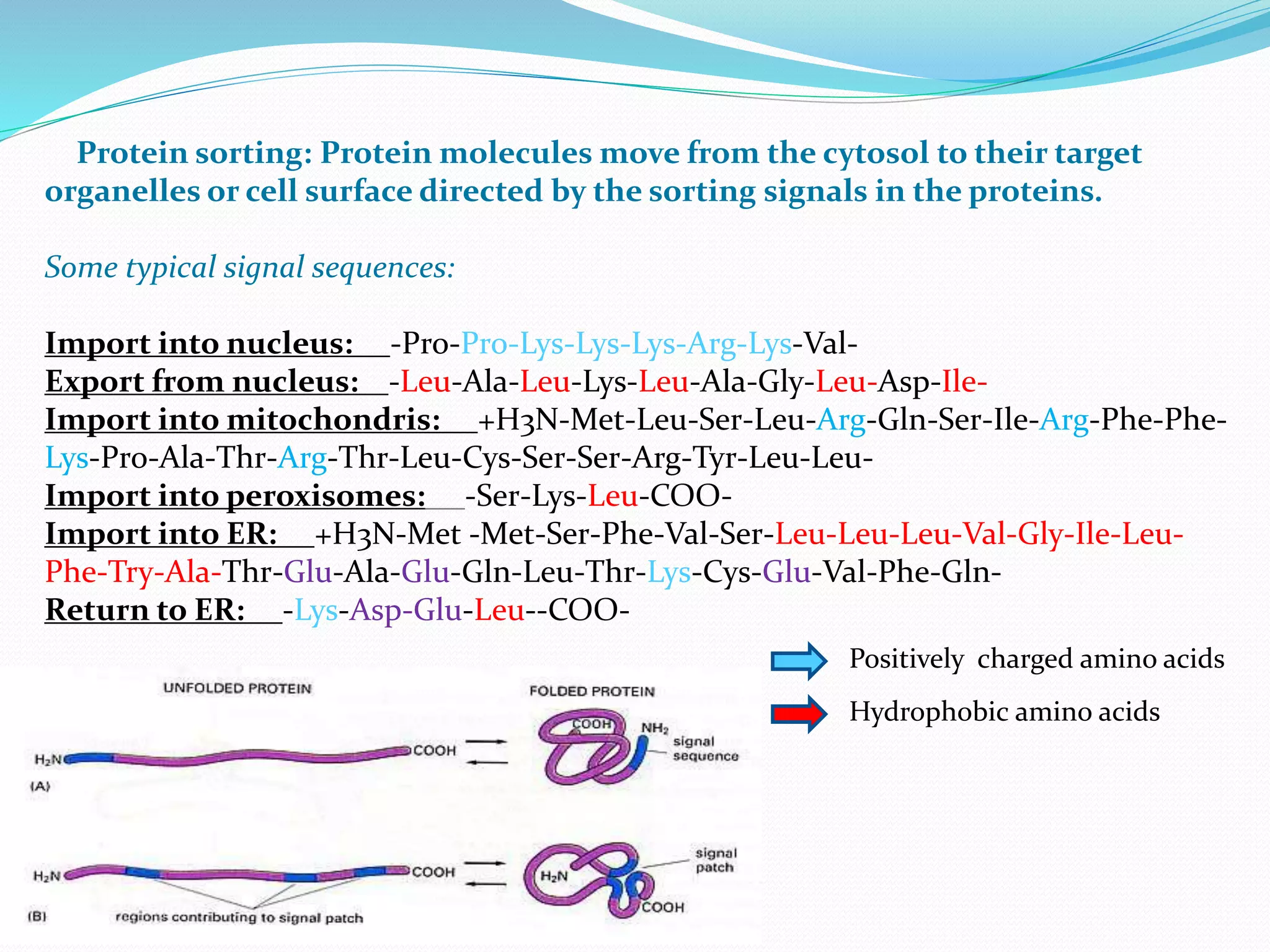
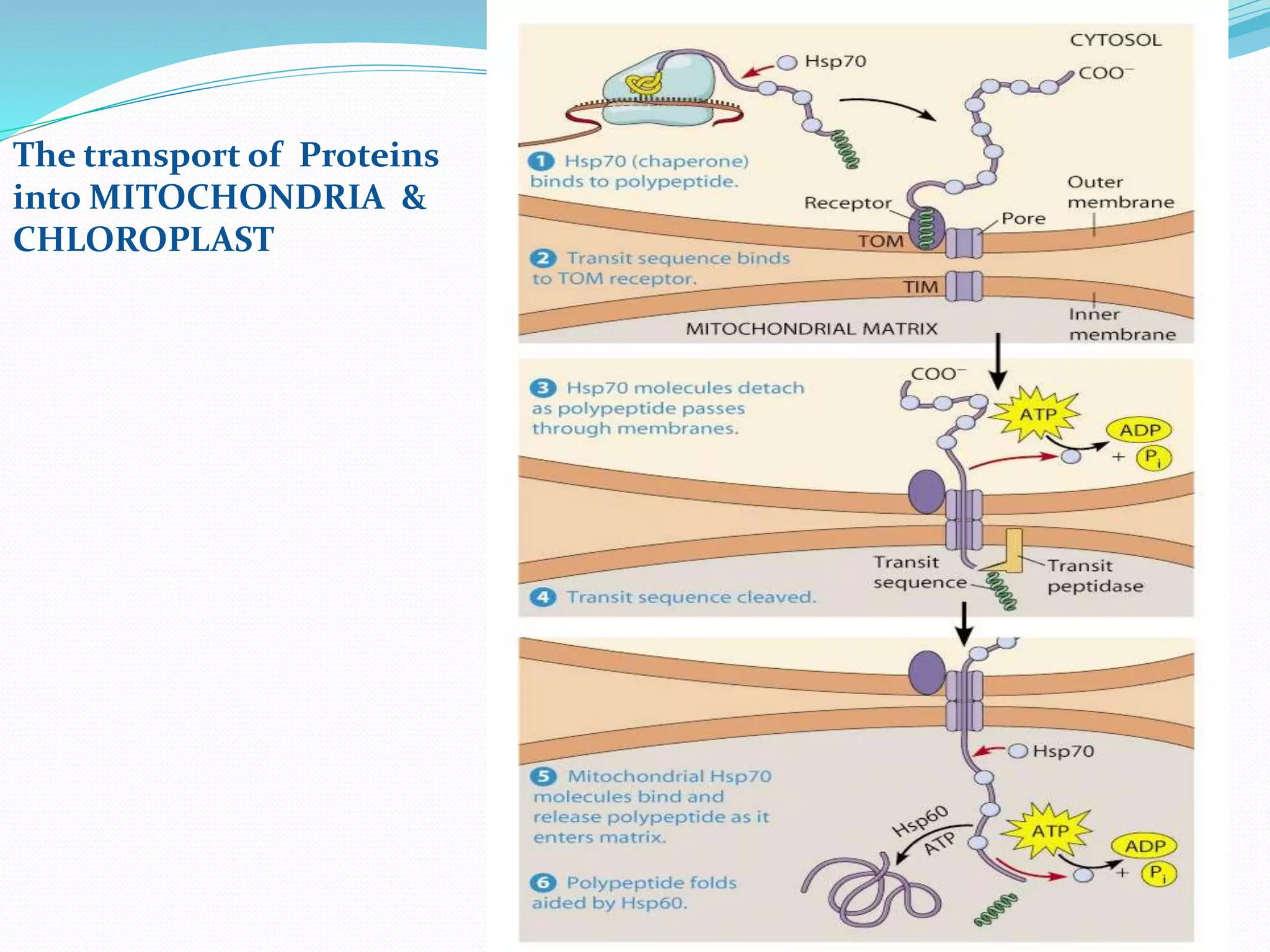
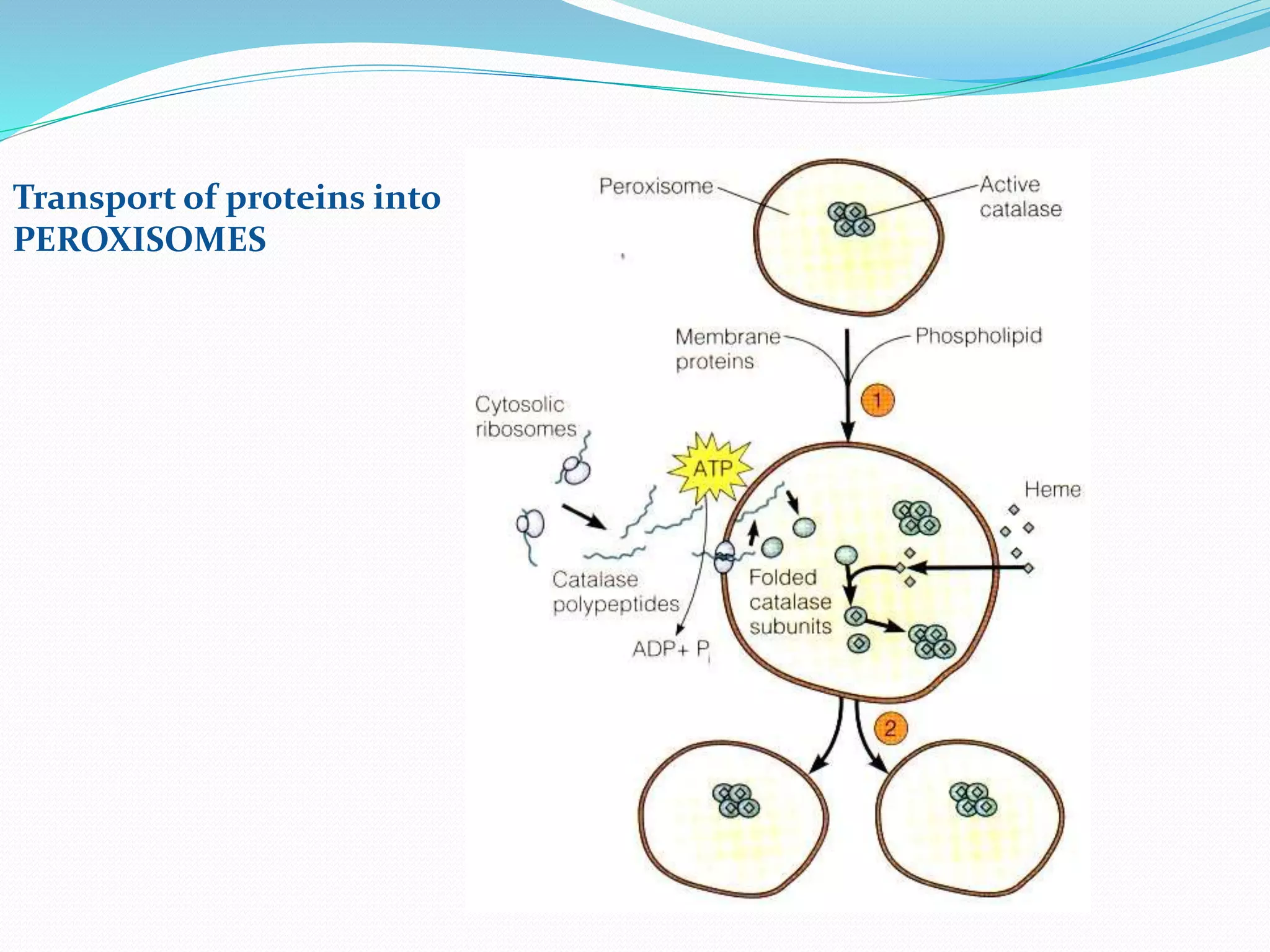
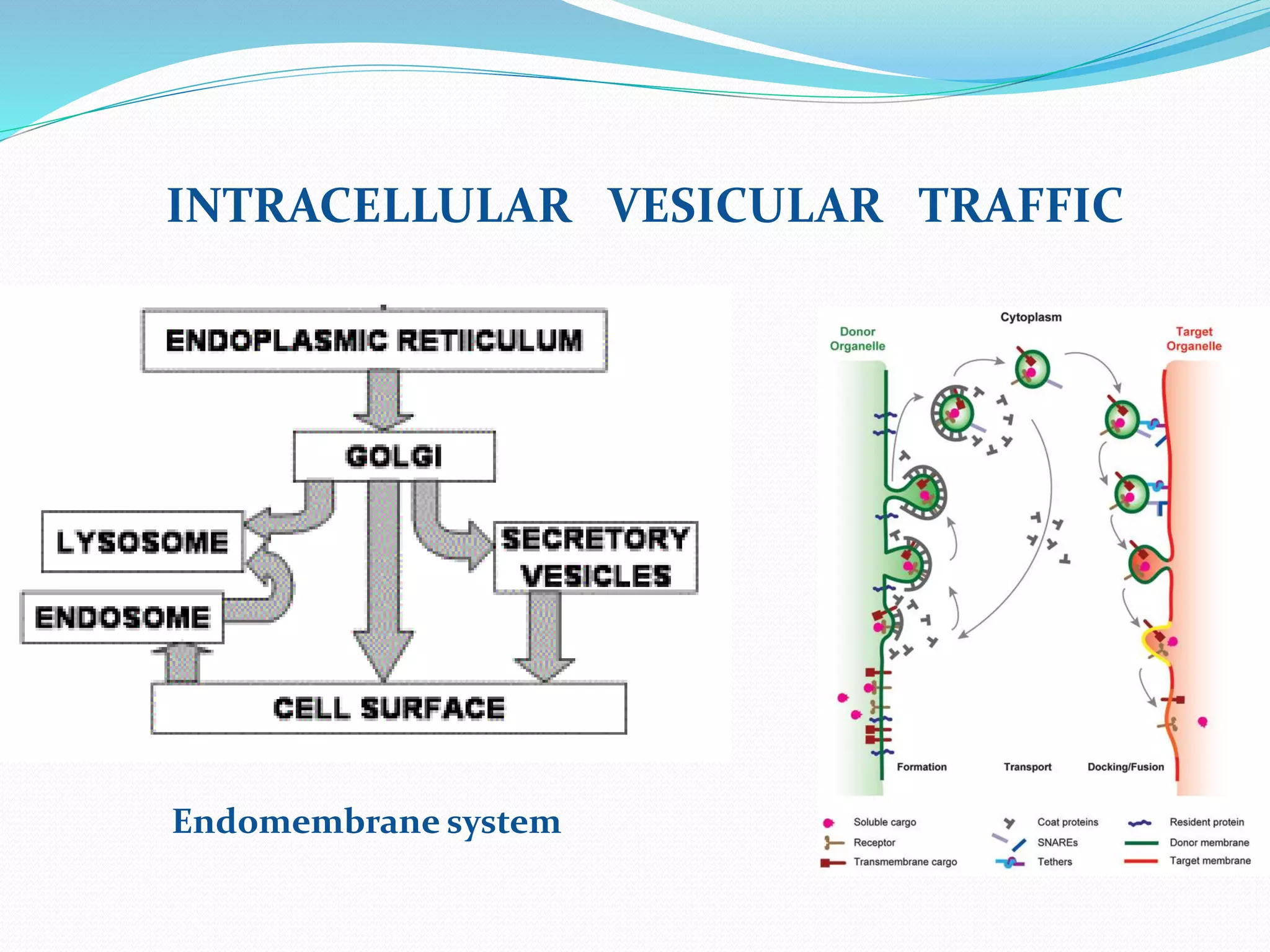
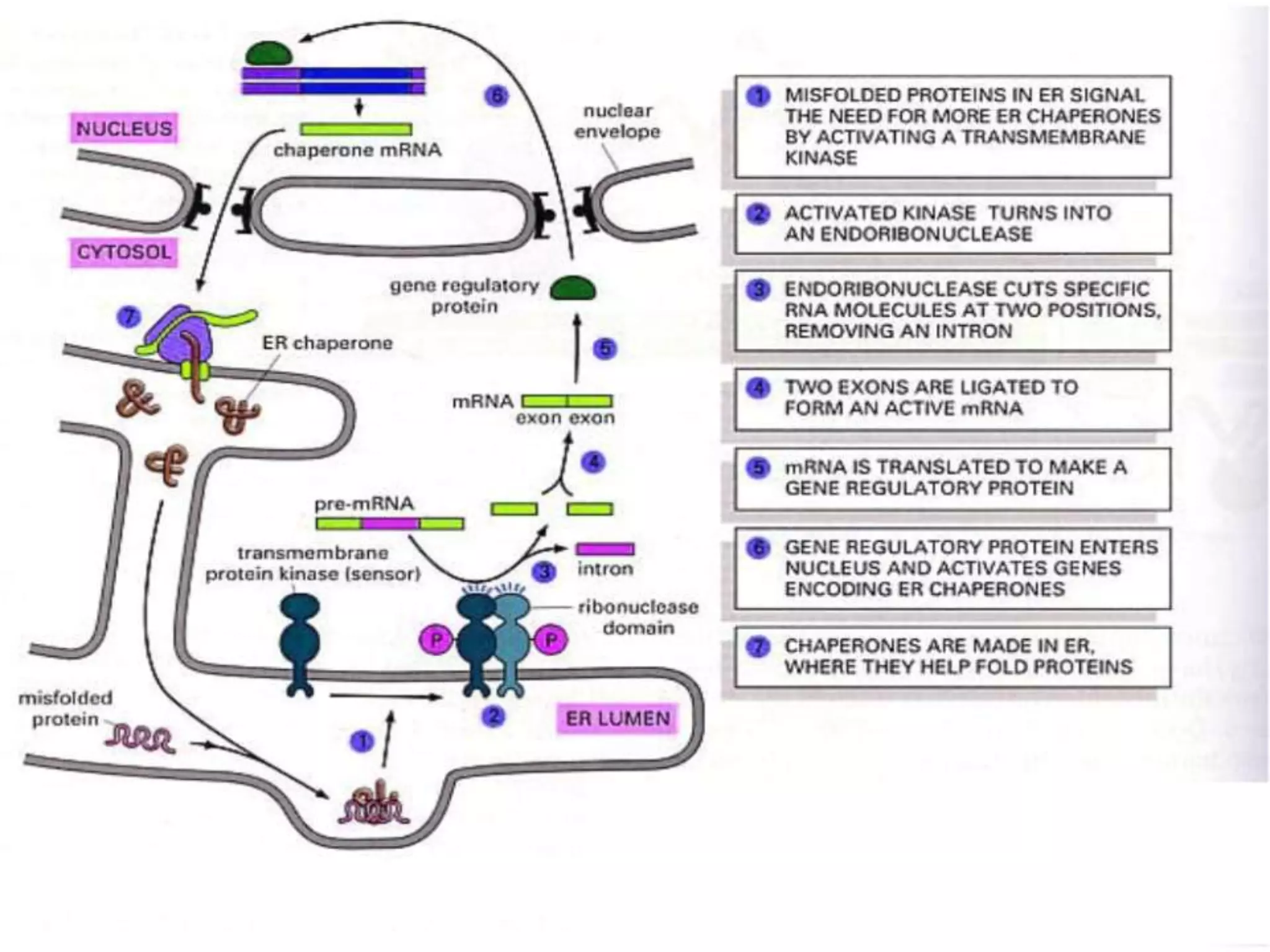
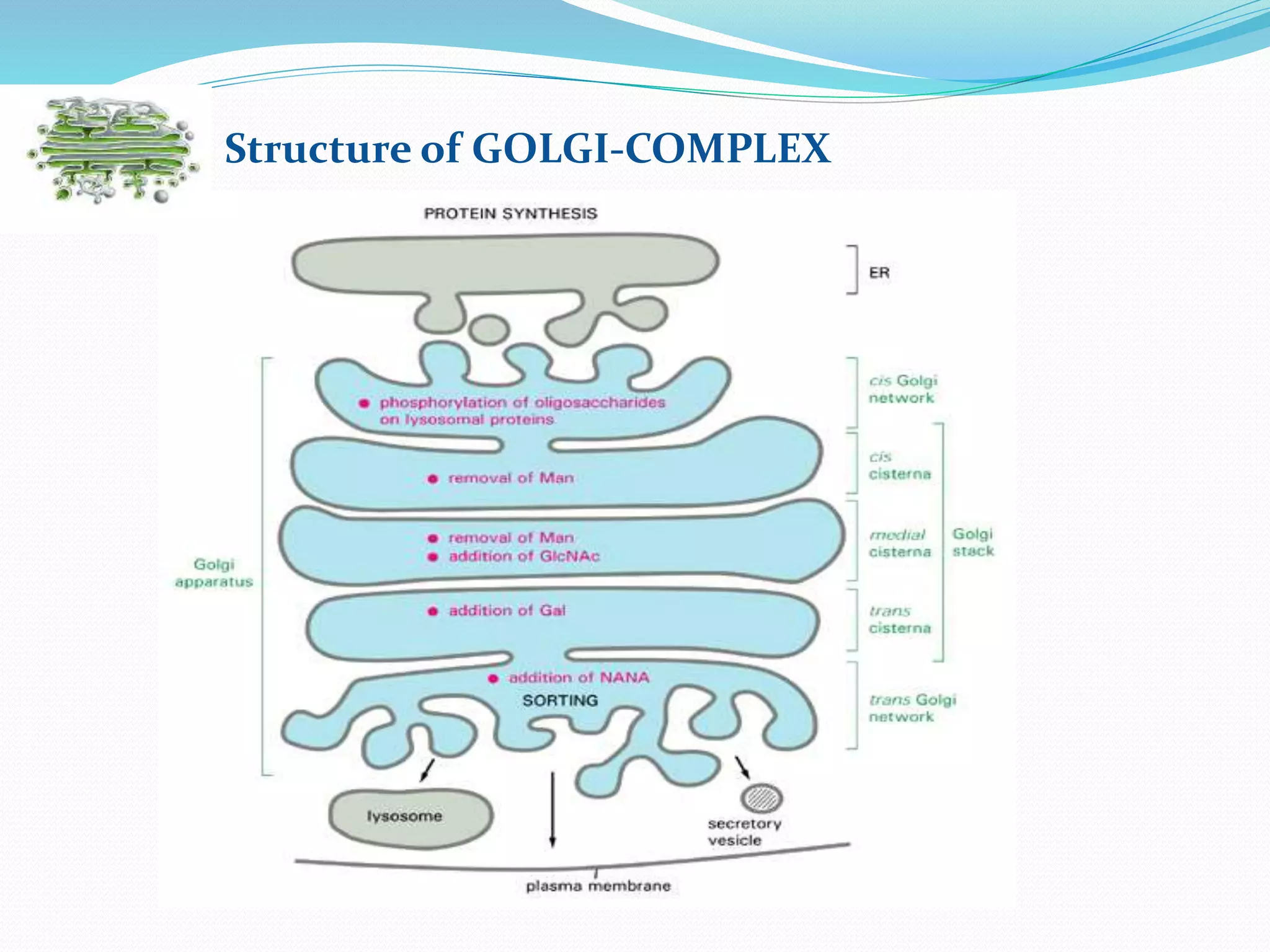
Protein sorting is the mechanism by which cells transport proteins to the appropriate locations inside or outside the cell. Sorting signals contained within the protein direct it to targets like organelles, membranes, or out of the cell. Correct sorting is important for cell function, as errors can lead to disease. The major intracellular compartments and their relative volumes are the cytosol, mitochondria, ER, Golgi apparatus, nucleus, peroxisomes, lysosomes, and endosomes. Protein sorting involves transport of proteins from the cytosol to target locations directed by sorting signals like sequences for nuclear import, mitochondrial import, or ER import.