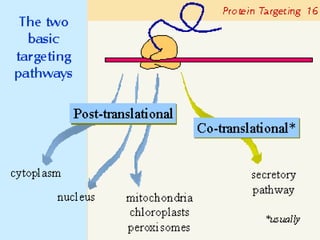
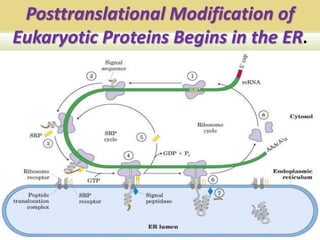
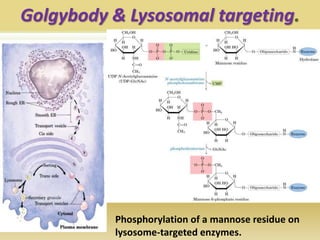
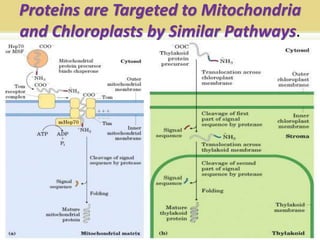
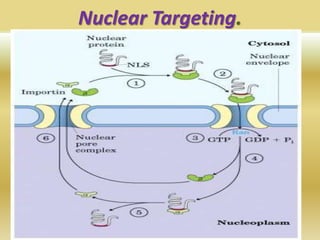
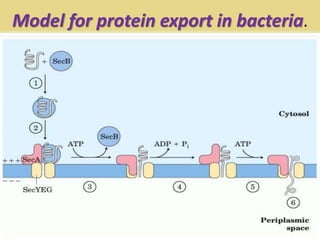
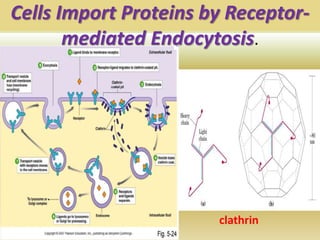
Protein targeting is the process by which proteins are directed to specific locations after synthesis. Signal sequences on proteins guide their transport, as discovered by Gunter Blobel who won the Nobel Prize for this work. Protein targeting is important because proteins must be sorted to the correct locations, like organelles, to properly function. Eukaryotic protein targeting is complex due to many intracellular compartments and can involve posttranslational modifications and receptor-mediated transport mechanisms. Correct protein sorting is vital for cell function and errors can cause disease.