Here are sample responses:
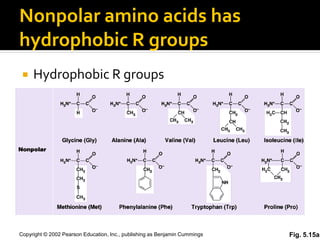
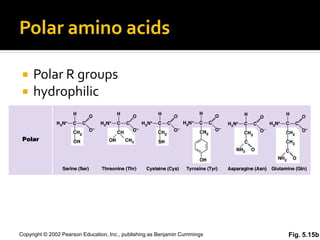
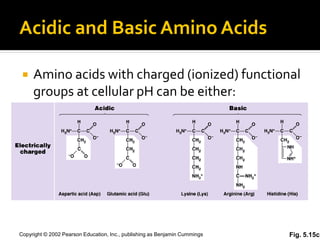
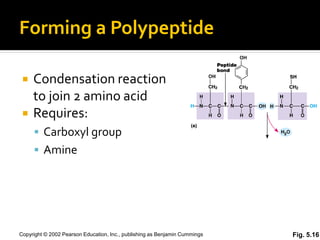
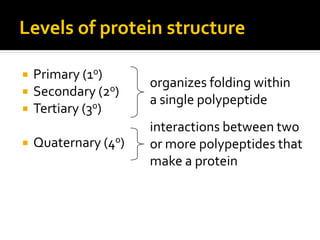
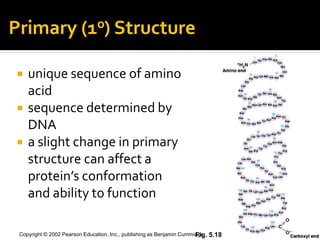
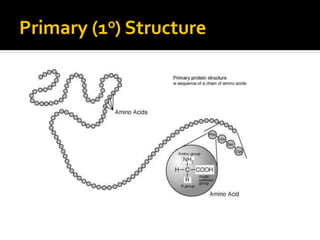
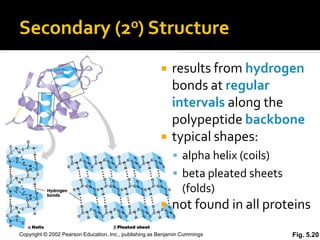
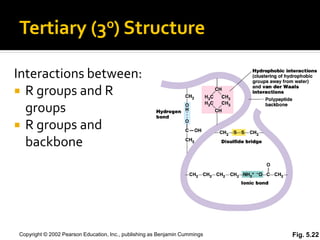
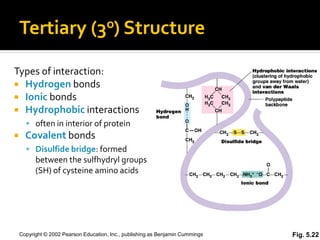
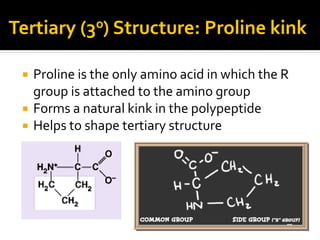
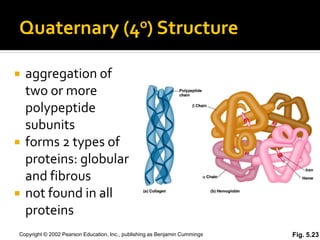
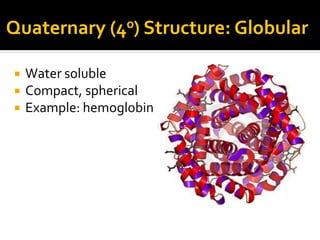
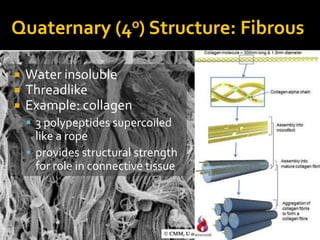
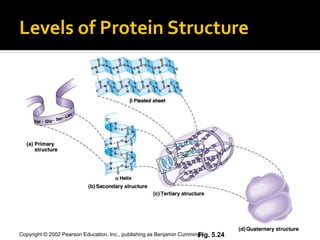
Secondary structure involves hydrogen bonding between amino acids along the polypeptide backbone, forming regular structures like alpha helices and beta sheets. Tertiary structure involves interactions between R groups of amino acids, forming the overall 3D shape of the protein.
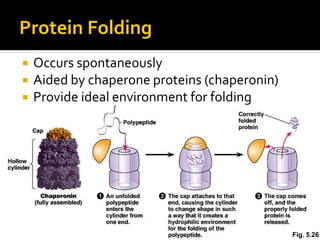
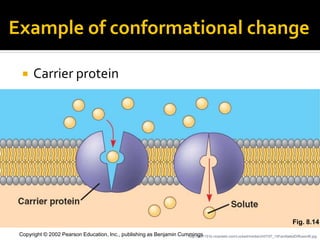
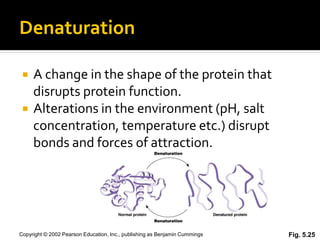
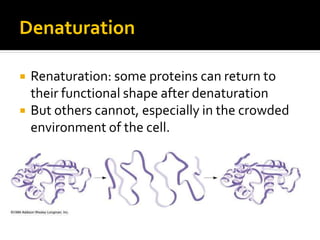
Conformational change alters a protein's shape but does not disrupt its function, allowing it to perform its role. For example, a carrier protein may change shape to bind a substrate. Denaturation permanently alters a protein's shape through environmental changes like heat, disrupting its function. Boiling an egg is an example - it denatures the proteins.


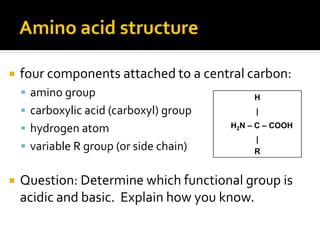
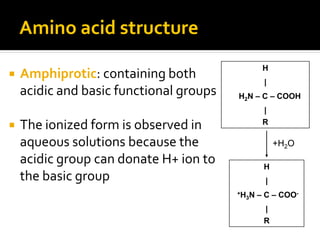
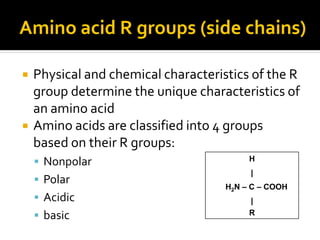




![HW Question
Contrast secondary and tertiary levels of
protein structure. [2 marks]
Compare conformational change and
denaturation. Use an example. [3 mark]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/proteinstructure-121003175932-phpapp01/85/Protein-structure-34-320.jpg)