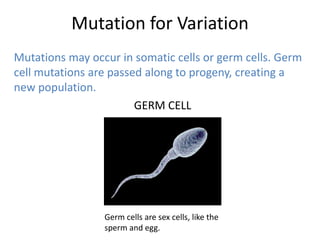
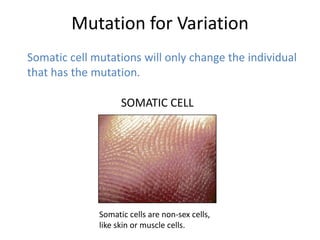
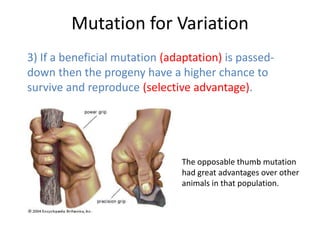
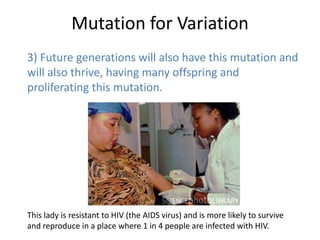
Genetic variation within species occurs due to mutations. Mutations can happen in somatic cells or germ cells. Germ cell mutations are passed to offspring and can create new variations within a population. Mutations may be harmful, neutral, or beneficial to an organism's survival and ability to reproduce. Beneficial mutations are more likely to proliferate in future generations as those organisms have a selective advantage. This leads to the adaptation of a species over time through natural selection.