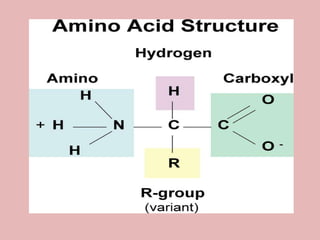
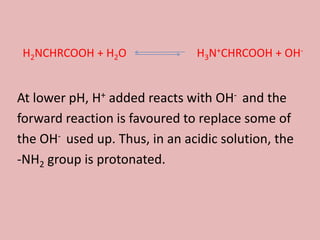
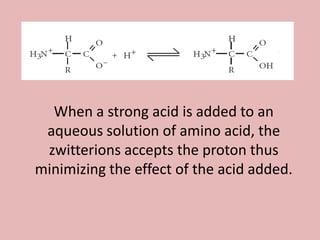
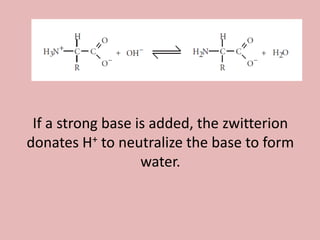
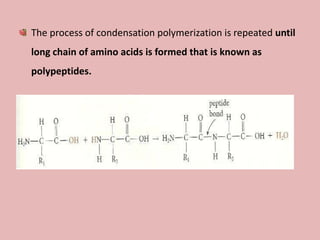
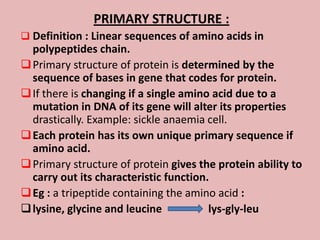
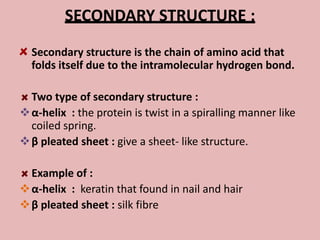
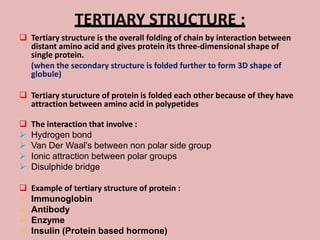
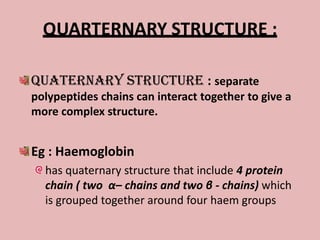
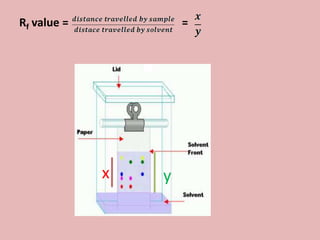
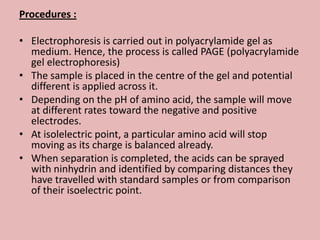
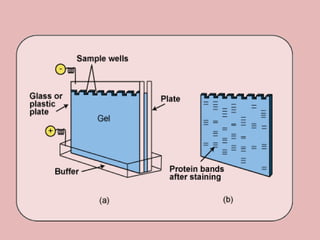
This document discusses proteins and amino acids. It begins by describing the general structure of amino acids, including that they contain a central carbon atom bonded to an amino group, carboxyl group, hydrogen atoms, and a side chain. It then discusses the condensation reaction of amino acids to form polypeptides, and describes the primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary structures of proteins. Methods for analyzing proteins using chromatography and electrophoresis are also summarized. The document concludes by listing the major functions of proteins in the body, such as providing structure, acting as enzymes and hormones, transporting molecules, and serving as an energy source.