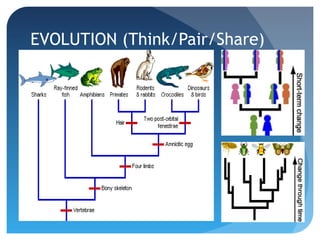
This document outlines major events in the evolution of life on Earth over the past 4.6 billion years, including the following key points:
- 3.5 billion years ago, unicellular life evolved and photosynthetic bacteria began releasing oxygen into the atmosphere.
- Around 500 million years ago, fish-like vertebrates evolved and invertebrates like trilobites were common in the oceans.
- By 360 million years ago, four-limbed vertebrates moved onto land and seed plants and large forests appeared.
- The mass extinction event around 248 million years ago led to the demise of over 90% of marine life and 70% of terrestrial life.