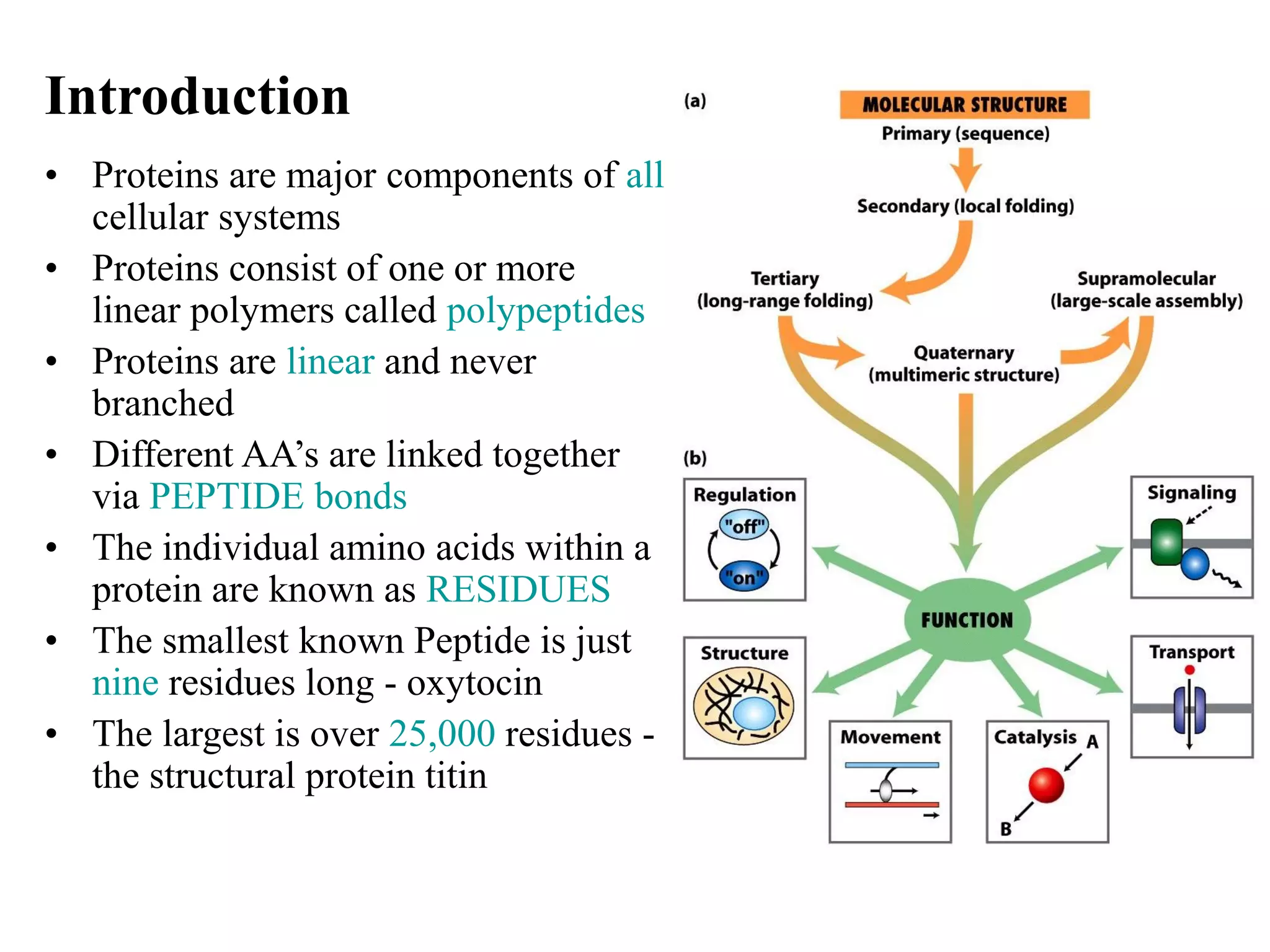
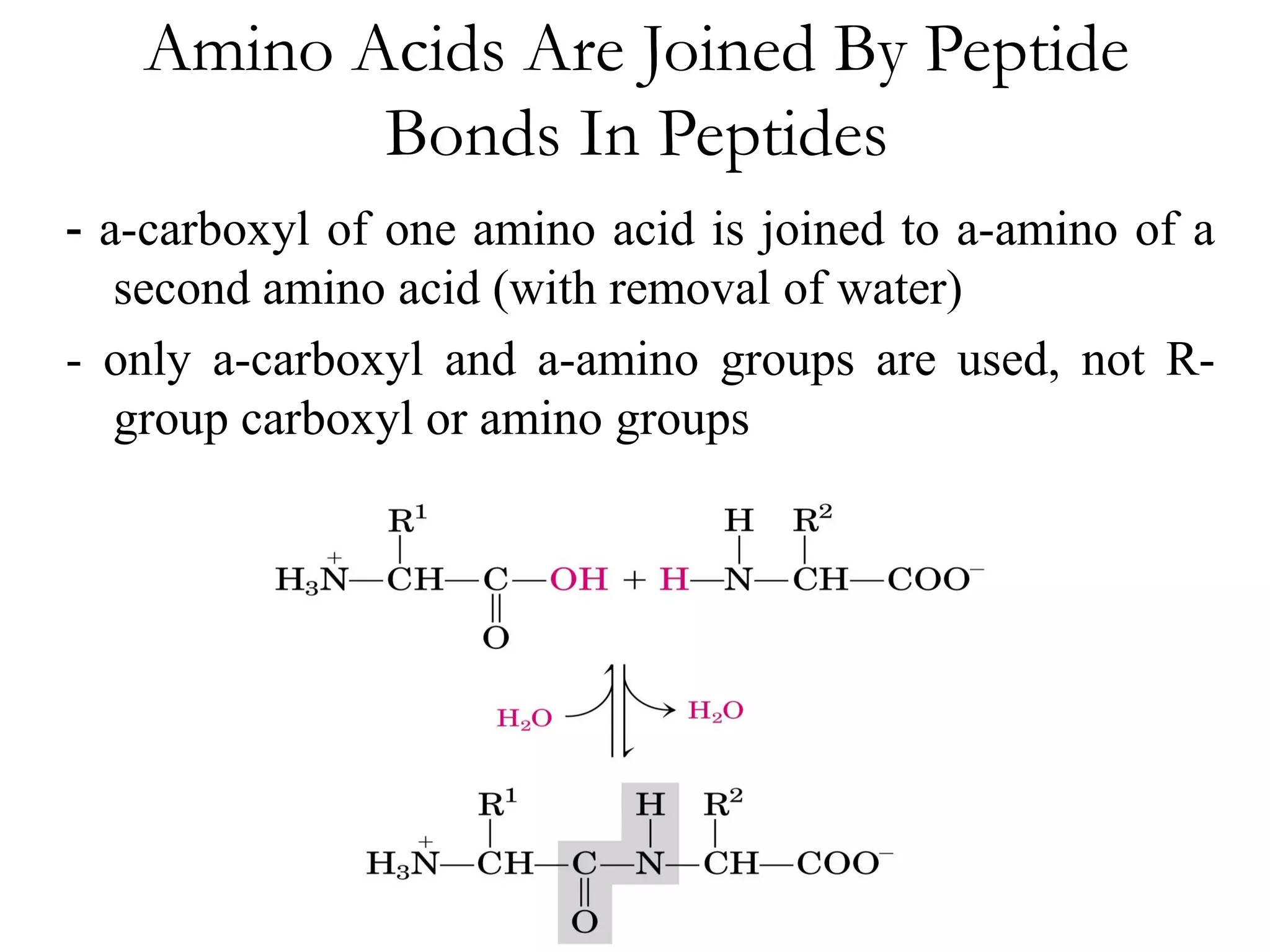
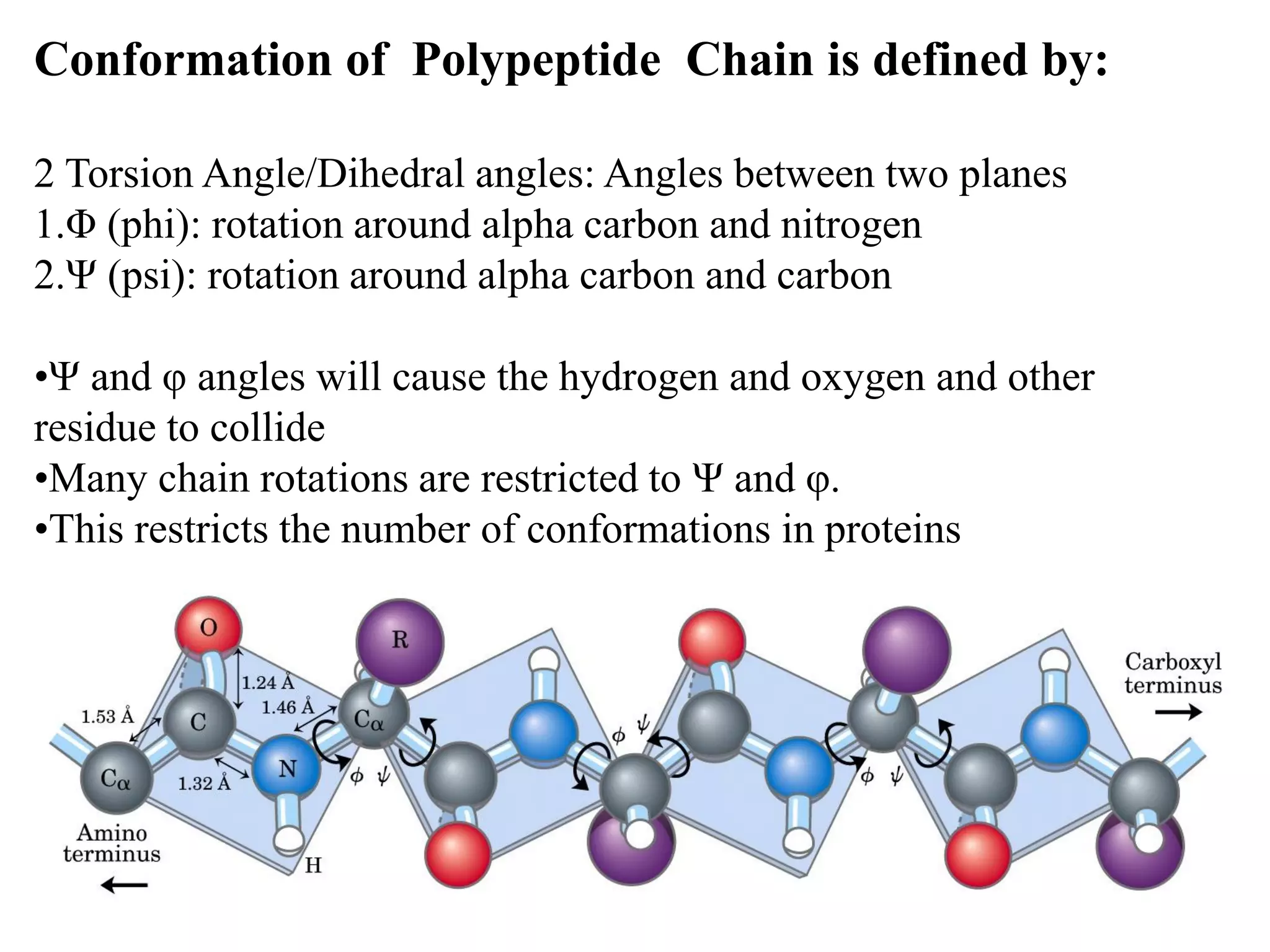
- Proteins are composed of amino acid polymers called polypeptides linked by peptide bonds. They form complex 3D structures through folding at various levels - primary, secondary, tertiary, and quaternary.
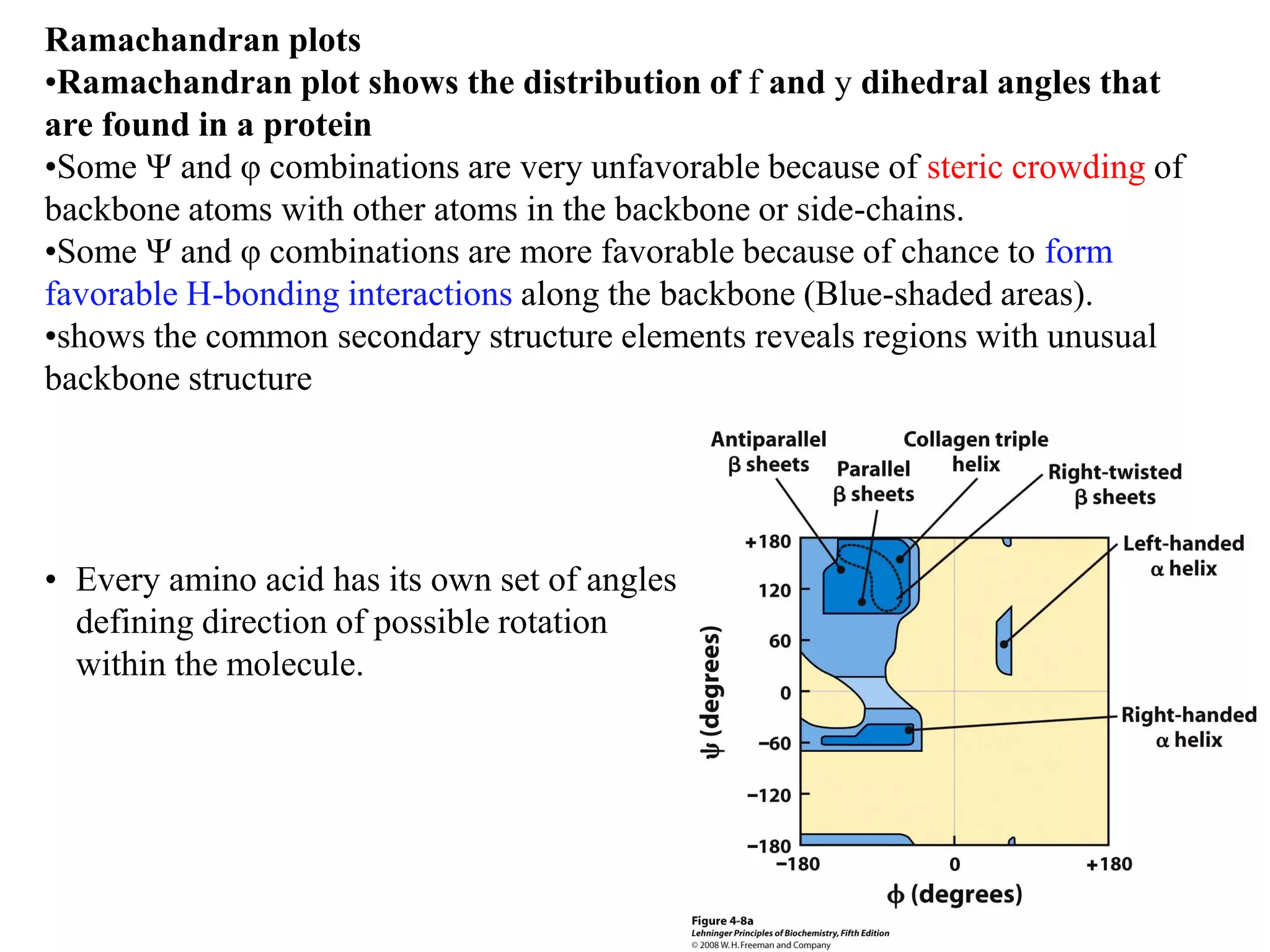
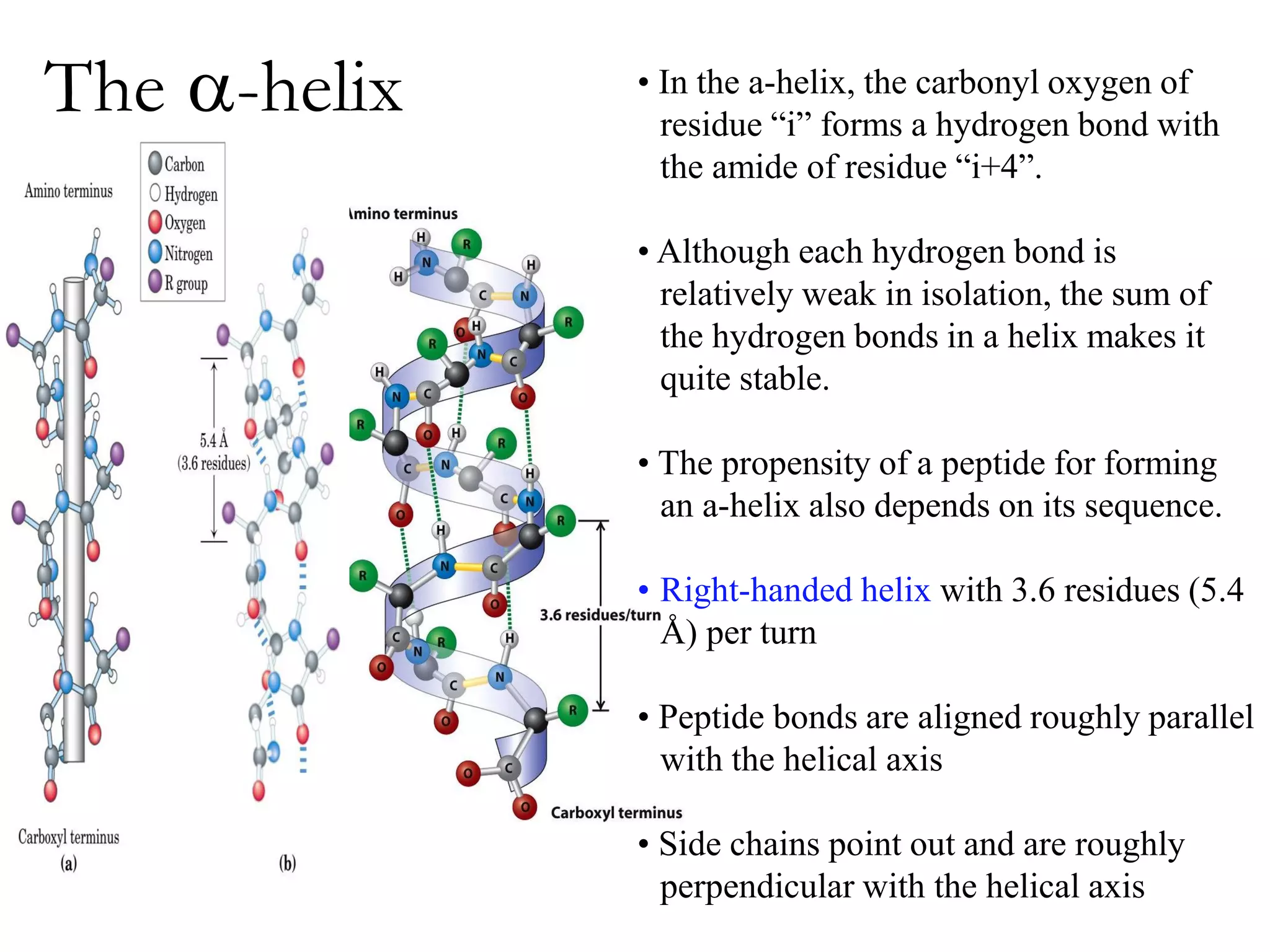
- Secondary structure includes alpha helices, beta sheets, and beta turns formed by hydrogen bonding between amino acids in the polypeptide chain.
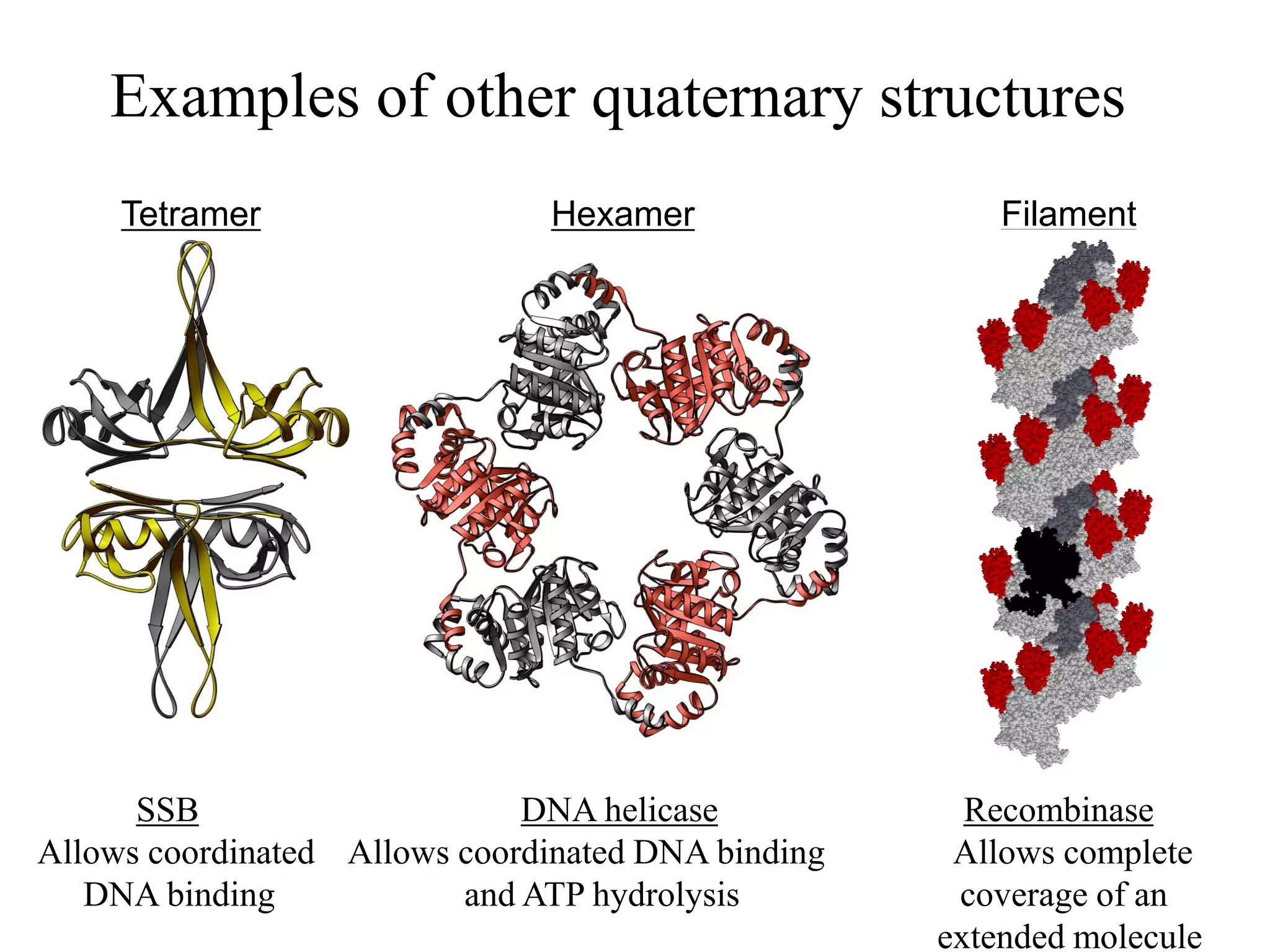
- Tertiary structure is the overall 3D shape of a protein formed by interactions between amino acid side chains. Quaternary structure involves the assembly of multiple protein subunits.
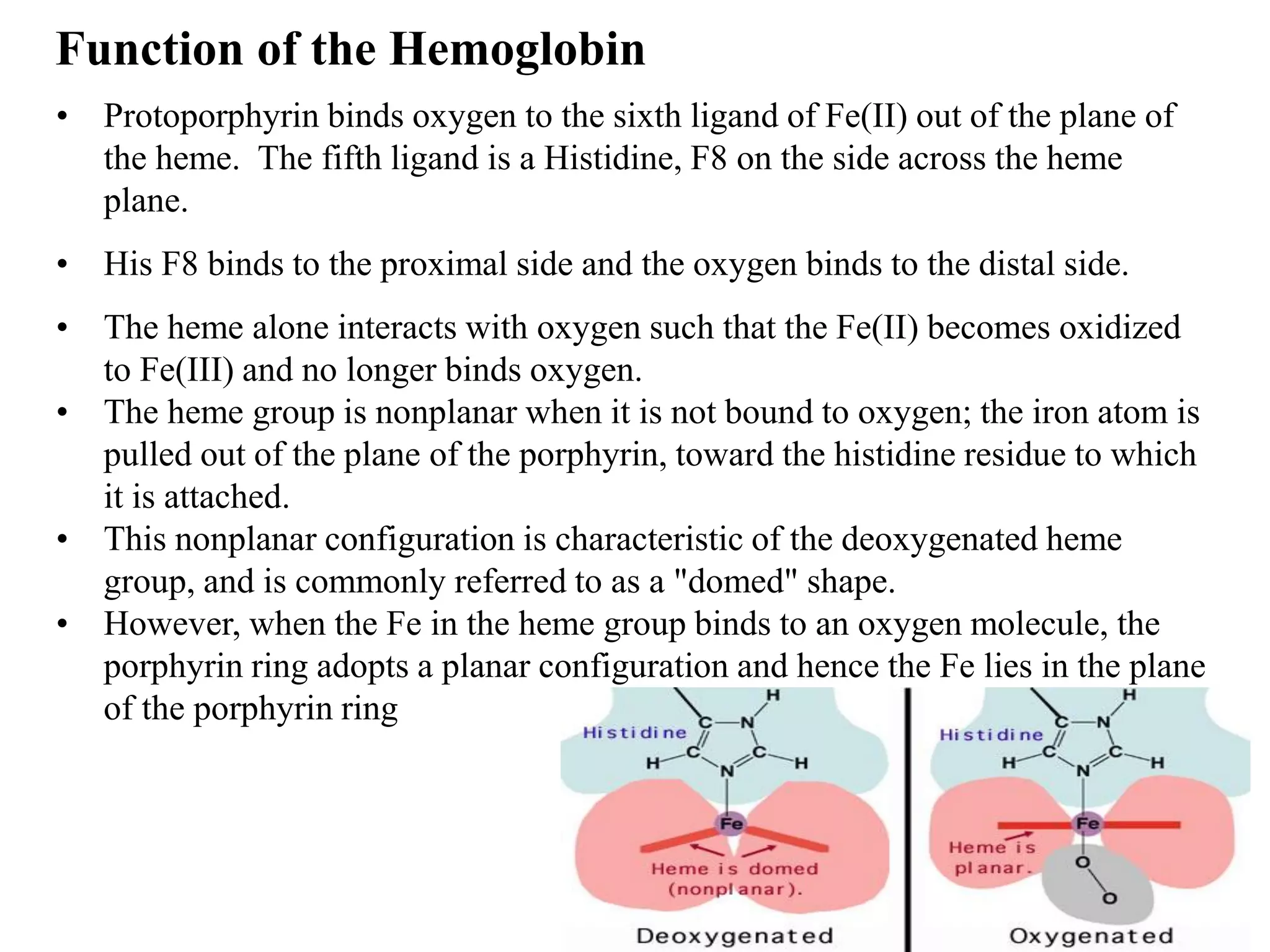
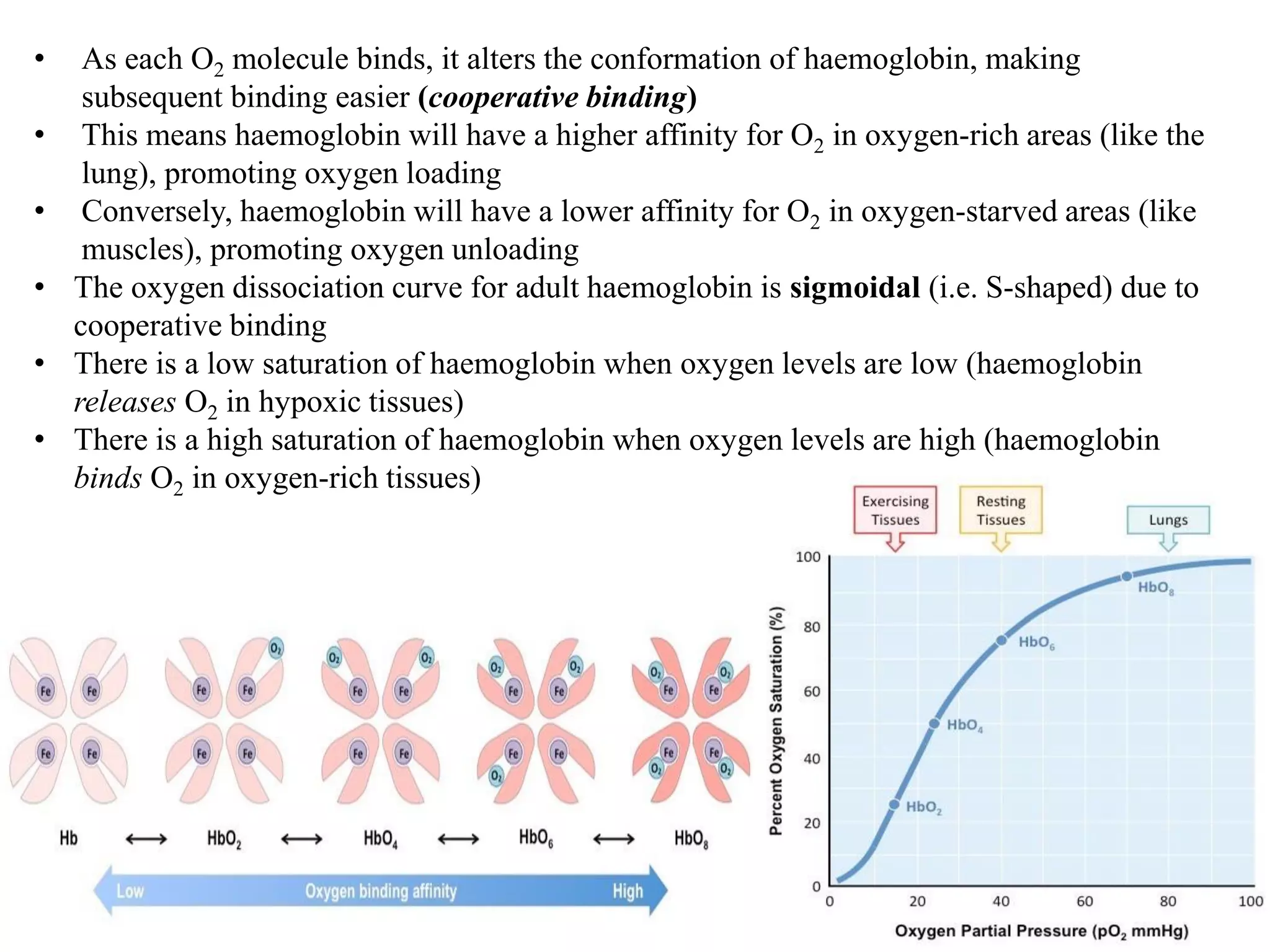
- Myoglobin and hemoglobin are oxygen-binding proteins with heme prosthetic groups. Hemoglobin has a cooperative binding mechanism that allows for oxygen delivery and release in tissues.





















![Hemoglobin
• Different Subunit Proteins (heteromeric), 2 a globin subunits and 2 b globin subunits
• Composed of four subunits, each containing a heme group: a ring-like structure Porphyrin
with a central iron atom that binds oxygen.
• Extensive interactions between unlike subunits a2-b2 or a1-b1 interface has 35 residues
while a1-b2 and a2-b1 have 19 residue contact.
• a2,b2 dimer which are structurally similar to myoglobin
• Transports oxygen from lungs to tissues. O2 diffusion alone is too poor for transport in
larger animals.
• Solubility of O2 is low in plasma i.e. 10-4 M. But bound to hemoglobin, [O2] = 0.01 M or
that of air.
• Two alternative O2 transporters are;
Hemocyanin, a Cu containing protein (Found in Arthropods and Mollusca).
Hemoerythrin , a non-heme containing protein (marine invertebrate).](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/proteins-220527171552-e071e756/75/proteins-pdf-28-2048.jpg)