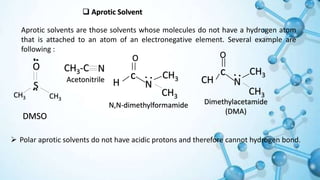
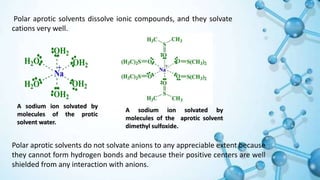
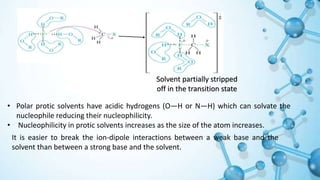
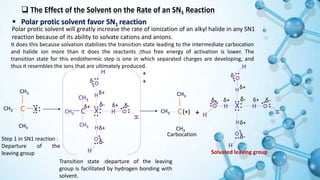
This presentation discusses solvent effects on SN1 reactions. It introduces different types of solvents including protic, aprotic, polar, and nonpolar. Protic solvents can hydrogen bond to nucleophiles, increasing their nucleophilicity. Polar protic solvents strongly solvate carbocations and halide ions, stabilizing the SN1 transition state and greatly increasing the reaction rate. The presentation examines how solvent properties like dielectric constant and hydrogen bonding ability influence solvation and reaction mechanisms.