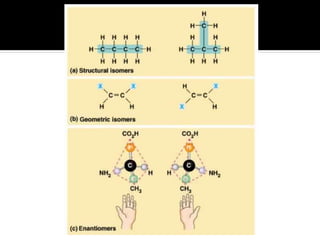
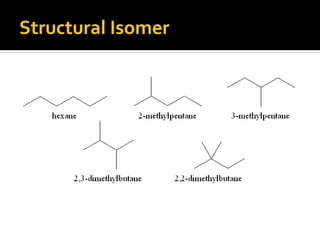
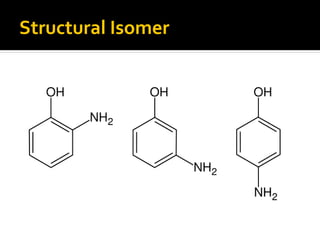
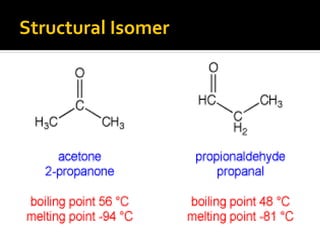
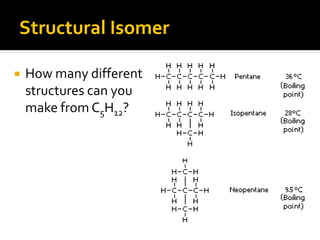
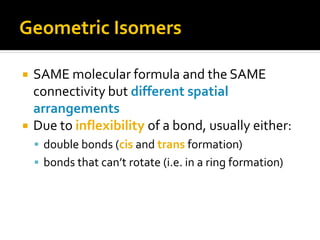
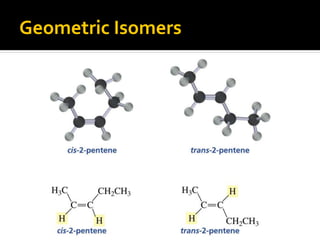
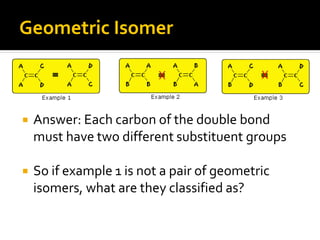
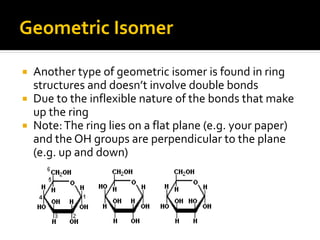
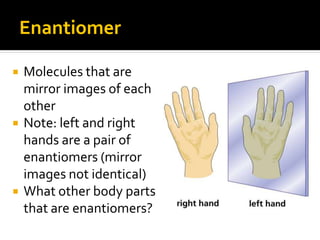
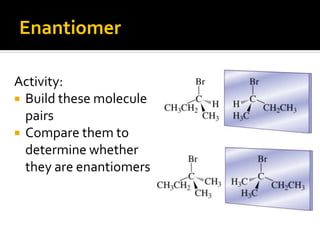
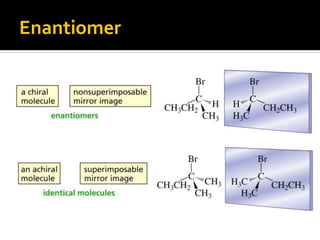
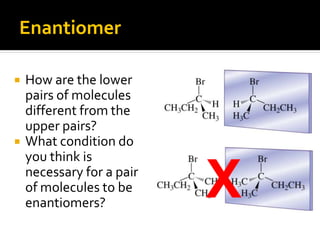
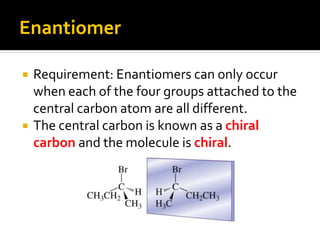
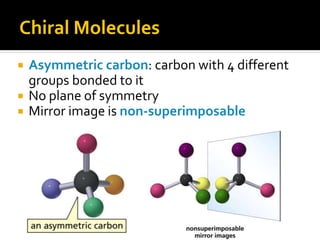
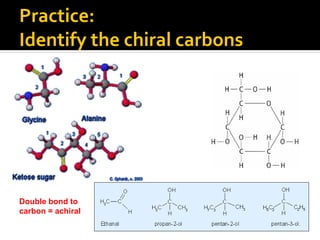
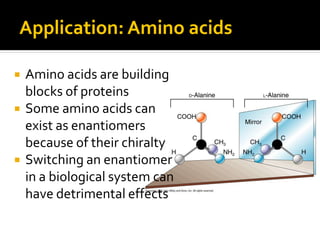
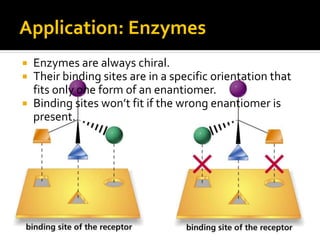
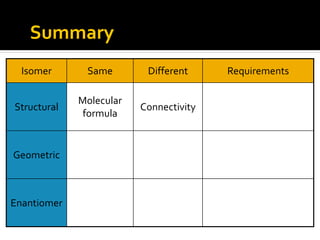
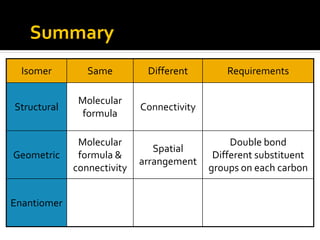
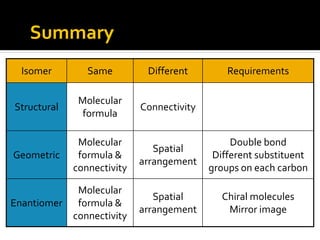
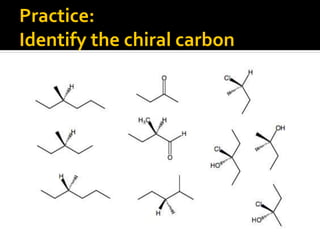
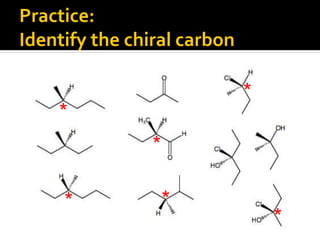
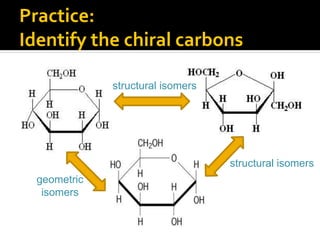
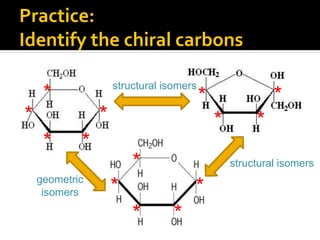
The document discusses three types of isomers: structural isomers, geometric isomers, and enantiomers. Structural isomers have the same molecular formula but different connectivity of atoms. Geometric isomers have the same molecular formula and connectivity but different spatial arrangements, usually due to double bonds or rings. Enantiomers are non-superimposable mirror images that contain a chiral carbon with four different groups attached.