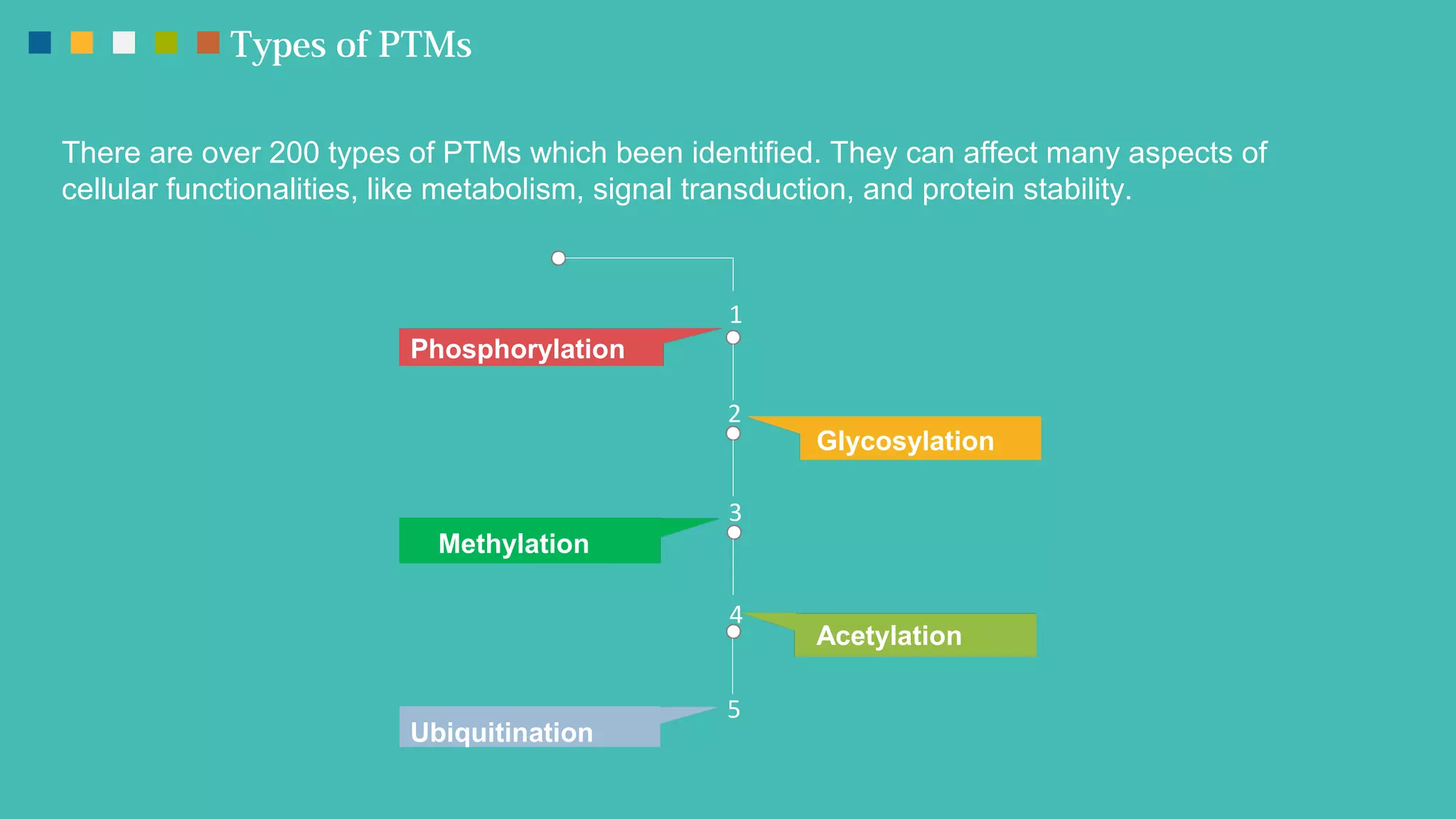
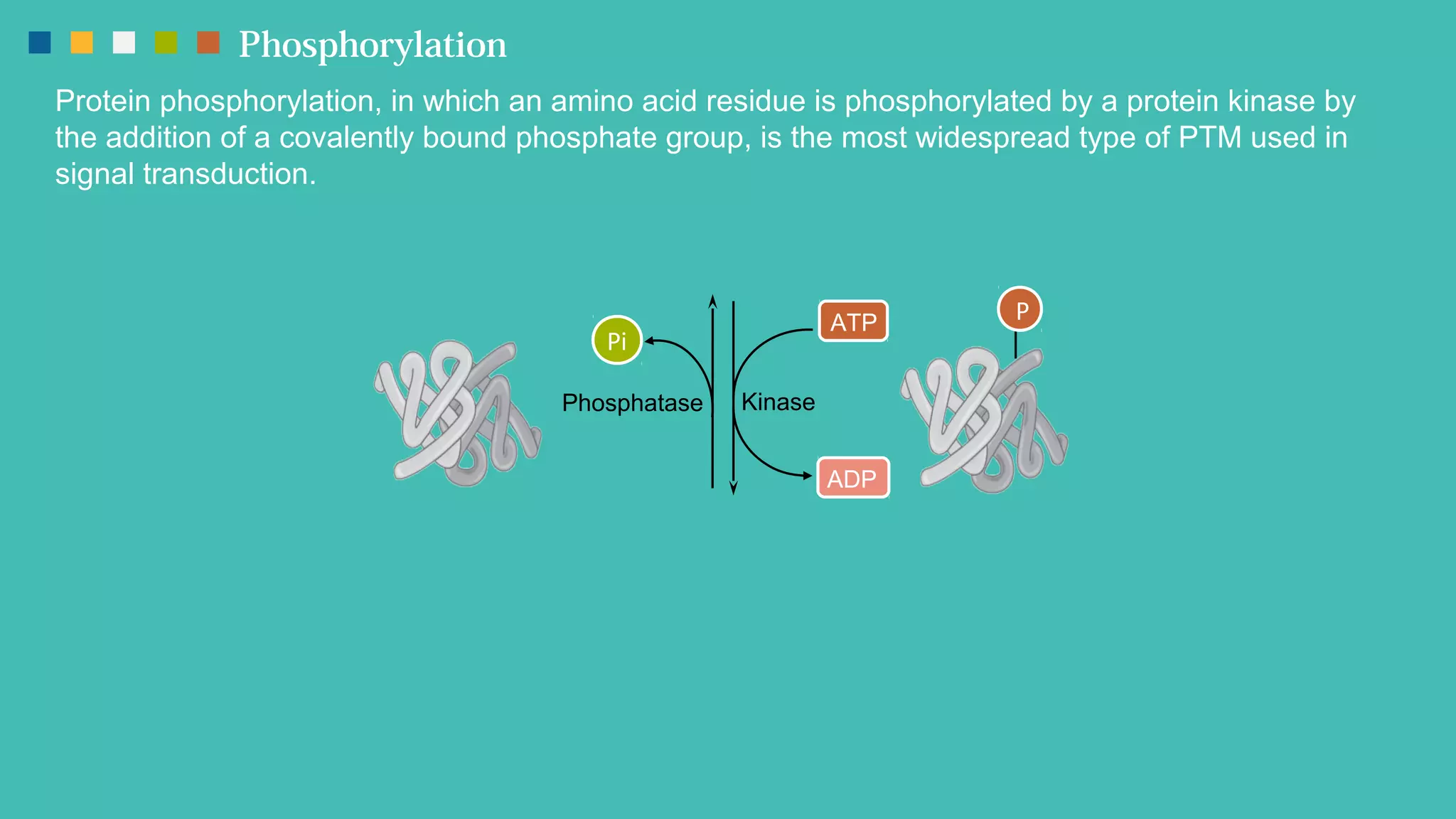
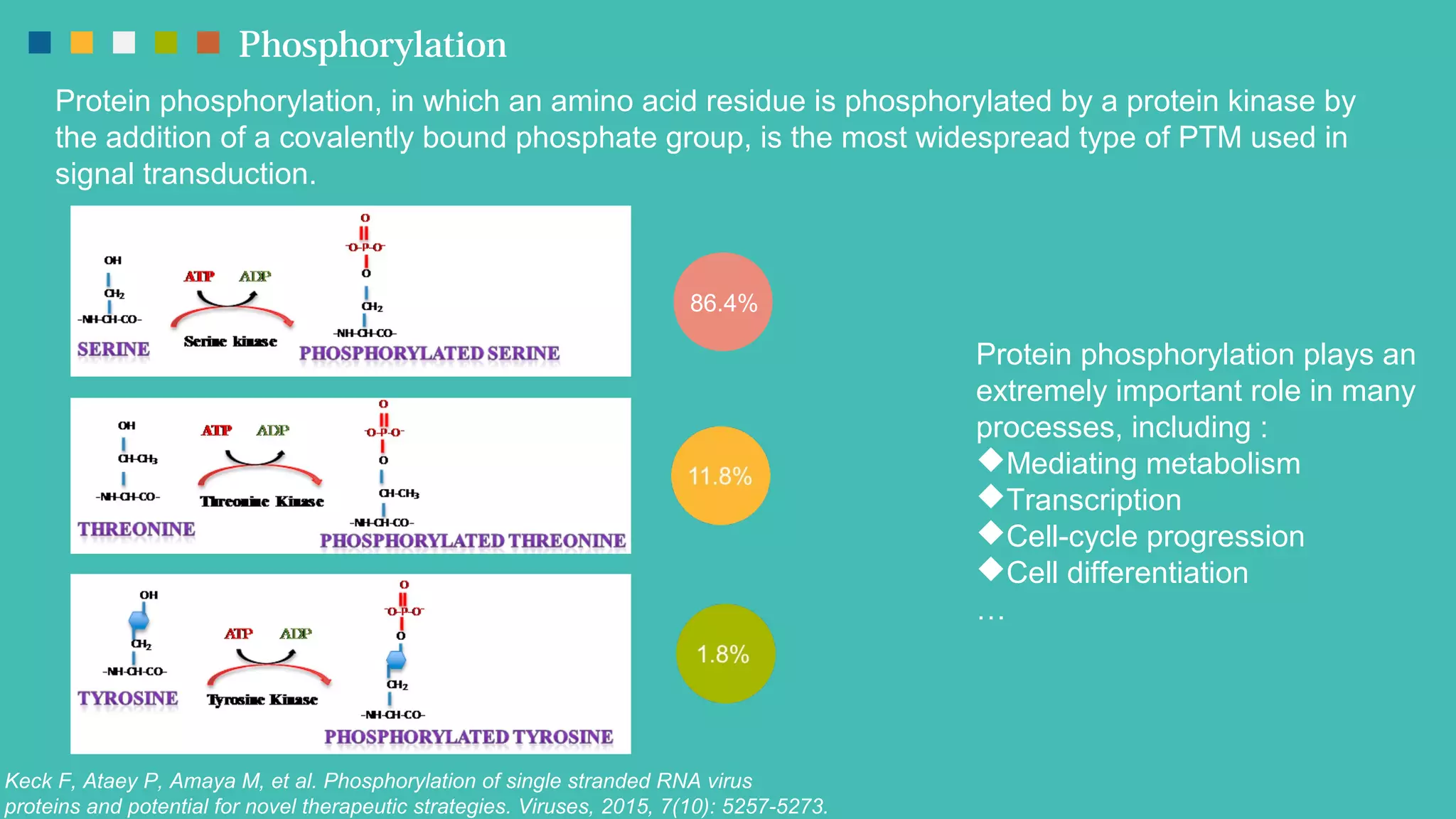
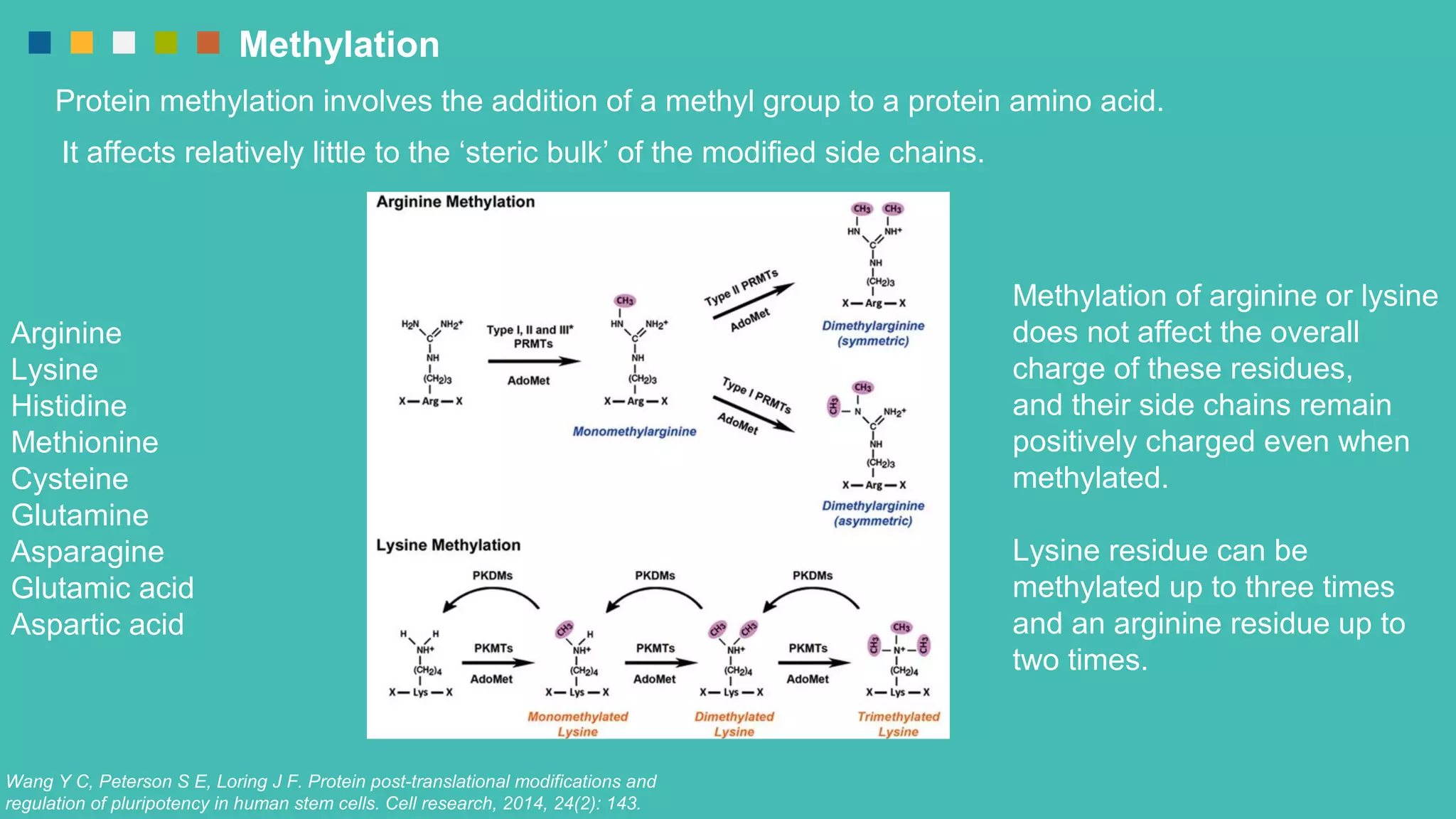
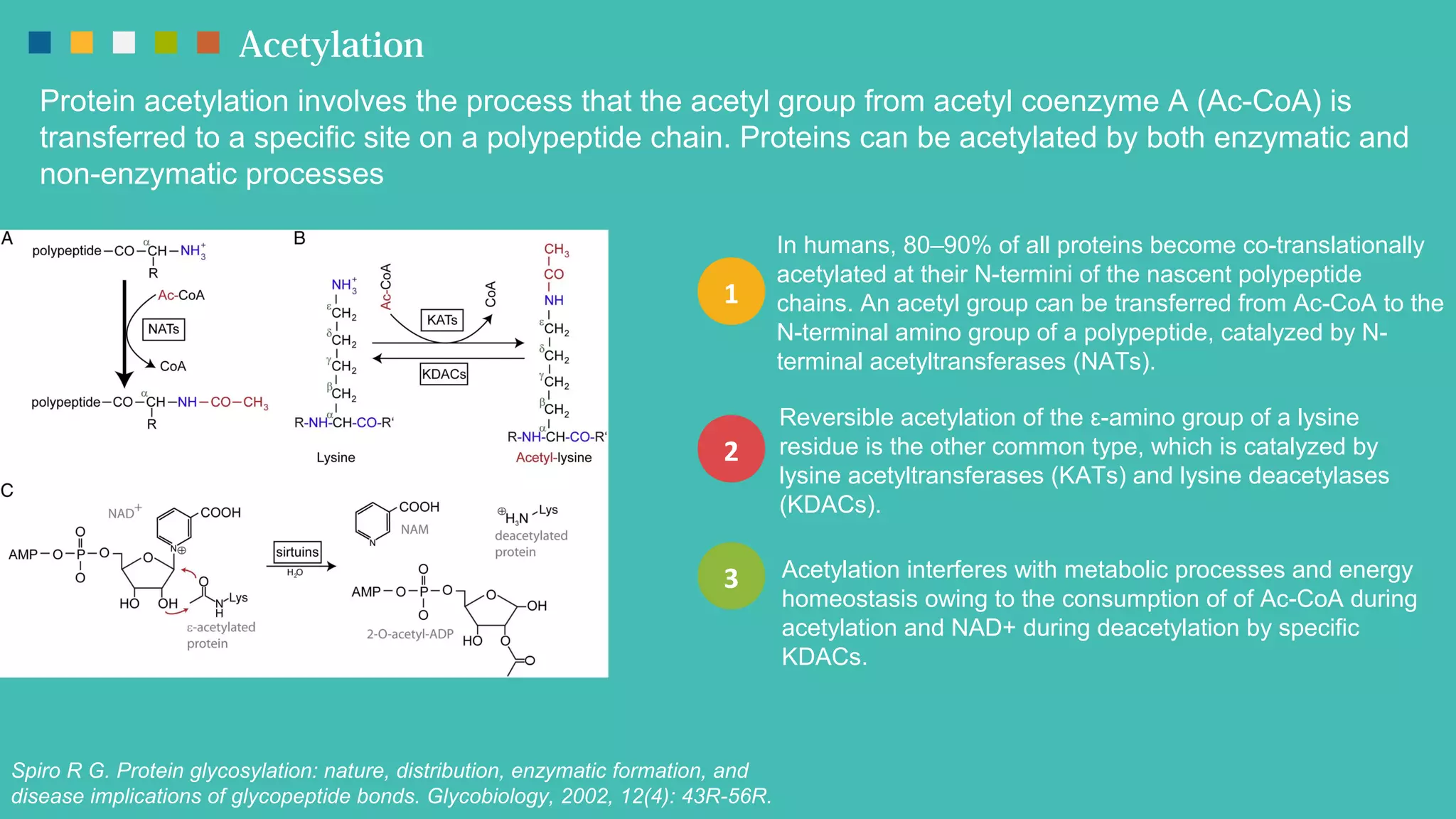
The document provides an overview of post-translational modifications (PTMs) and their role in increasing proteome complexity, noting that while there are about 25,000 genes in humans, the total number of proteins can exceed one million due to PTMs. It details various types of PTMs, including phosphorylation, methylation, glycosylation, acetylation, and ubiquitination, describing their mechanisms and importance in cellular functions such as metabolism, signal transduction, and protein stability. Additionally, Creative Proteomics offers services for analyzing these modifications to aid scientific research.