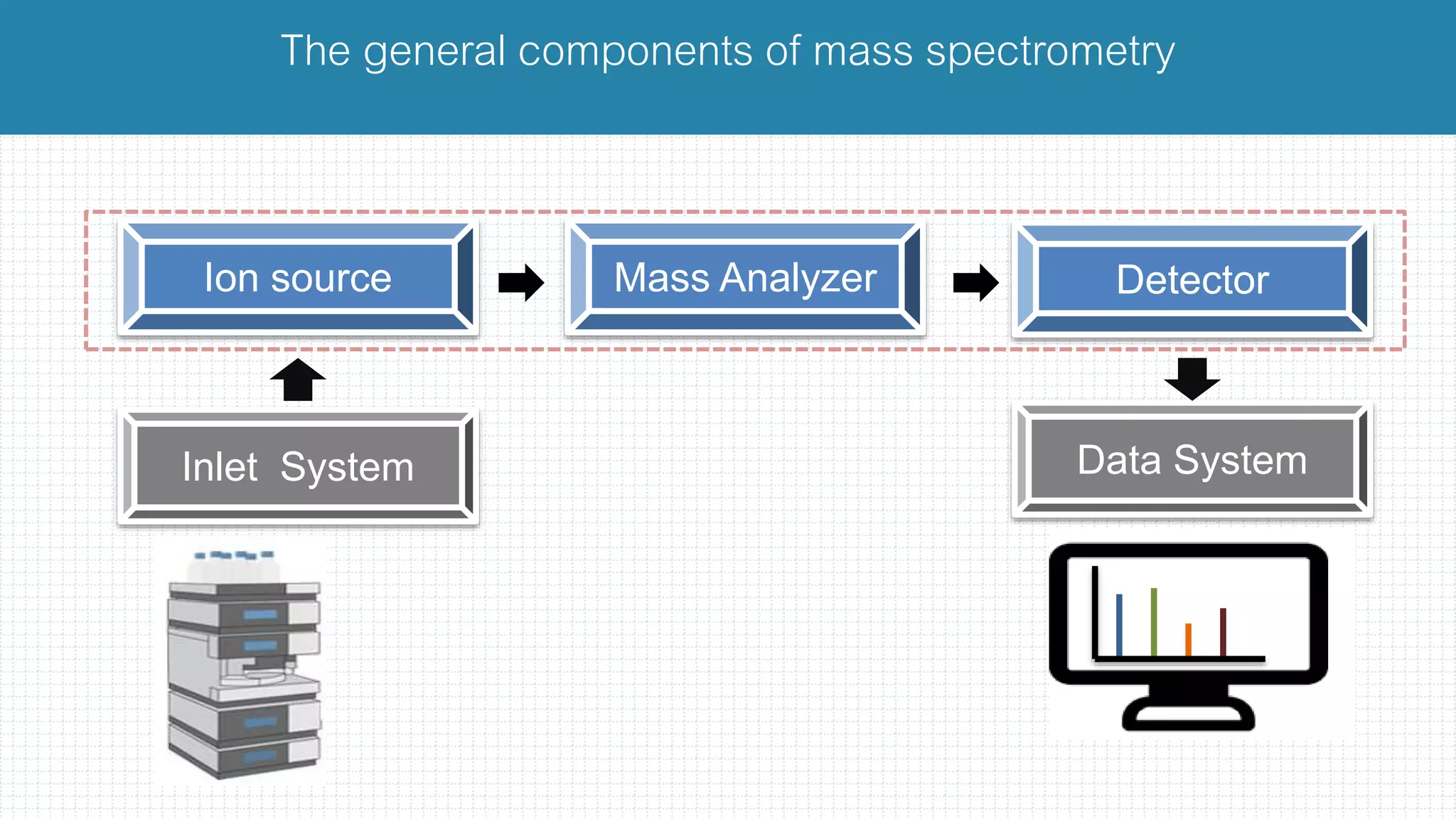
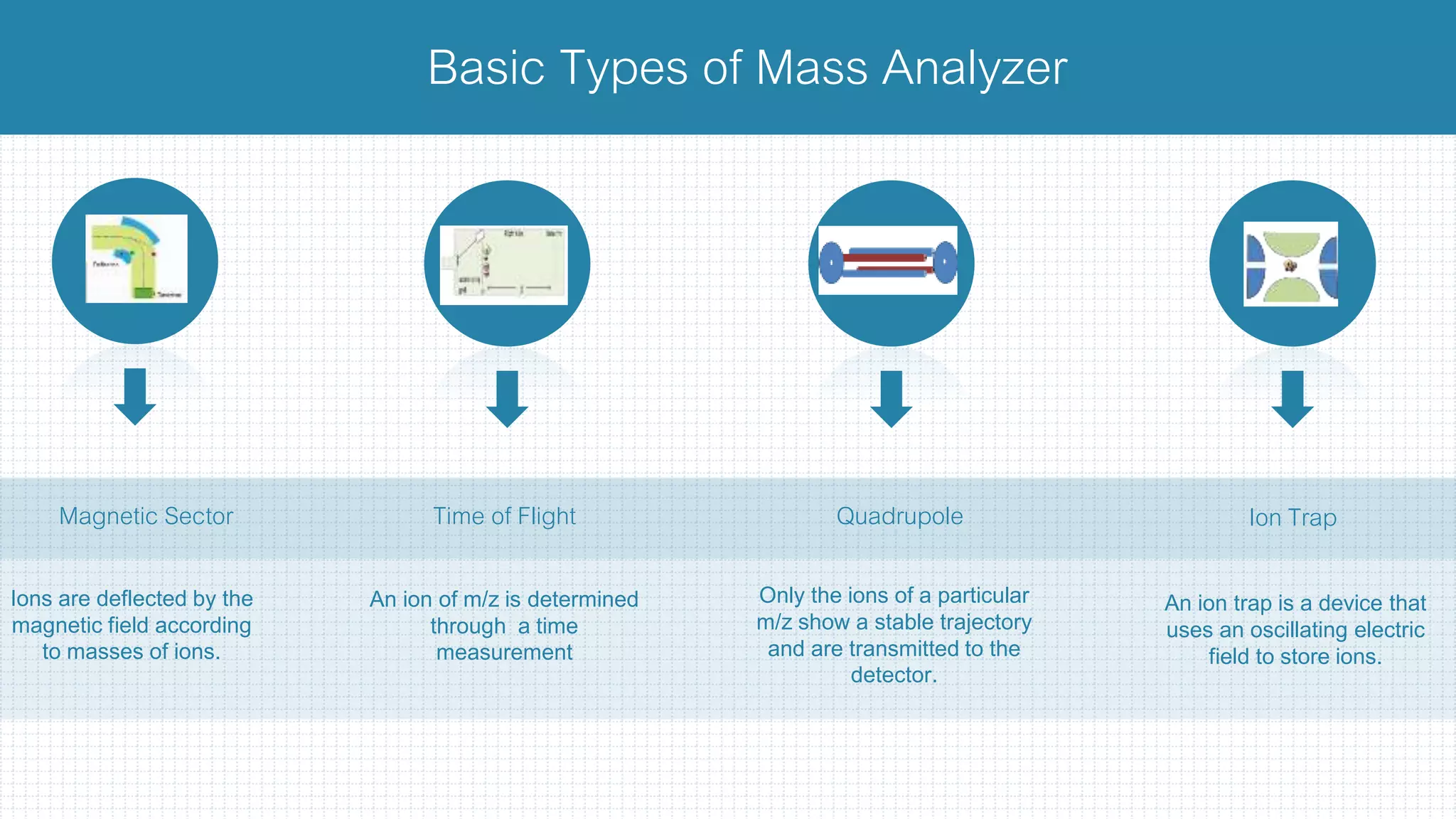
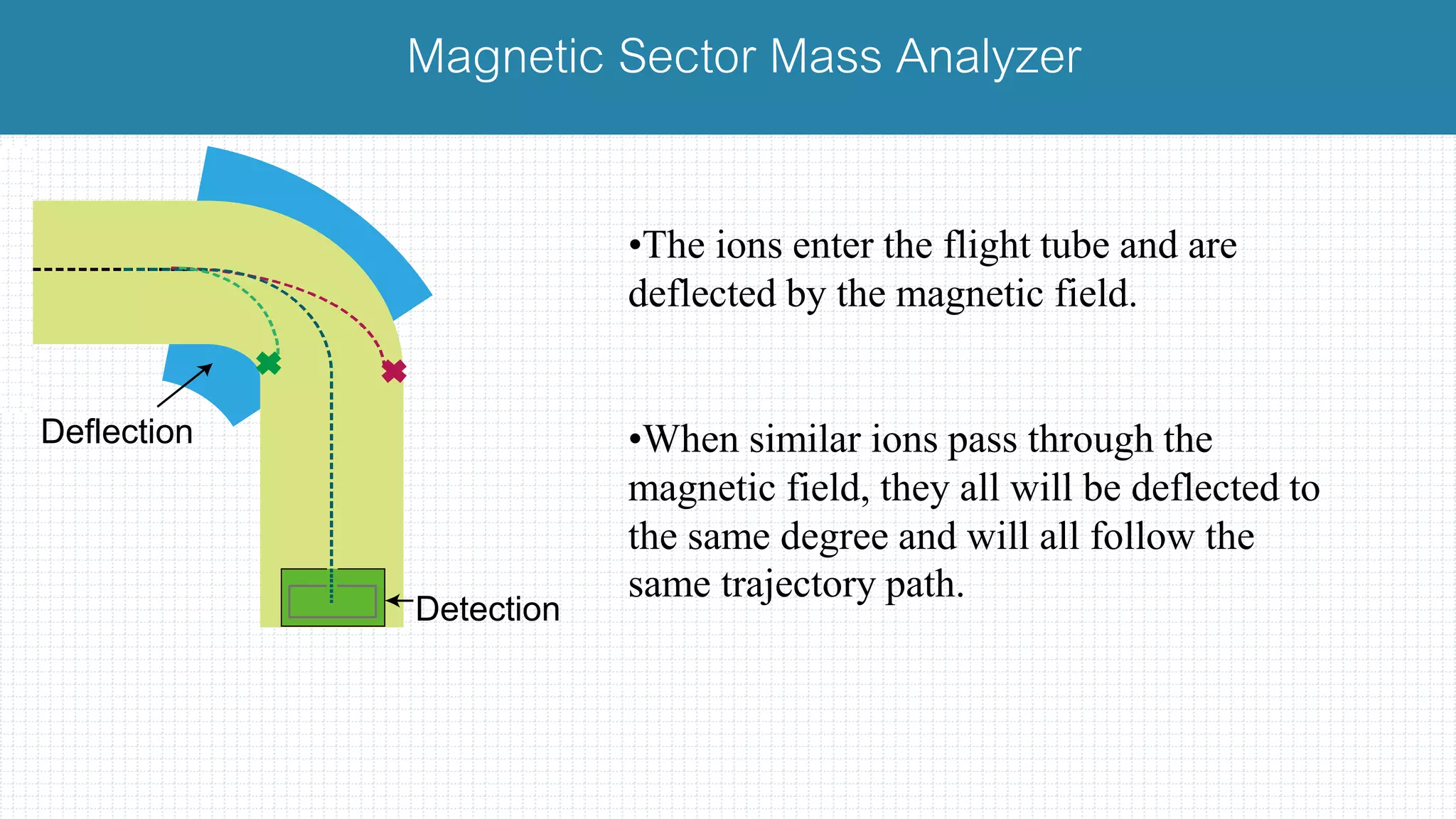
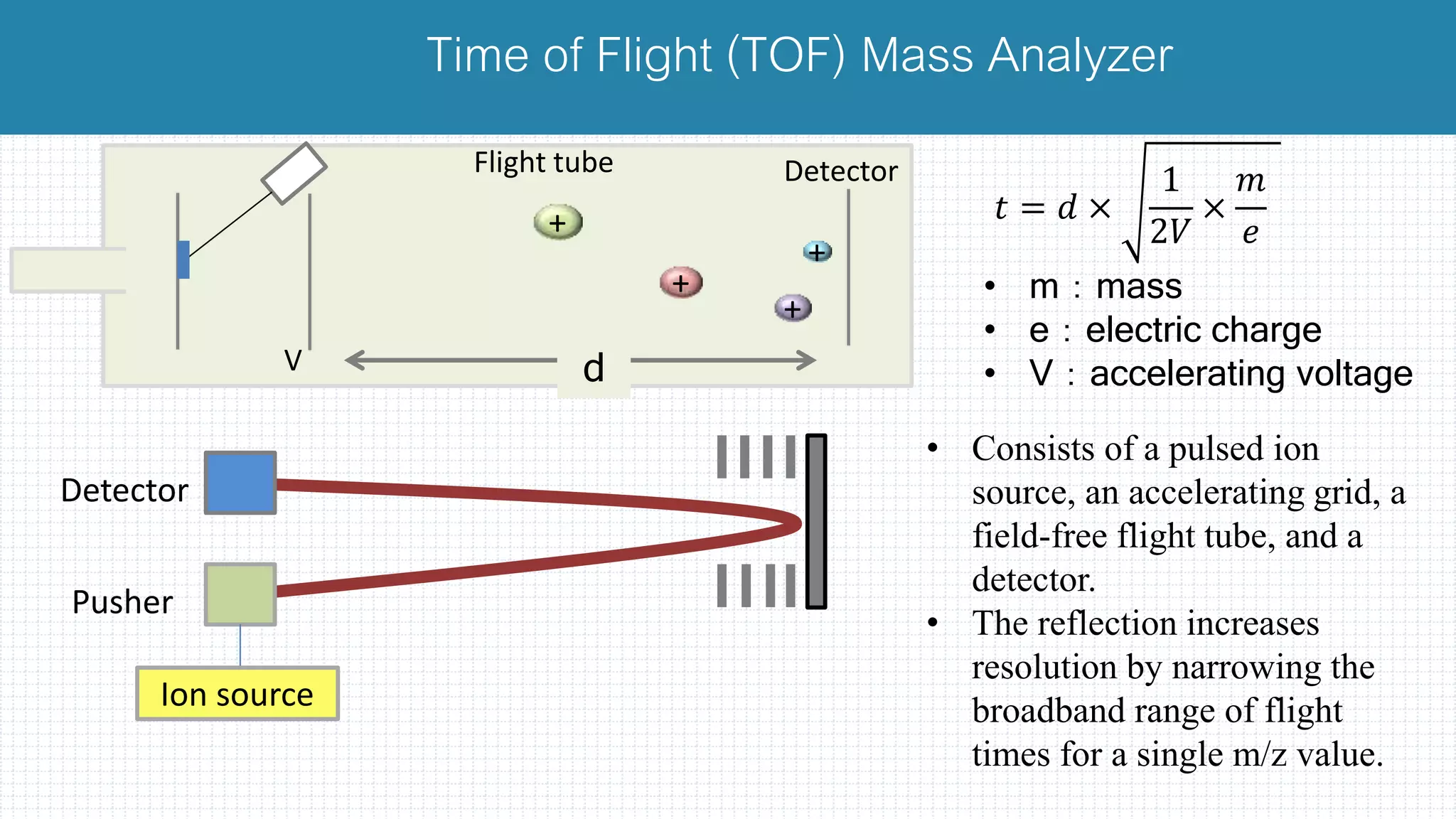
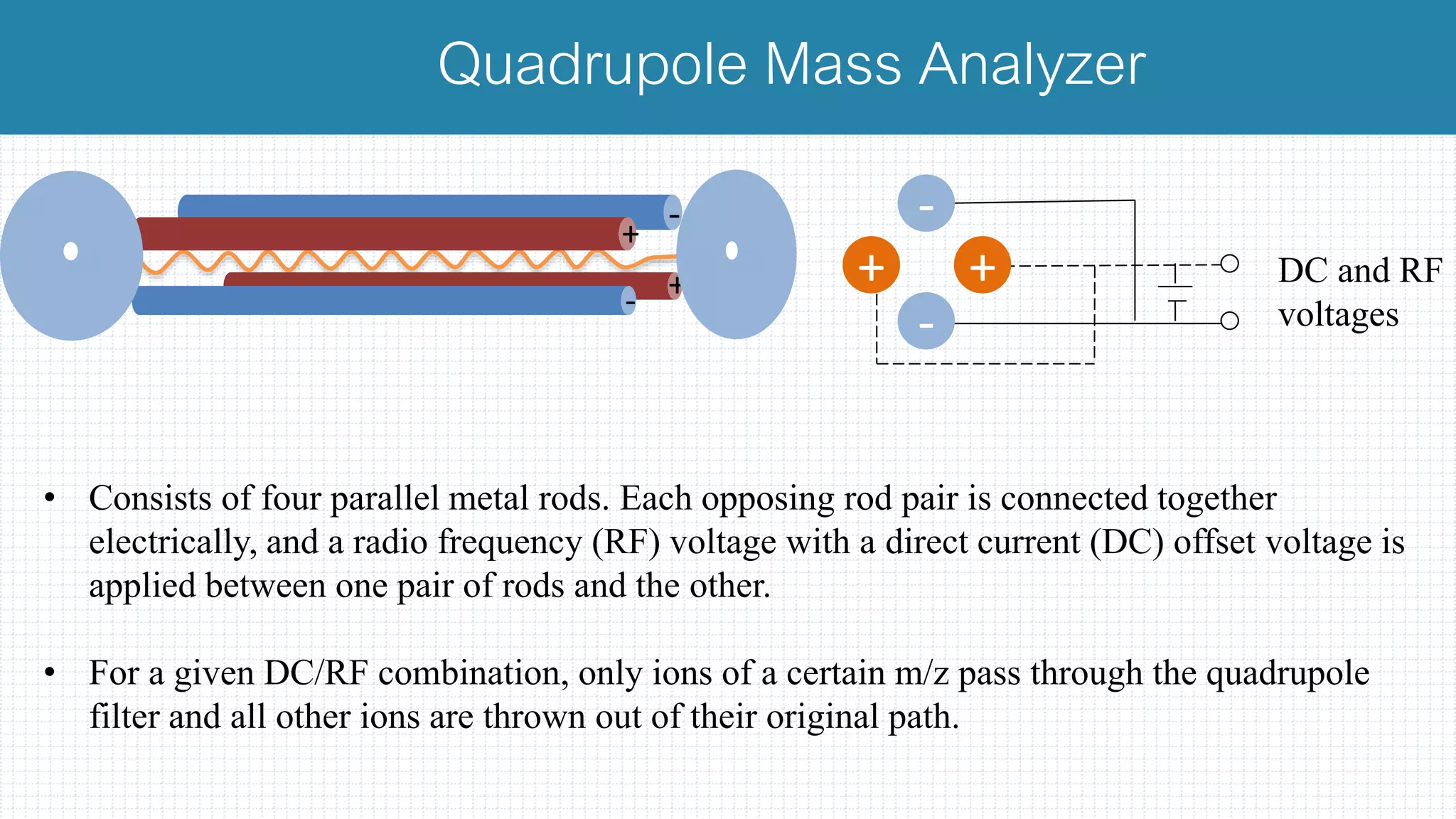
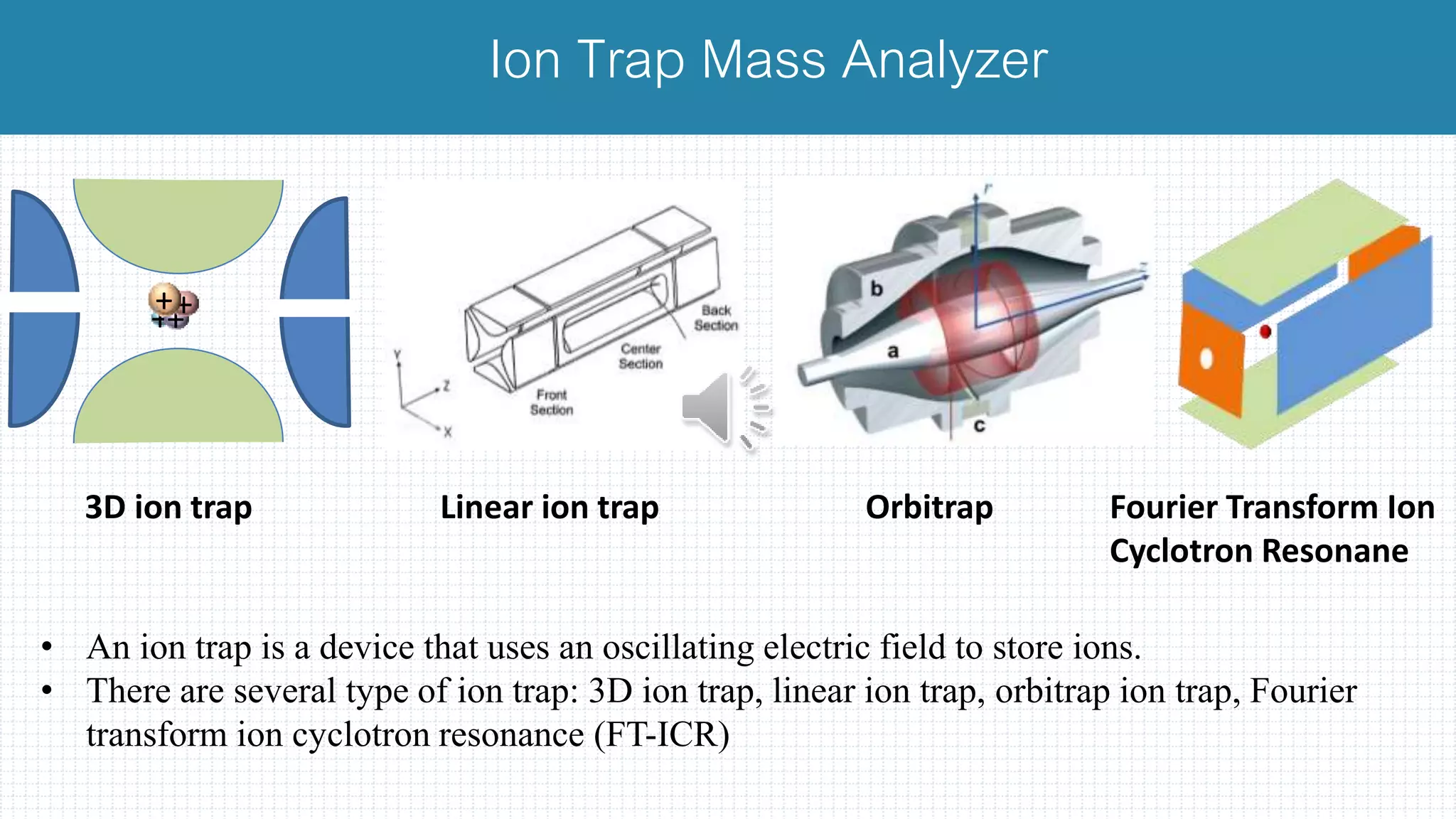
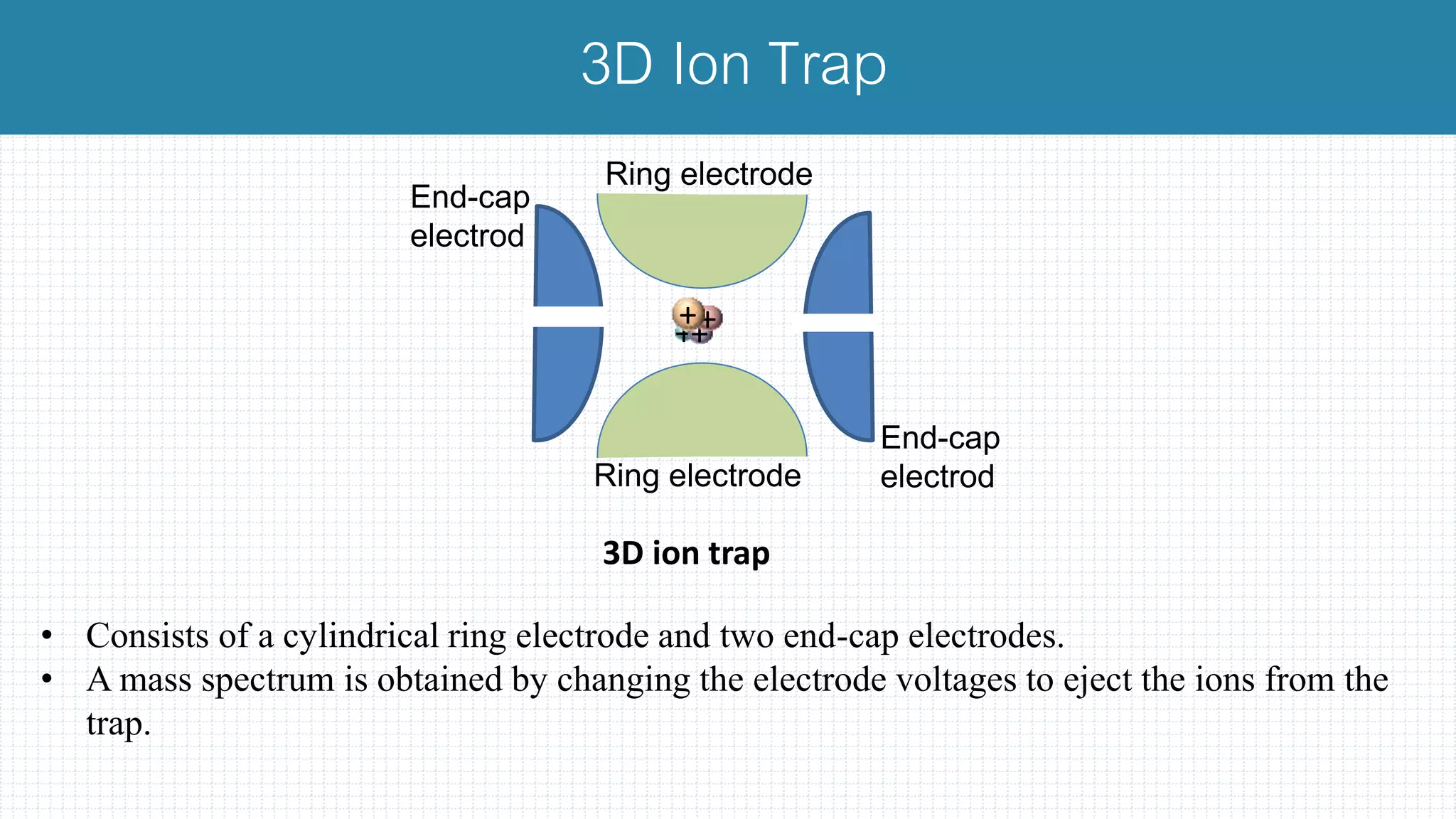
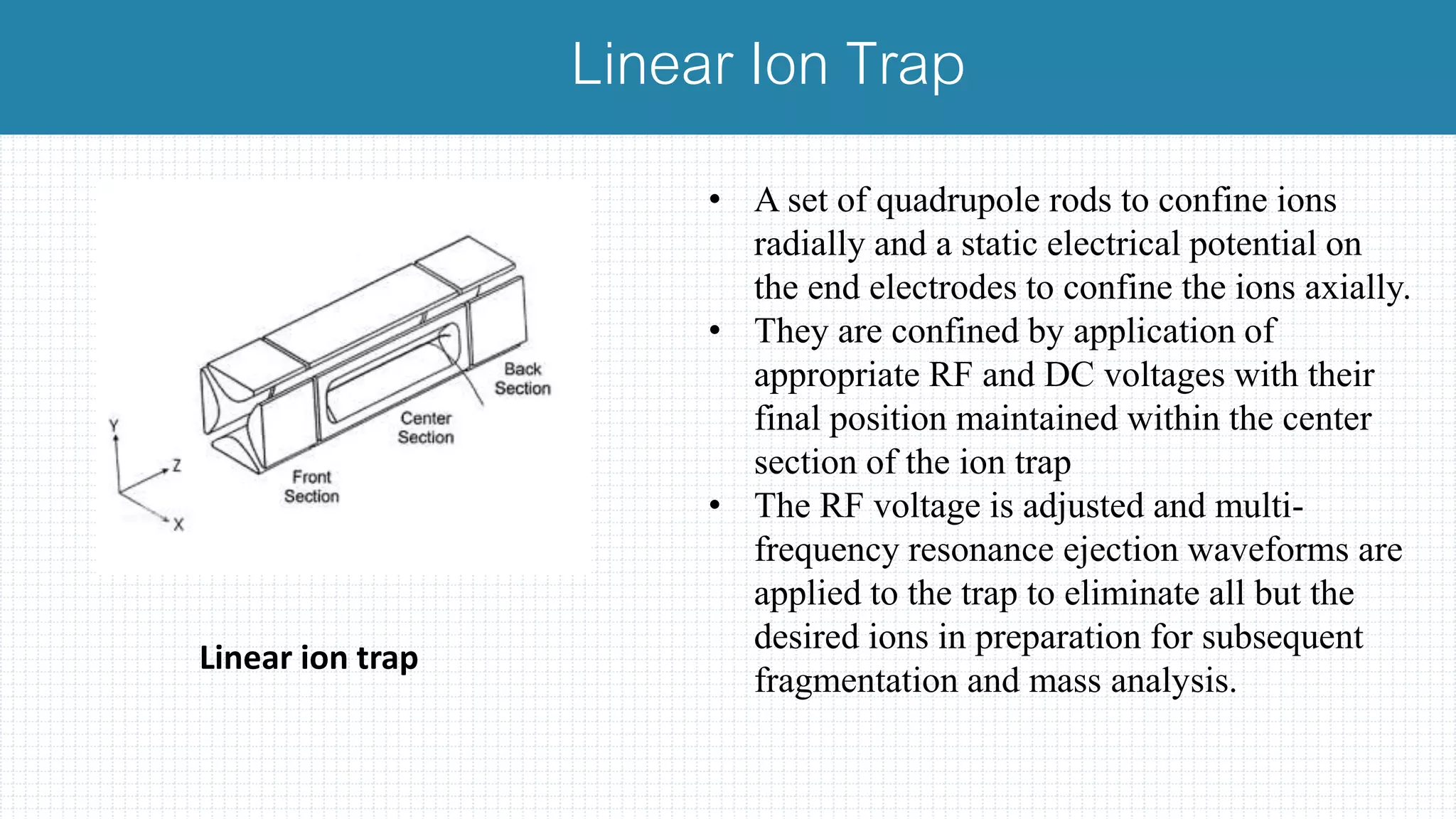
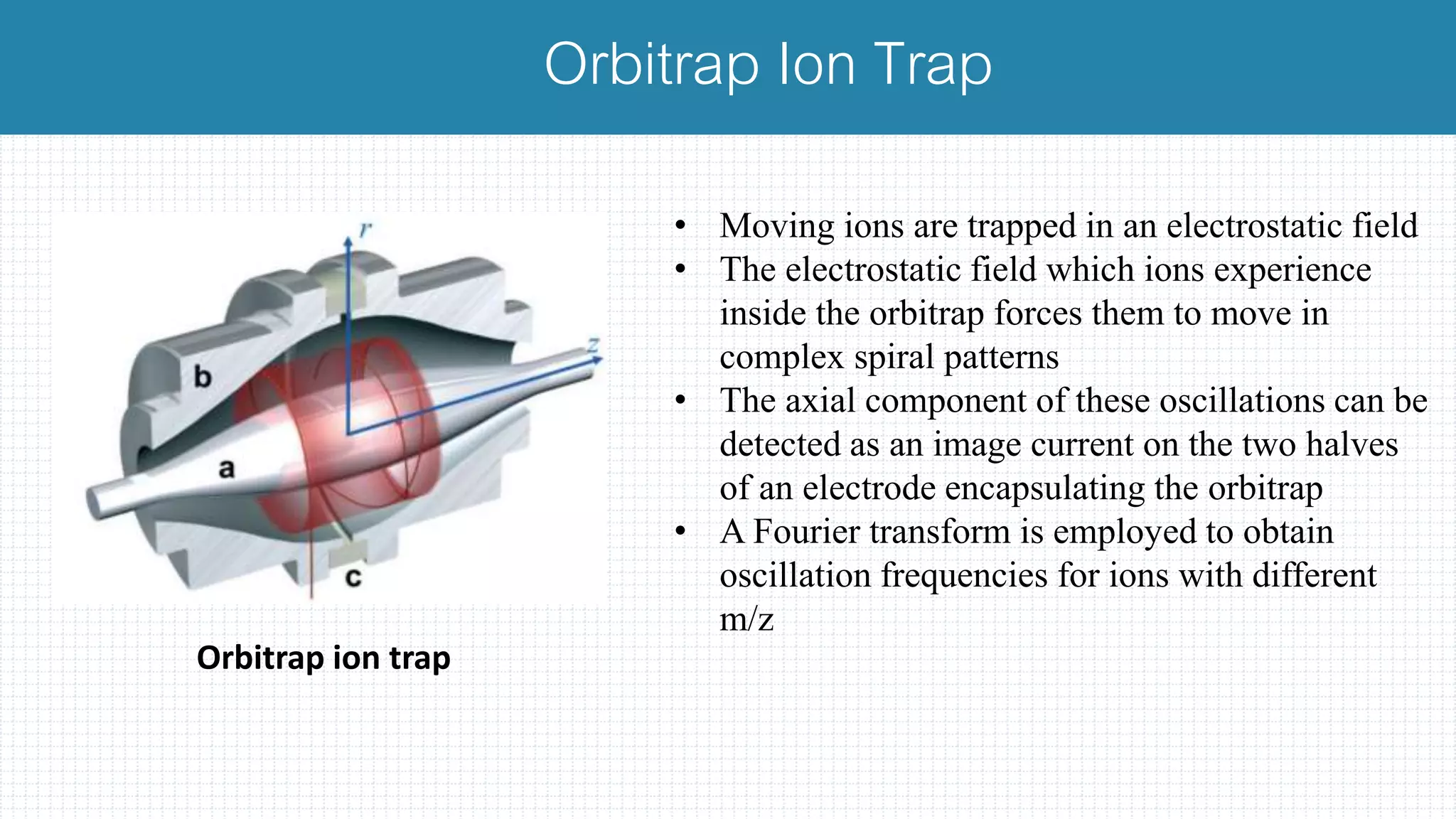
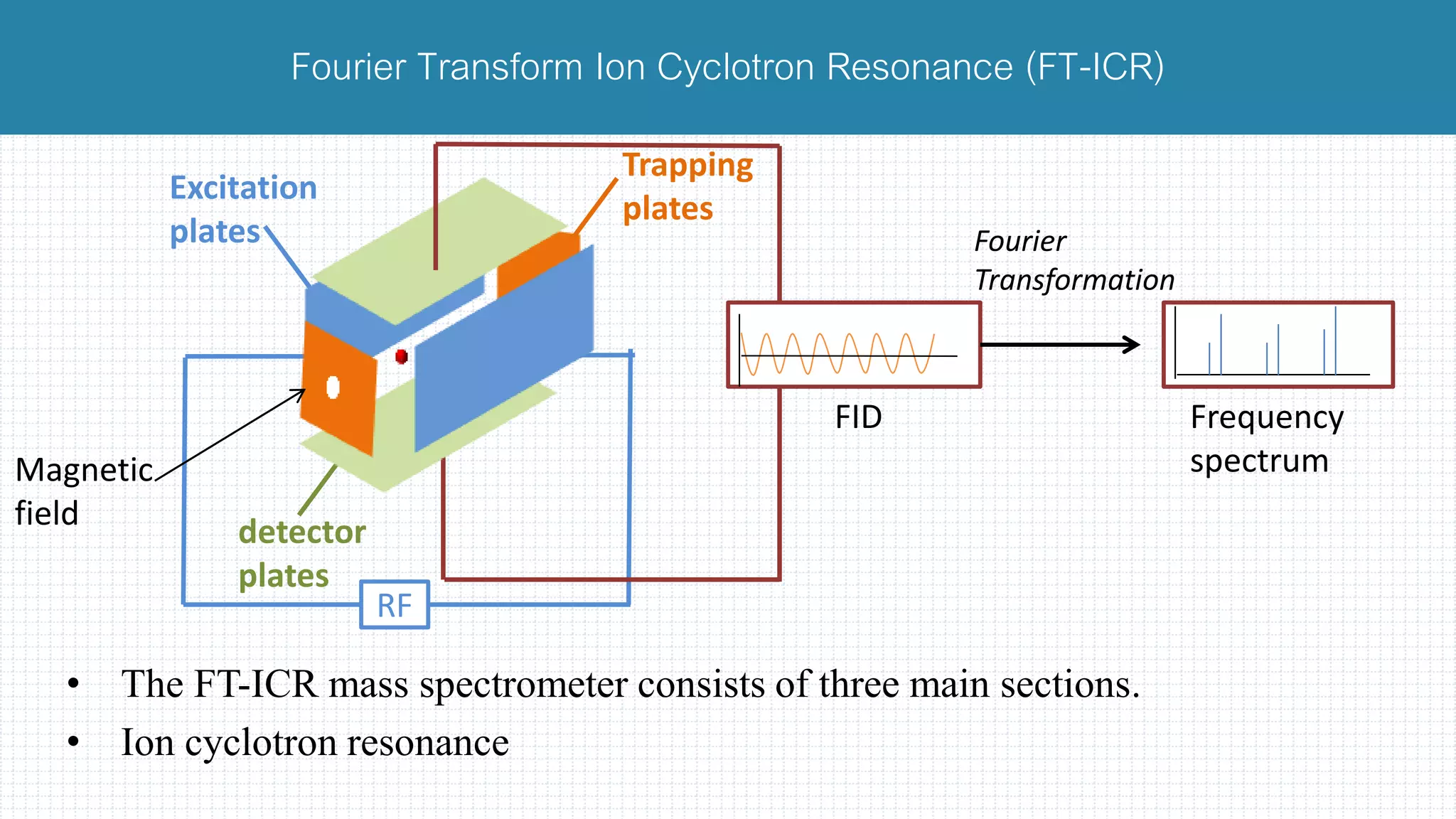
The document provides a comprehensive introduction to mass spectrometry, detailing its core components like the ion source, mass analyzers, and detectors. It explains various types of mass analyzers including magnetic sector, time of flight (TOF), quadrupole, and different ion traps, highlighting their operational principles and applications. Additionally, it references important literature and sources related to mass spectrometry.