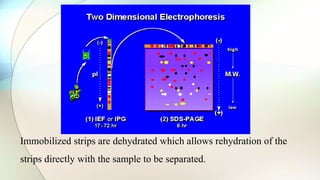
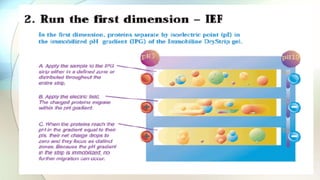
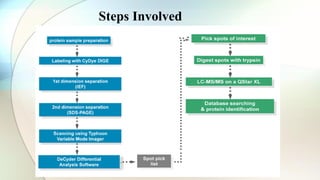
The document discusses the study of amino acids' properties, focusing on their pKa values, isoelectric points, and how titration curves can be used to analyze them. It details the 2D-PAGE technique for separating and identifying proteins based on their isoelectric point and molecular mass, highlighting its advantages in handling complex biological samples. Additionally, the document addresses challenges in protein analysis, including molecular weight limitations and reproducibility issues, while introducing 2D-DIGE as an advanced method to improve sensitivity and resolve gel variations.