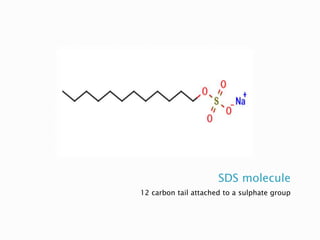
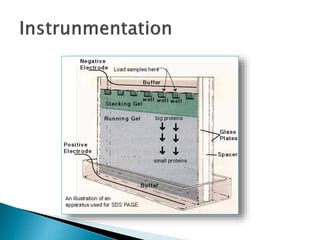
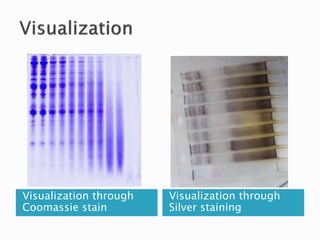
SDS-PAGE is a technique used to separate proteins by molecular weight. Proteins are denatured and given a negative charge by SDS detergent before running through a polyacrylamide gel matrix by electrophoresis. Smaller proteins migrate faster through the gel, allowing separation by size. After electrophoresis, proteins bands can be visualized using stains like Coomassie blue or silver stain to analyze characteristics like molecular weight, purity, and subunit composition.