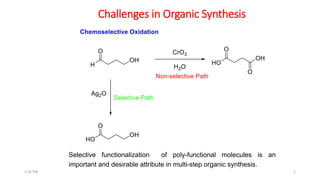
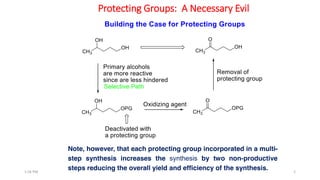
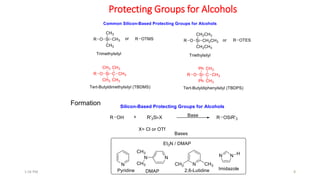
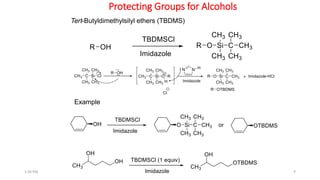
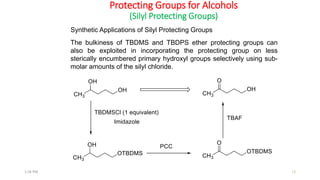
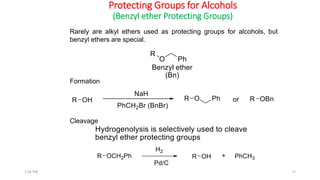
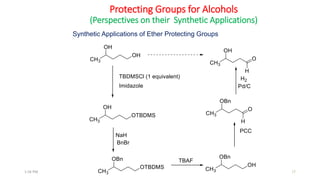
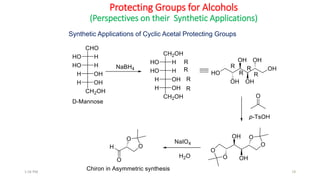
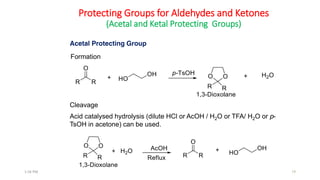
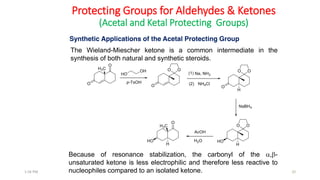
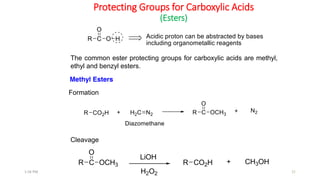
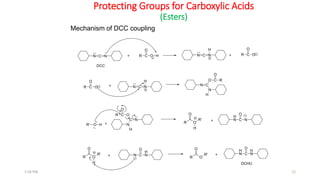
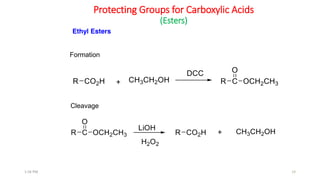
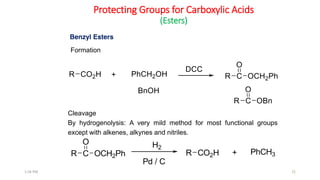
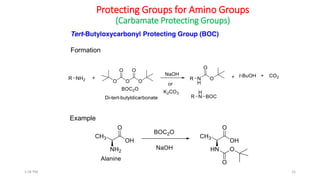
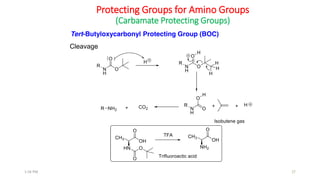
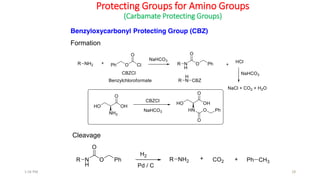
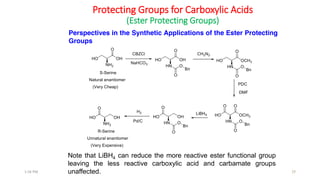
Protecting groups are molecular frameworks that are introduced onto reactive functional groups in organic molecules to block their reactivity during chemical transformations of other parts of the molecule. The document discusses various commonly used protecting groups for alcohols, aldehydes/ketones, carboxylic acids, and amines. Protecting groups must be stable under reaction conditions but also removable under mild conditions when no longer needed. Examples of protecting groups discussed include tert-butyldimethylsilyl ethers, acetals, esters like methyl and benzyl esters, and carbamates like tert-butyloxycarbonyl and benzyloxycarbonyl.