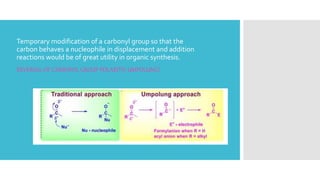
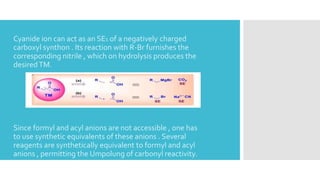
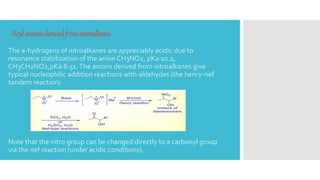
The document discusses the concept of umpolung in organic chemistry, which is the reversal of polarity of a functional group through chemical modification. Specifically, it describes strategies for temporarily modifying carbonyl groups so that the carbon behaves as a nucleophile rather than an electrophile. Several methods are presented for generating equivalents of formyl and acyl anions, including using derivatives of 1,3-dithianes, nitroalkanes, cyanohydrins, enolethers, and lithium acetylides, which allow the "umpolung" of carbonyl reactivity and new disconnection pathways in retrosynthesis. An example of using a dithiane approach in the synthesis of the antibiotic vermic