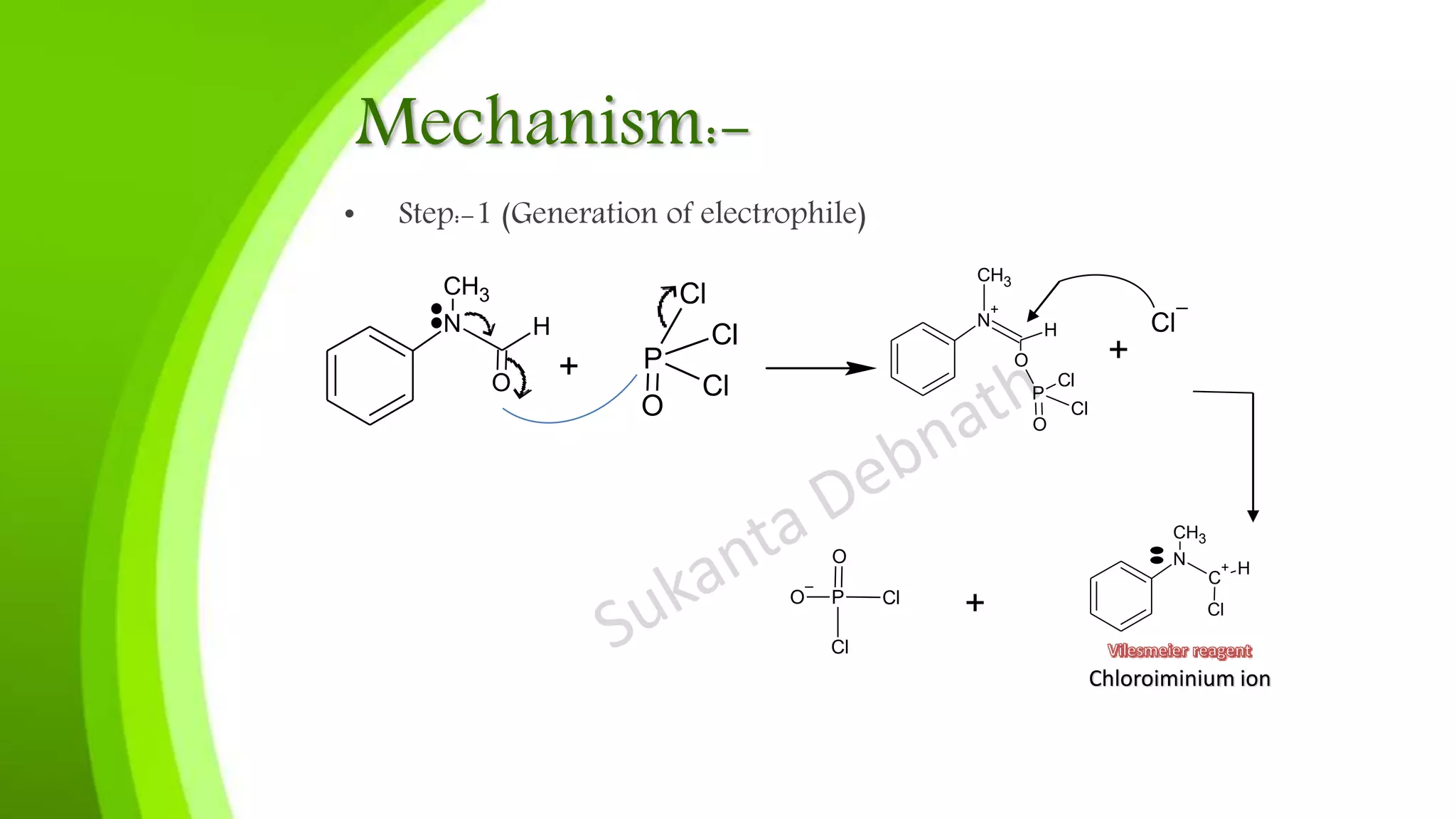
The Vilsmeier-Haack reaction involves the reaction of substituted amides with phosphorus oxychloride and electron-rich arenes to produce aryl aldehydes or ketones. The document outlines the reaction mechanism, which includes the generation of the chloroiminium ion and the electrophilic attack on aromatic compounds. Applications of this reaction include the formylation of various compounds and the synthesis of heterocycles such as pyrroles and quinolines.