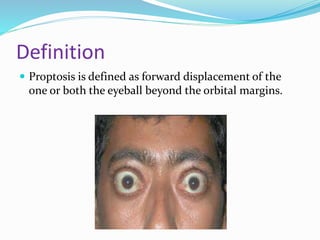
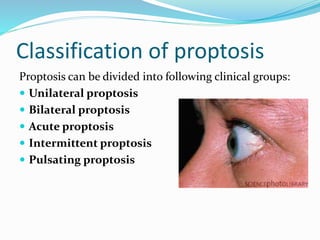
This presentation defines proptosis as the forward displacement of one or both eyeballs beyond the orbital margins. Proptosis is diagnosed when the distance from the orbital rim to the cornea is greater than 22mm or there is an asymmetry of more than 2mm between the eyes. Exophthalmos refers specifically to globe protrusion caused by endocrine dysfunction. Proptosis can be classified as unilateral, bilateral, acute, intermittent, or pulsating based on characteristics. Common causes include tumors, infections, trauma, vascular lesions, cysts, and endocrine disorders. Proptosis is measured using an exophthalmometer to determine if the corneal apex protrudes abnormally from the orbit. Imaging tests like CT and