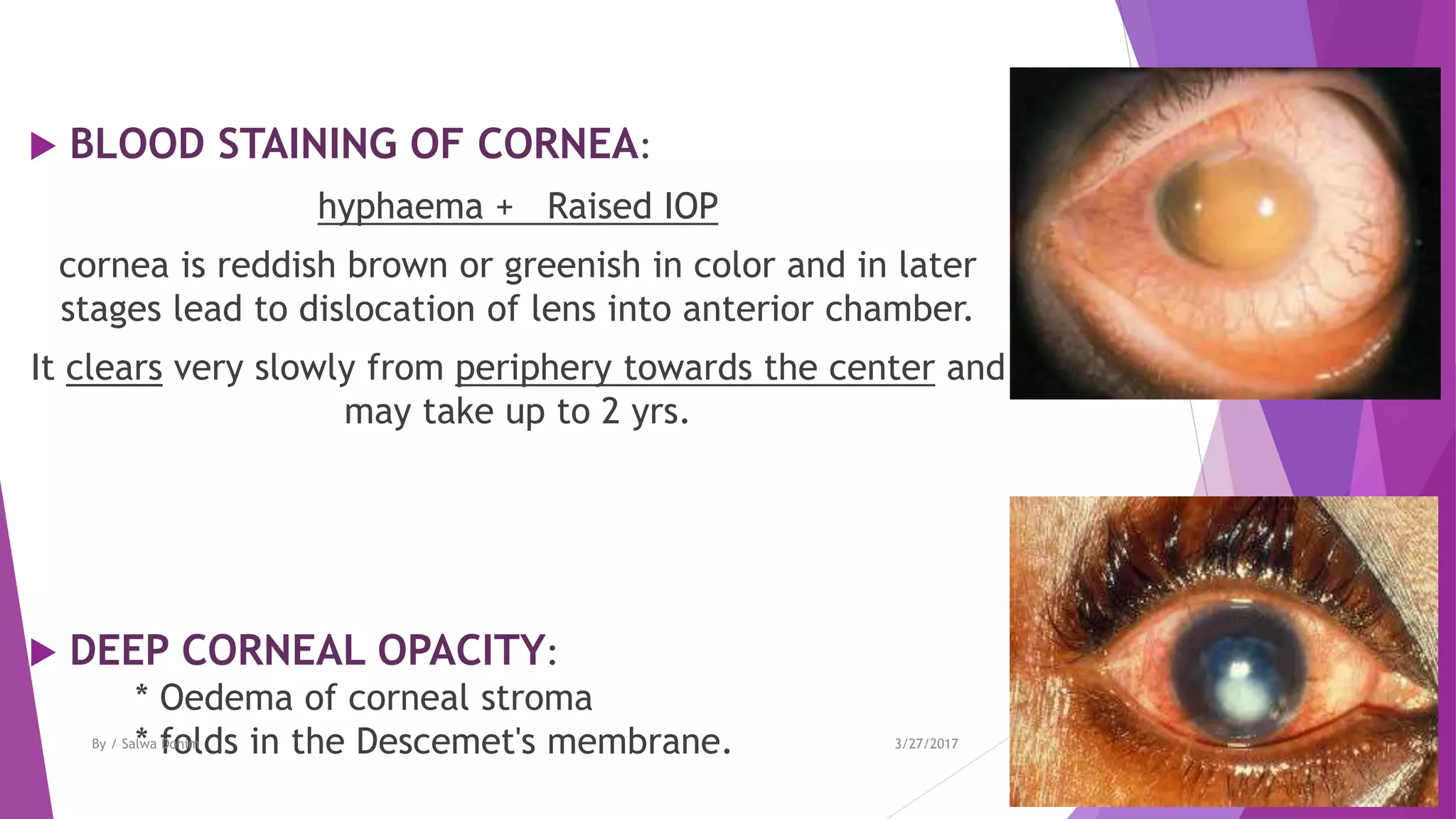
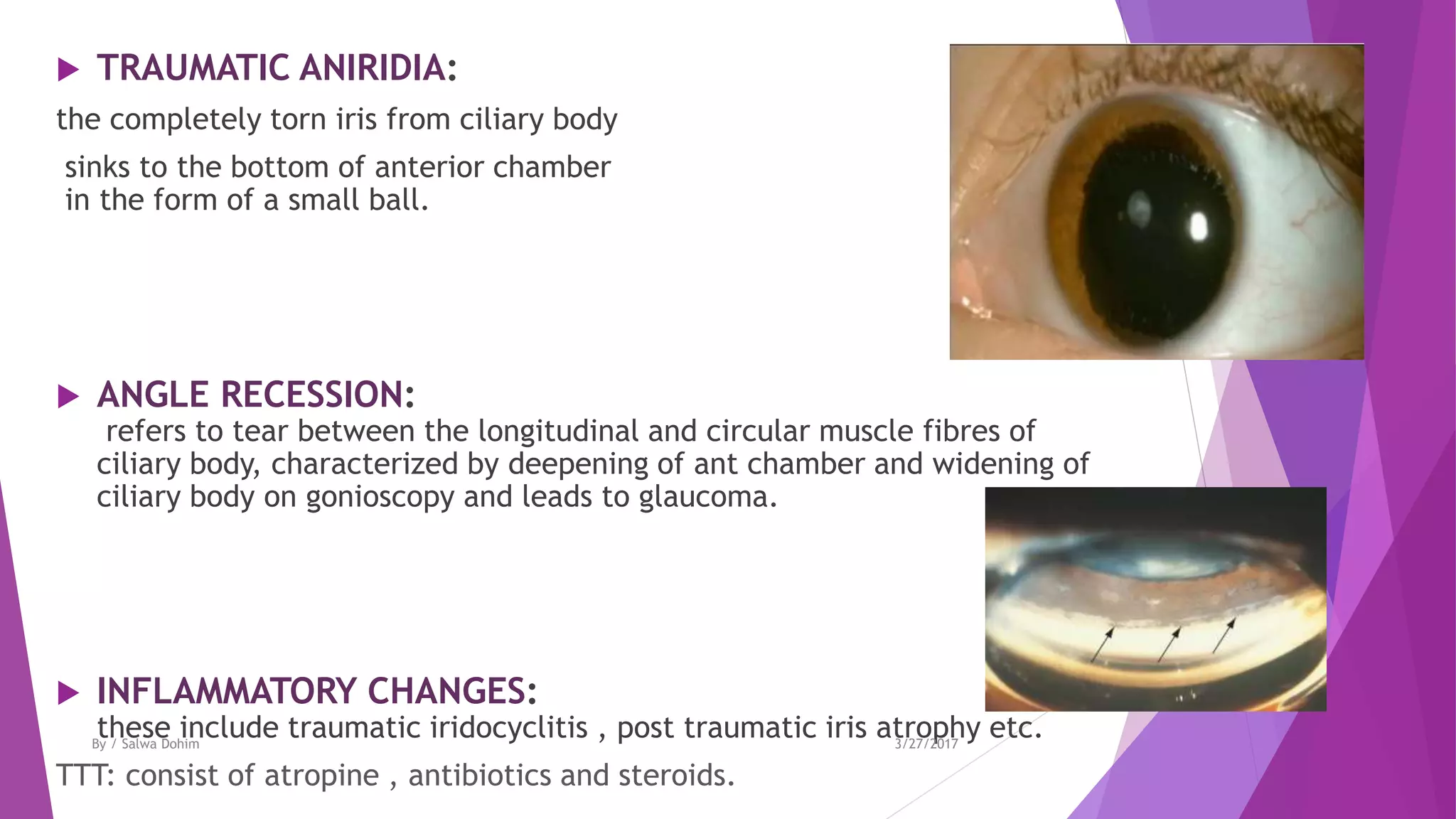
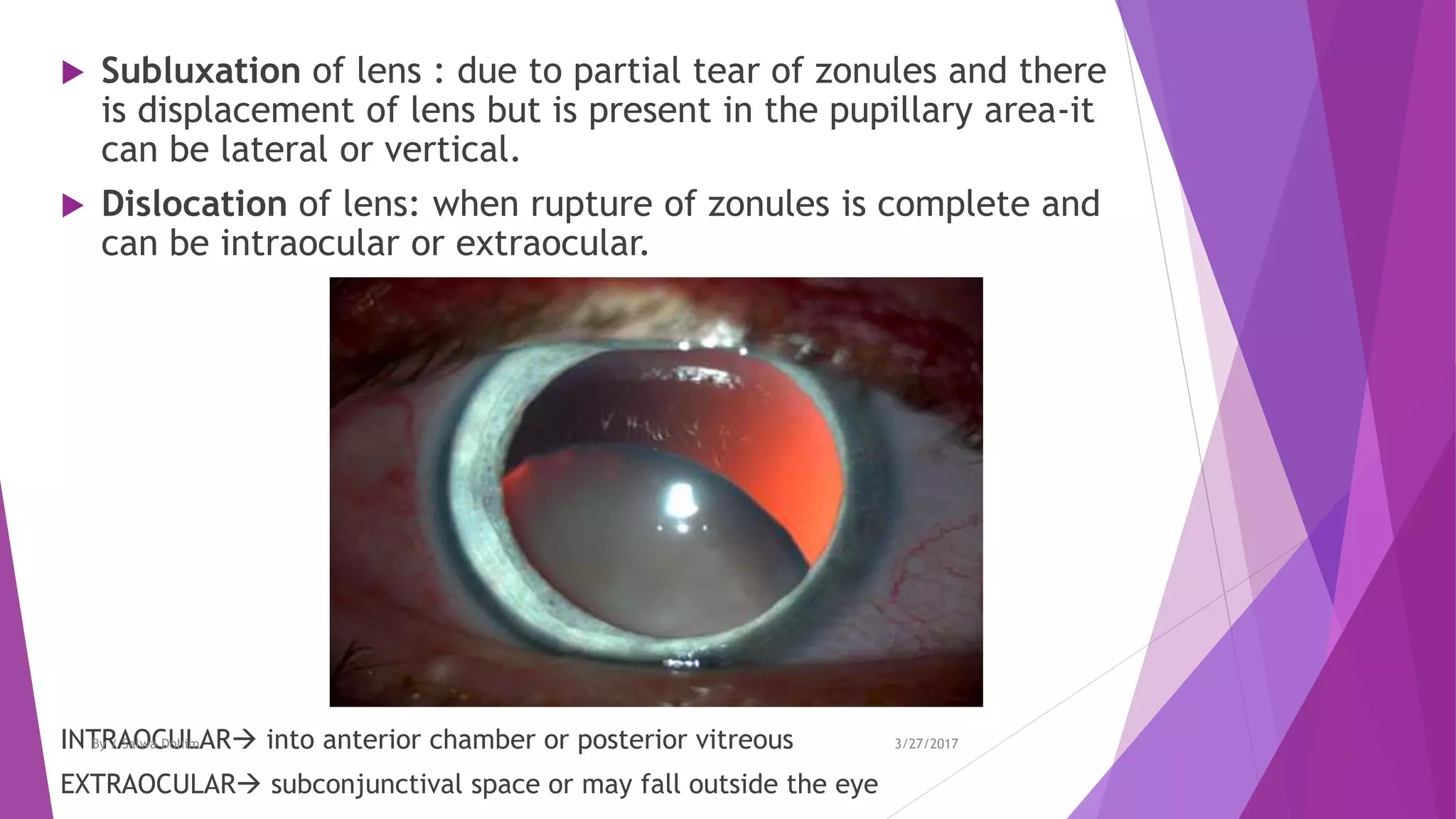
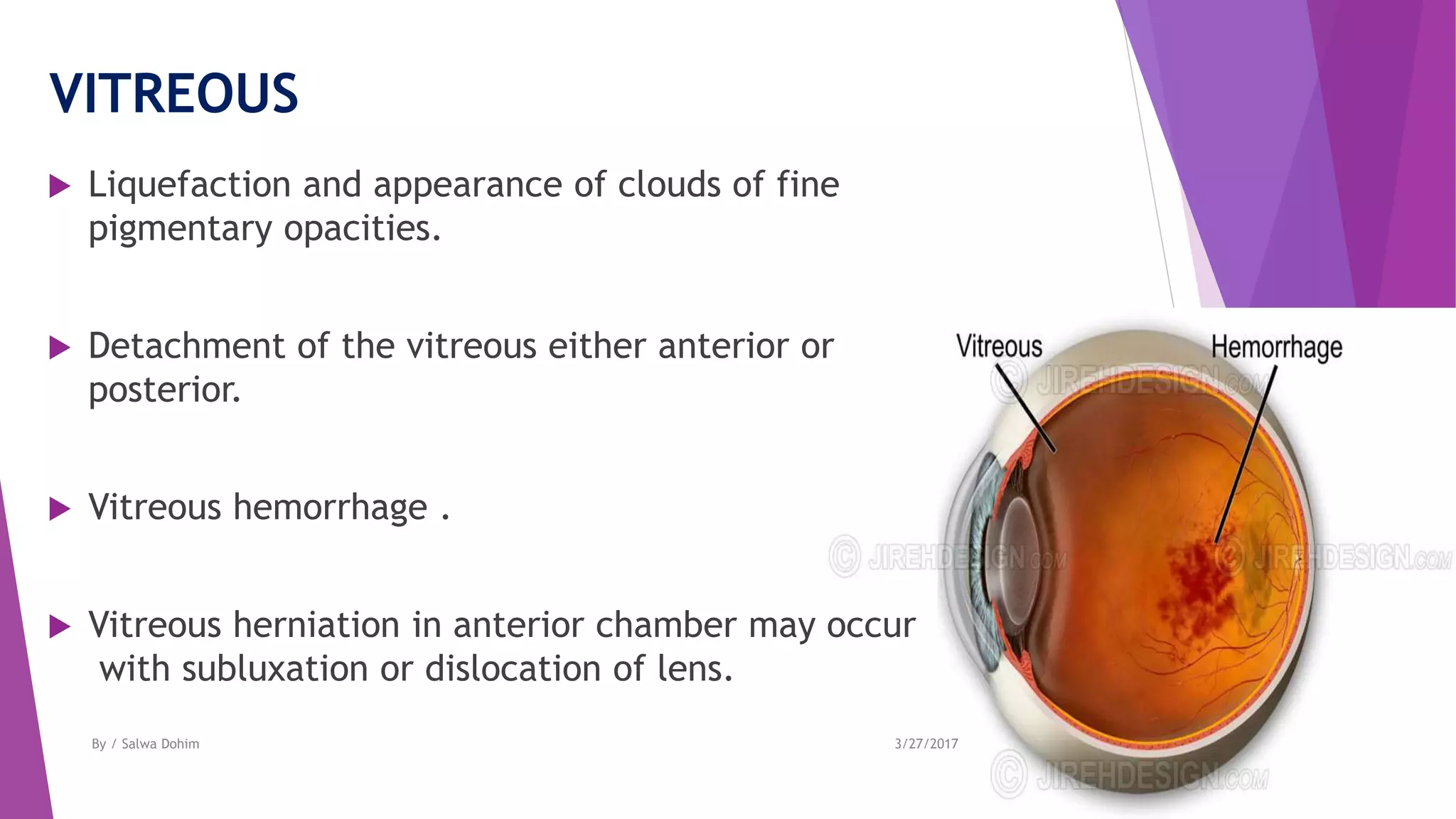
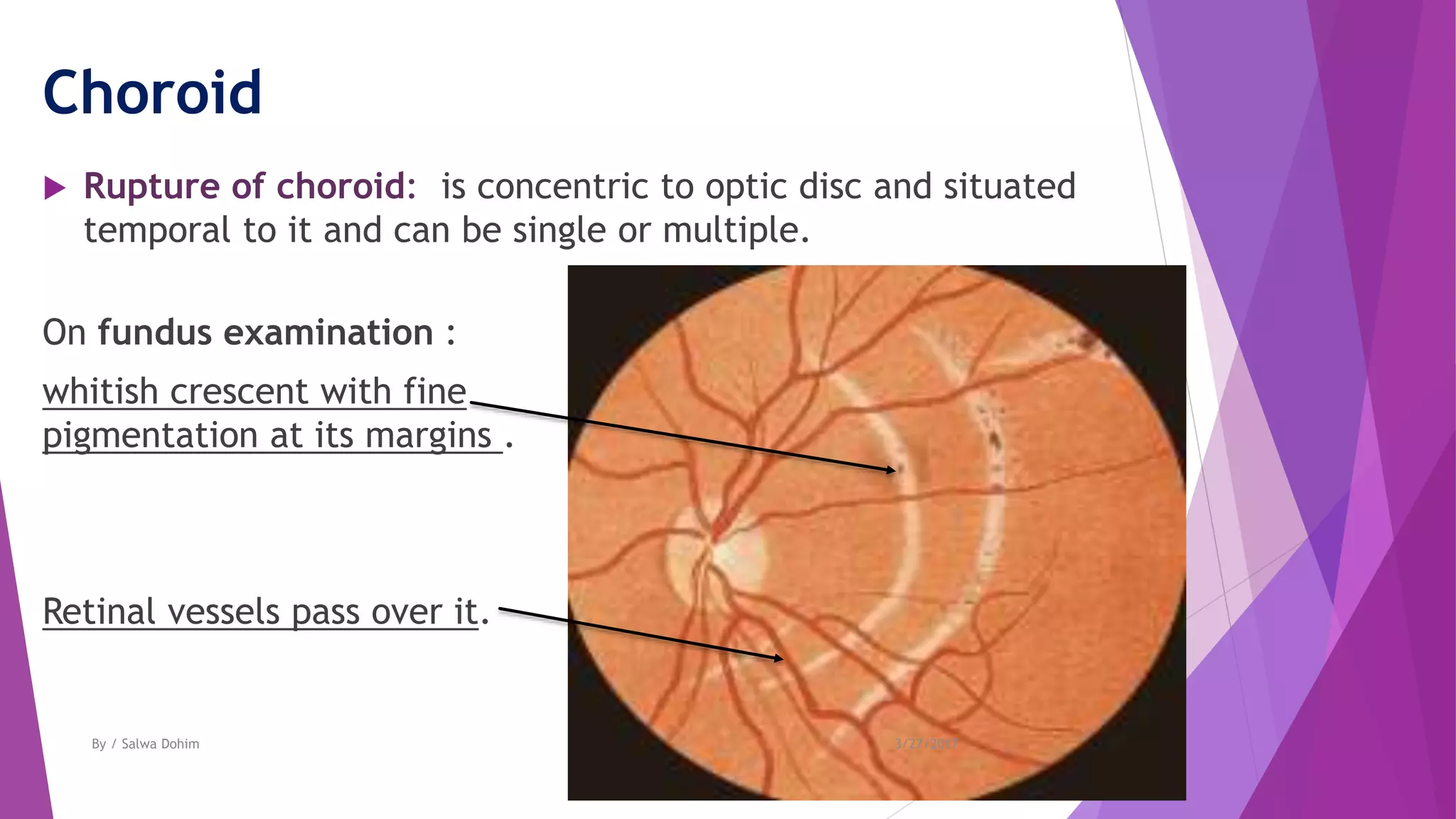
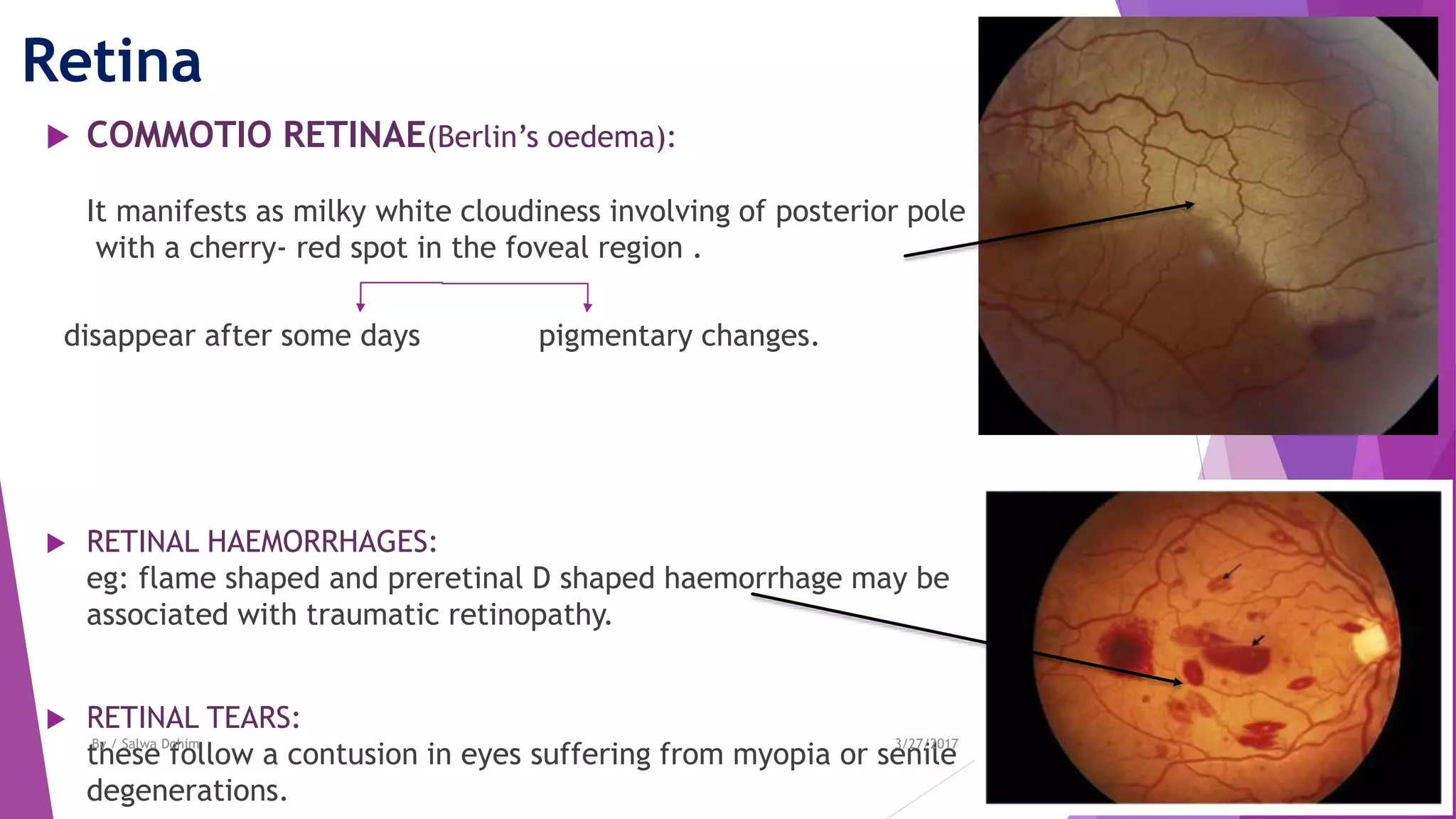
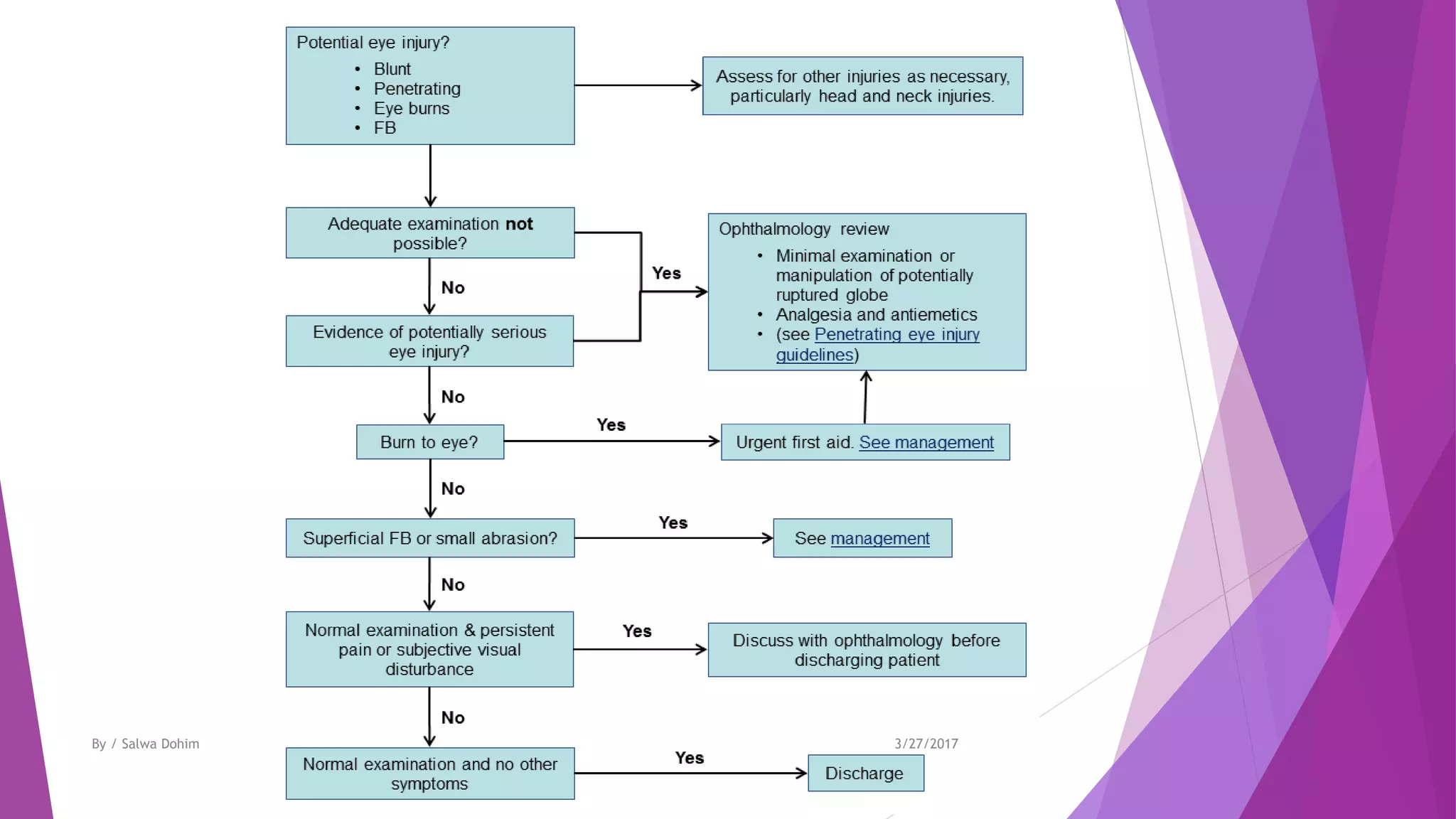
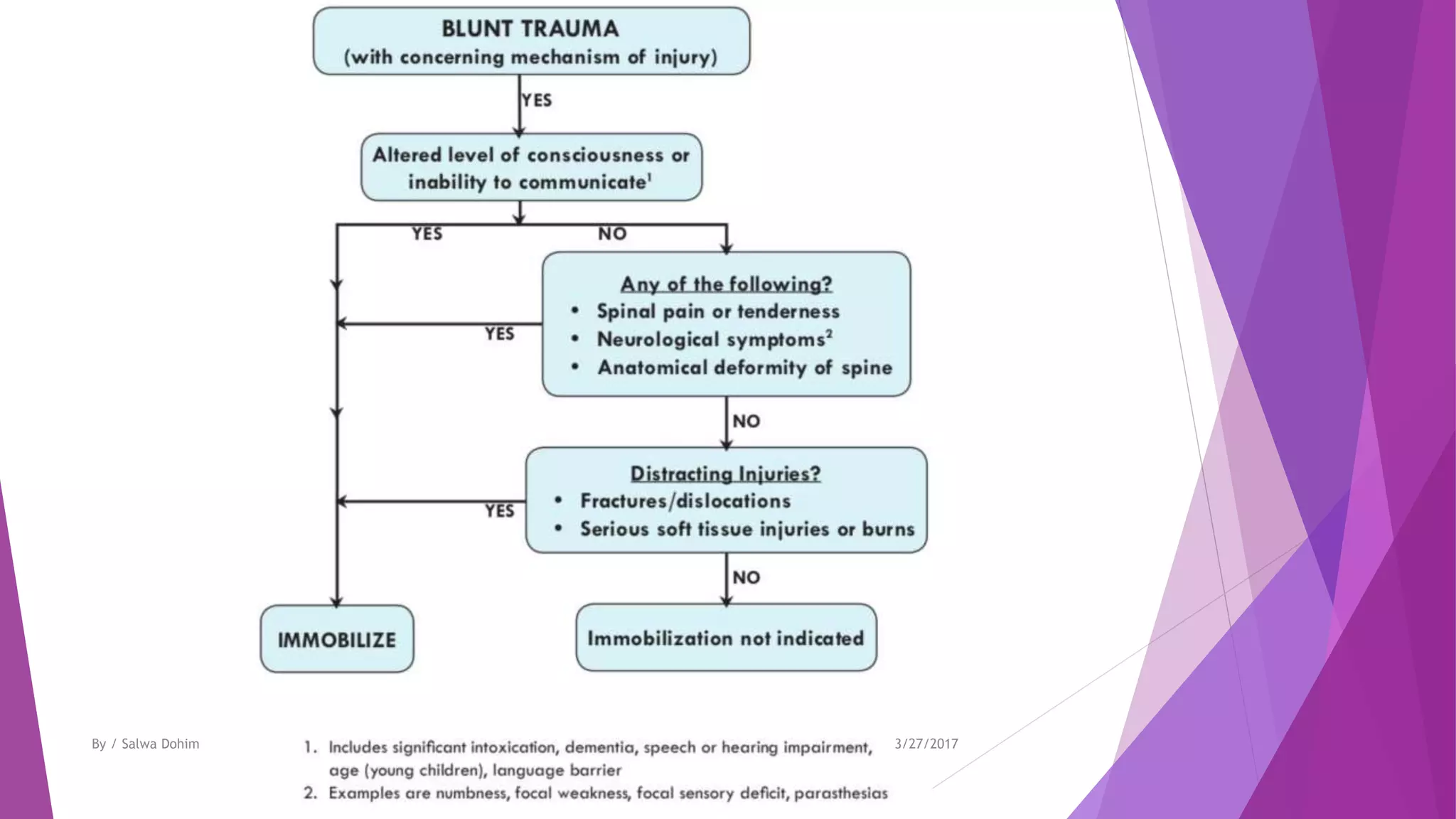
The document discusses blunt trauma to the eye. It describes the different types of ocular injuries that can result from blunt trauma, including closed globe injuries and globe rupture. Closed globe injuries involve damage to structures like the cornea, iris, lens, vitreous humor, and retina. Globe rupture is a full-thickness wound of the eyeball that can occur directly at the site of impact or indirectly from a compression force inside the eye. The document provides details on the mechanisms of various blunt eye injuries and their clinical presentations.