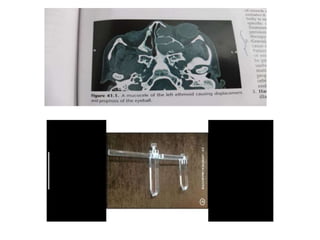
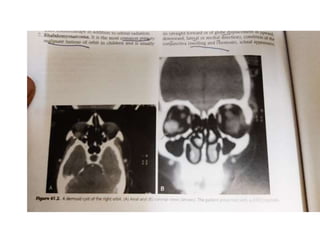
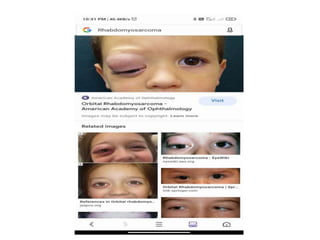
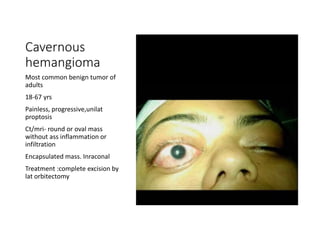
Proptosis is the forward displacement of the eyeball due to a disease process within or adjacent to the orbit. The eyeball can be displaced in different directions due to the rigid walls of the orbit. Common causes of proptosis include neoplastic masses like rhabdomyosarcoma or optic glioma in children, vascular lesions such as venous varices or cavernous hemangiomas in adults, and inflammatory or infectious processes. Evaluation involves a detailed history, physical exam to assess eye displacement and vision, and imaging tests like CT or MRI. Management depends on the underlying cause and may include biopsy, chemotherapy for cancers, surgery to remove masses, or orbital decompression for conditions like Graves' disease.