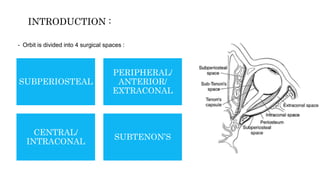
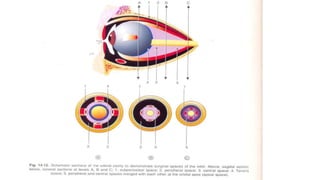
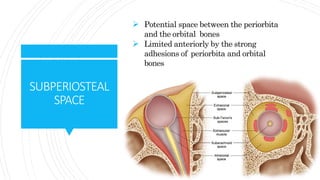
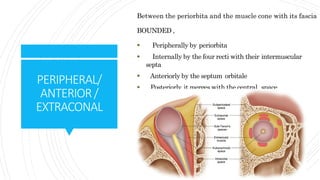
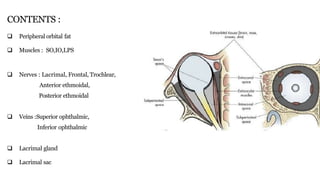
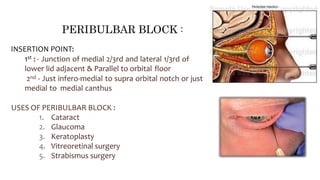
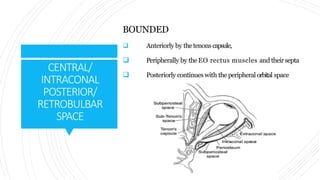
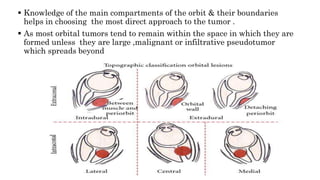
1) The orbit is divided into 4 main spaces: subperiosteal, peripheral/anterior/extraconal, central/intraconal, and sub-tenon's.
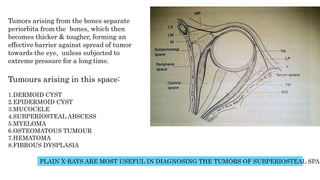
2) Each space has distinct boundaries and contents, and different types of tumors typically arise in the various spaces. For example, dermoid cysts and epidermoid cysts arise in the subperiosteal space.
3) Knowledge of the orbital anatomy helps surgeons choose the best surgical approach depending on the location and type of tumor present. Peripheral tumors can often be approached anteriorly while more central tumors may require a lateral orbitotomy.