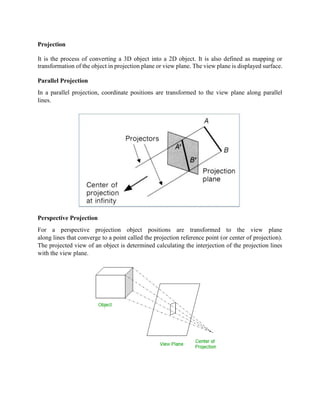
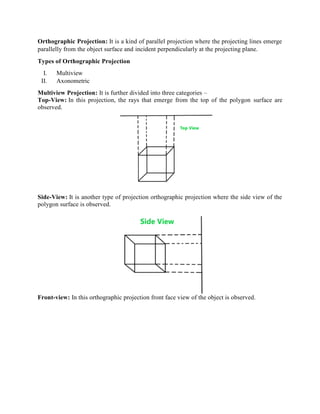
Projection is the process of mapping a 3D object onto a 2D plane. There are two main types of projection: parallel projection, where lines project parallel to each other, and perspective projection, where lines converge to a point. Parallel projection includes oblique projection, where lines hit the plane at a non-90 degree angle, and orthographic projection, where lines hit perpendicular. Orthographic projection can be multiview projection showing top, side and front views, or axonometric projection where the object is rotated for multiple views.