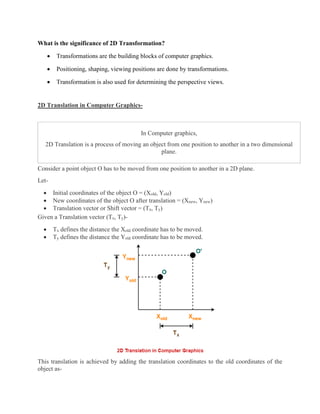
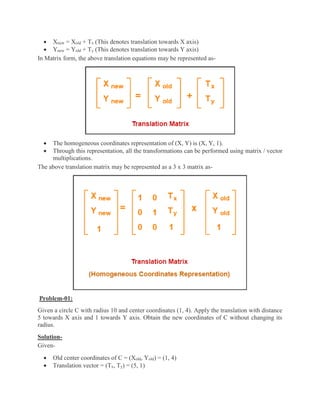
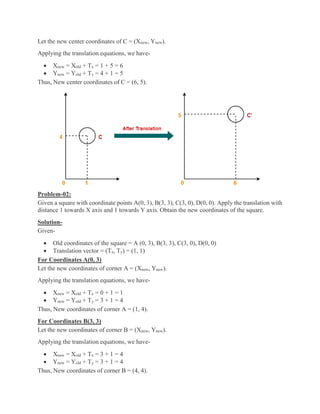
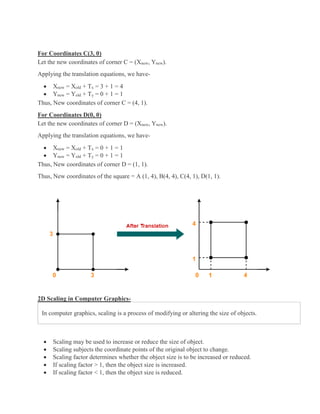
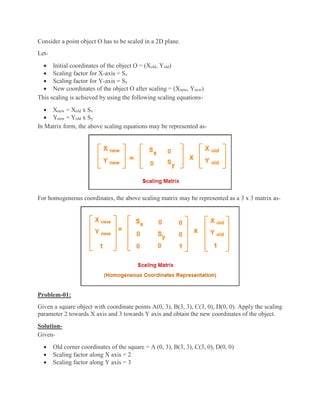
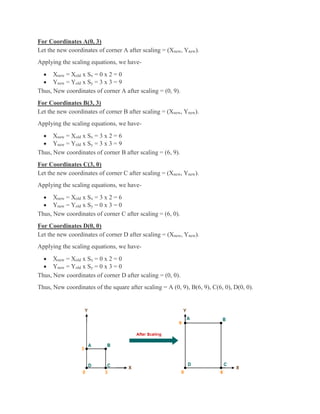
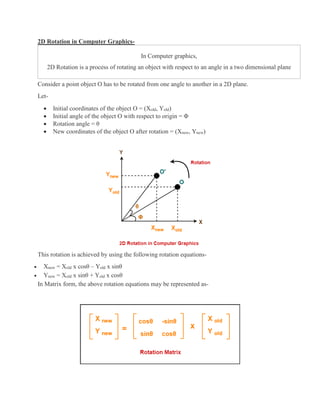
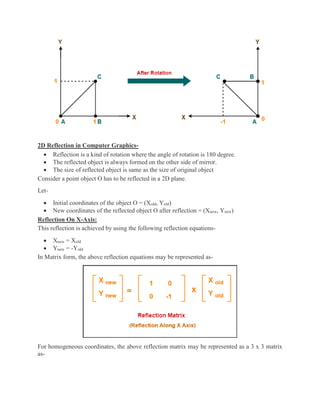
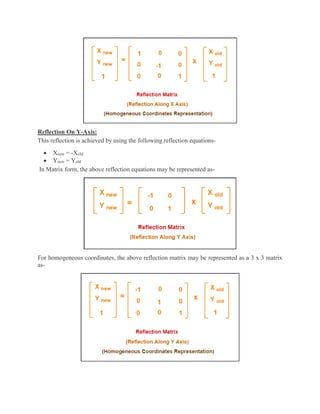
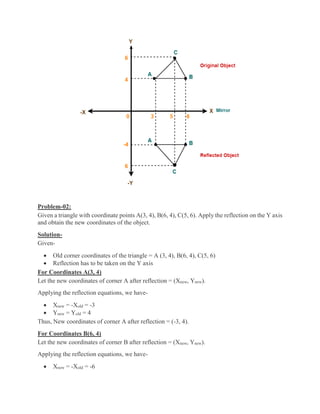
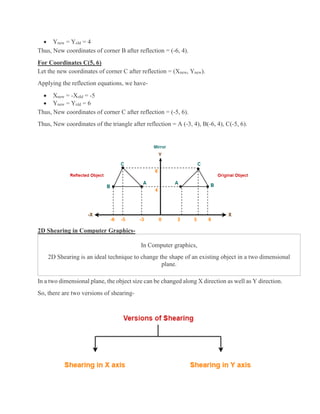
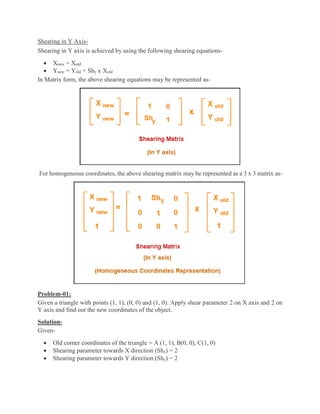
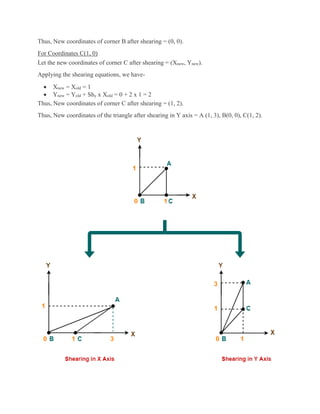
2D transformations are used in computer graphics to modify and reposition graphics. The key 2D transformation techniques are translation, rotation, scaling, reflection, and shearing. Translation moves an object by adding offsets to its coordinates. Rotation modifies an object's position by applying rotational matrices. Scaling enlarges or shrinks an object by multiplying its coordinates. Reflection mirrors an object across an axis by inverting one coordinate. Shearing skews an object by adding its coordinates. Homogeneous coordinates allow representing transformations using matrix multiplications.