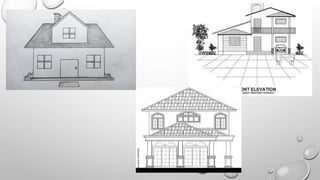
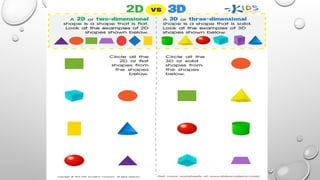
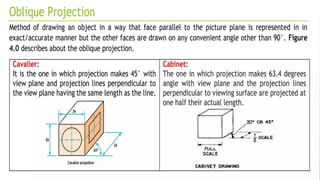
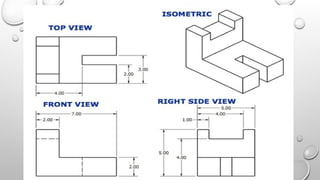
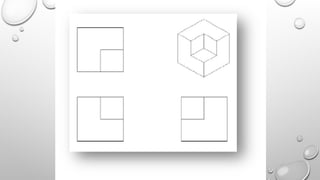
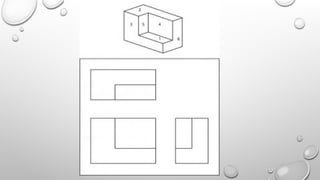
The document explains the concepts of 2D and 3D drawings, detailing how 2D drawings represent objects on a flat surface while 3D drawings include depth, height, and width. It discusses various methods of projection used in drafting, including parallel and perspective projections, and their applications in mechanical drawings. Additionally, it breaks down types of orthographic, axonometric, oblique, and perspective projections, highlighting their characteristics and uses.