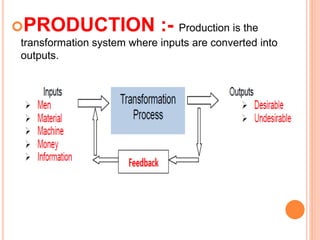
This document provides an overview of production management. It defines production as the transformation of inputs into outputs. Production management deals with decision making related to production to ensure goods are produced according to specifications, in the required amount and on schedule at minimum cost. The objectives of production management include producing quality products at minimum cost and the right quantity at the right time. Other topics discussed include plant location, layout, work measurement, and production control elements like planning, routing, scheduling, and inspection.