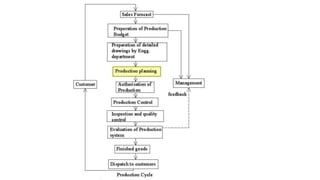
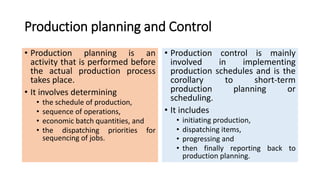
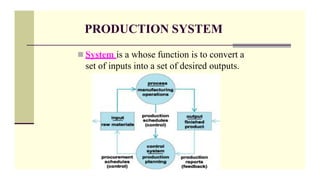
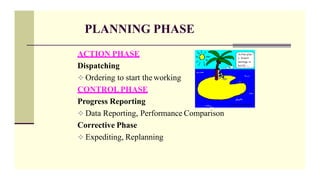
This document provides an overview of production planning and control for the subject IE6605 at VIRUDHUNAGAR DEPARTMENT OF MECHANICAL ENGINEERING. It discusses key concepts like production system, production planning items, controlling items, nature of MRP, production planning, routing, scheduling, loading, dispatching, inspection, evaluating, objectives of production planning and control, time dimensions, planning phase, production control, material requirement planning, and key factors of MRP. The document is intended to educate students on the core concepts and functions of production planning and control.