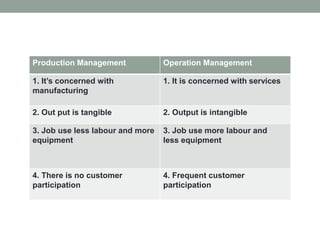
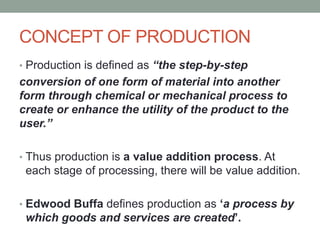
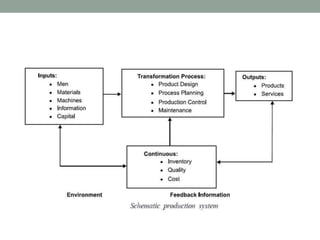
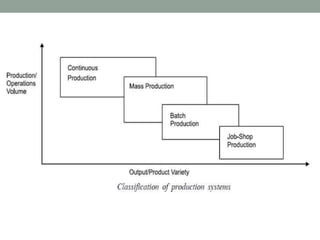
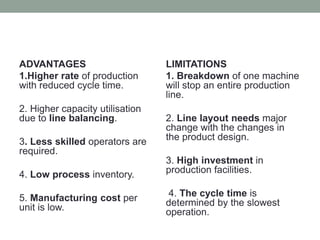
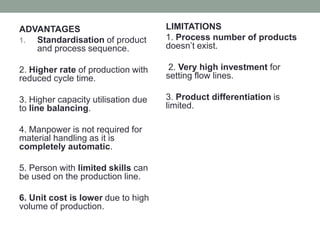
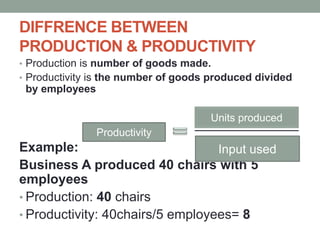
This document provides an overview of production management. It discusses key concepts like the definition of production, different production systems (job shop, batch, mass, continuous), objectives of production management, and the role of technology and innovation in production. The main types of production systems are described in terms of their characteristics, advantages, and limitations. The document emphasizes that the goal of production management is to produce quality goods and services at the right time, quantity, and cost.