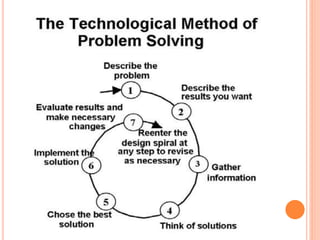
Problem solving involves several steps: (1) identifying and defining the problem; (2) formulating strategies to solve the problem through analysis and synthesis; (3) organizing relevant information and allocating resources; (4) monitoring progress toward the solution; and (5) evaluating the solution. There are two types of problems - well-defined problems that have clear goals and paths to solutions, and ill-defined problems that lack clarity. Developing strong problem solving skills is important because it allows one to overcome challenges, stand out from others, and boost confidence when facing new issues.