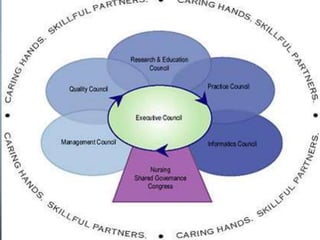
Shared governance is a model that promotes shared decision making between management and staff in a healthcare organization. It is based on four key principles: partnership, equity, accountability, and ownership. There are several models of shared governance including congressional, councilor, and unit-based models. Implementation occurs over three phases starting with staff representatives and evolving to councils with authority. Barriers to adoption include resistance to changing roles and lack of communication. Governing boards are responsible for strategic planning, budget approval, and oversight of quality assurance. Federal requirements specify board composition for health centers.