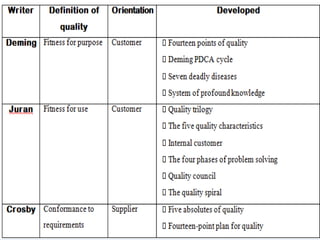
This document discusses three influential quality management experts: W. Edwards Deming, Joseph M. Juran, and Philip B. Crosby. It outlines their key contributions which helped revolutionize quality practices. Deming emphasized continuous quality improvement and introduced the PDCA cycle. Juran developed the quality trilogy of quality planning, control, and improvement. Crosby defined quality as conformance to requirements and advocated preventing errors rather than inspection. Together, these experts transformed approaches to quality management.