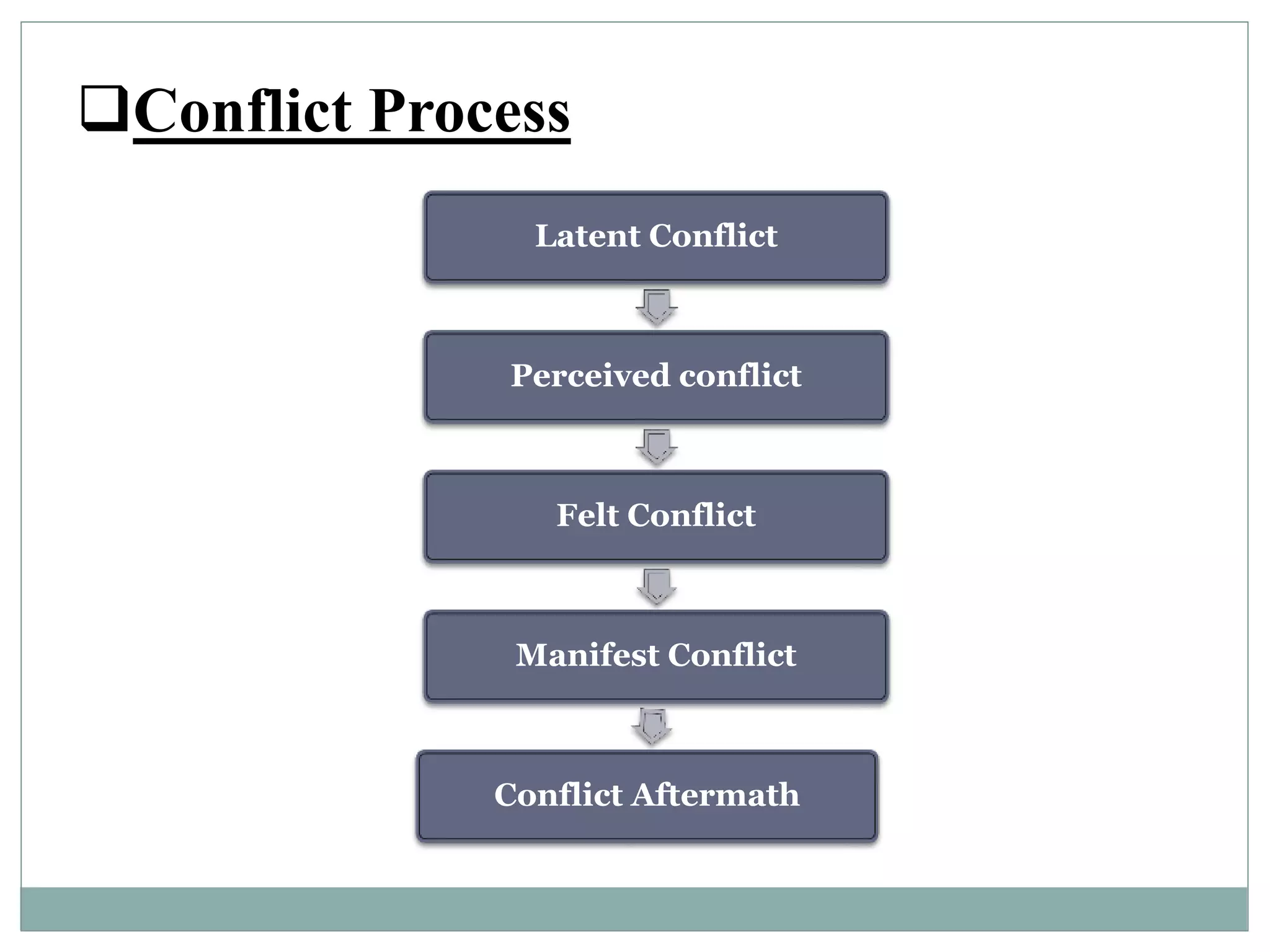
Conflict refers to disagreements that arise from differences in opinions, goals, or views between individuals or groups. There are several types of conflict, including intra-individual, interpersonal, intra-group, and inter-group. Conflicts are generally inevitable and can have both positive and negative effects on organizations. Conflict arises through a process that includes latent conflict, perceived conflict, felt conflict, manifest conflict, and conflict aftermath. Proper conflict management is important for organizational success.