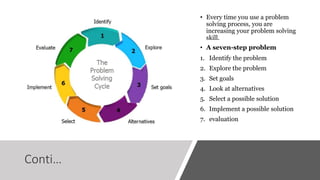
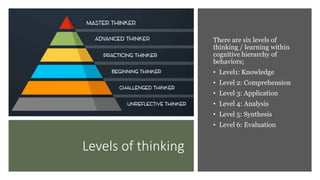
The document discusses the nature, types, and processes of human thinking and reasoning, emphasizing that thinking is a cognitive activity aimed at problem-solving. It outlines various types of thinking including perceptual, conceptual, creative, and logical thinking, along with the cognitive hierarchy of learning levels. Additionally, it addresses alterations in thinking due to psychosis and defines reasoning as a structured process aimed at achieving specific goals.